Valid H12-821_V1.0 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing H12-821_V1.0 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest H12-821_V1.0 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com H12-821_V1.0 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com H12-821_V1.0 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access H12-821_V1.0 Dumps Premium Version
(1265 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 60/107
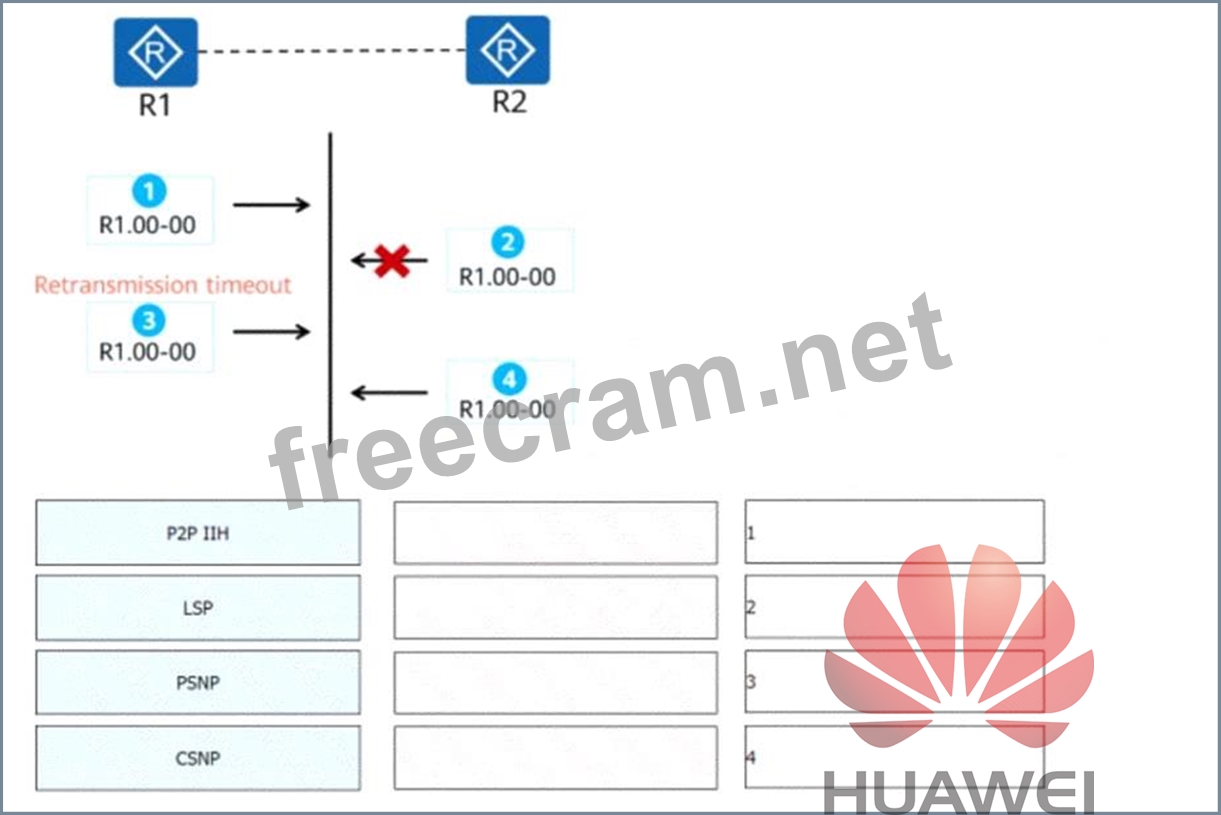
On a P2P IS-IS network, after a neighbor relationship is established between R1 and R2, R2 finds that its LSDB is not synchronized. Then, R2 requests corresponding LSPs from R1 for LSDB synchronization. The following figure shows the synchronization process. Drag the following packet types to the steps in which they are used.(Token is reusable)

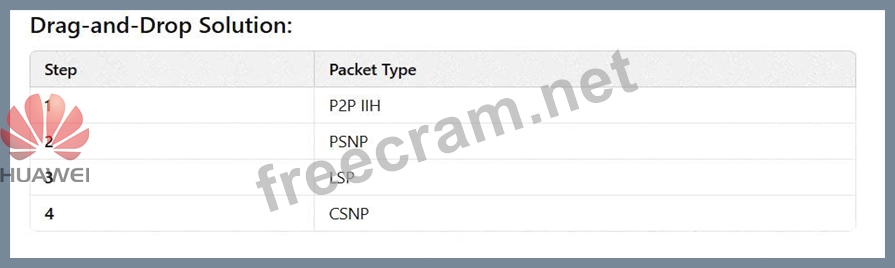
Correct Answer:
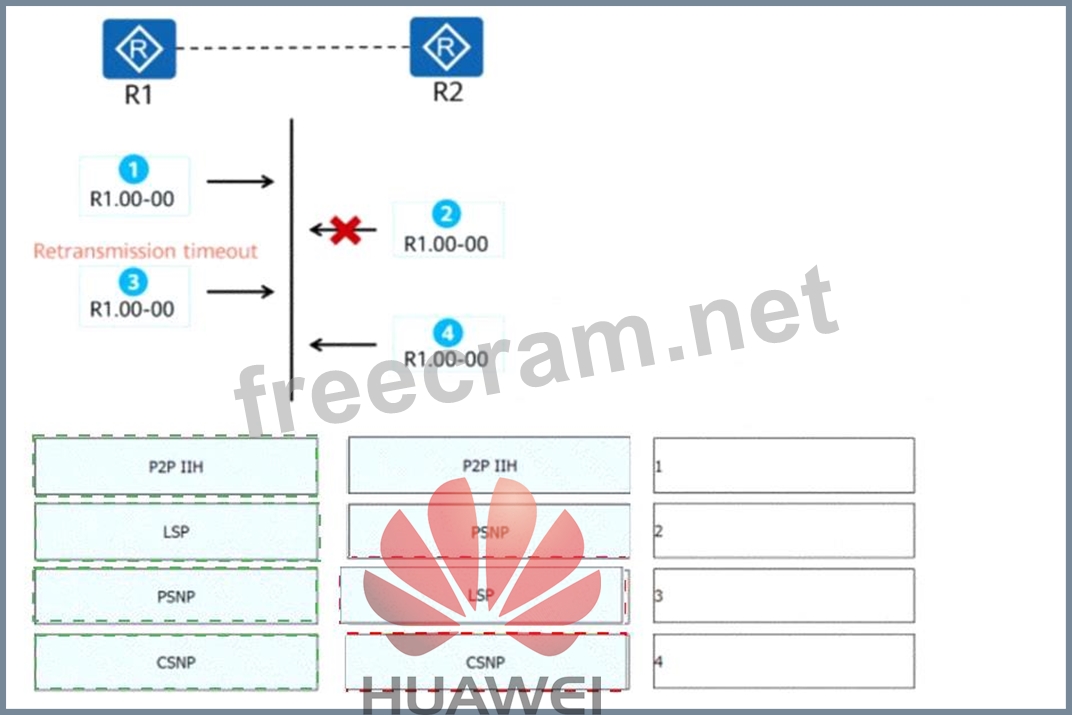
Explanation:
A screenshot of a computer Description automatically generated
Explanation of IS-IS Packet Types and Synchronization Process:
In the given scenario, R2 requests LSPs from R1 to synchronize its Link State Database (LSDB). The following IS-IS packet types are involved in this synchronization process:
1. P2P IIH (Point-to-Point IS-IS Hello):
* Purpose: Establishes and maintains IS-IS neighbor relationships.
* Step: This packet is exchanged initially to detect and maintain the adjacency between R1 and R2.
2. PSNP (Partial Sequence Number PDU):
* Purpose: Requests missing or outdated LSPs (Link State PDUs) from a neighbor to synchronize the LSDB.
* Step: In this case, R2 sends a PSNP to R1 to request the missing or outdated LSP.
3. LSP (Link State PDU):
* Purpose: Contains routing information and is used to update the LSDB.
* Step: R1 sends the requested LSPs to R2 for synchronization.
4. CSNP (Complete Sequence Number PDU):
* Purpose: Lists all LSPs in the sender's LSDB to help neighbors verify and request missing LSPs.
* Step: R1 sends a CSNP during retransmission timeout to notify R2 of its LSPs.
- Question List (107q)
- Question 1: In PIM-DM, which of the following processes are involved in ...
- Question 2: On a WLAN, engineers can use the VLAN pool mechanism to assi...
- Question 3: Which of the following statements regarding different LSA ty...
- Question 4: In VRRP networking, devices assume the Master and Backup rol...
- Question 5: On a network, each router has a local core routing table and...
- Question 6: L2TP does not provide security encryption. Therefore, other ...
- Question 7: The Origin attribute is used to define the origin of BGP pat...
- Question 8: Which of the following attacks is not the network layer atta...
- Question 9: By default, if no router ID is configured but multiple loopb...
- Question 10: Which of the following statement regarding the display ospf ...
- Question 11: Compress the 2001:0DBB:B8:0000:C030:0000:0000:09A0:CDEF addr...
- Question 12: Which of the following statements regarding Local-Preference...
- Question 13: On an enterprise network, the directly connected interfaces ...
- Question 14: On the network shown in the following figure, the management...
- Question 15: Which of the following statements is false about the default...
- Question 16: Which of the following statements regarding the stateful ins...
- Question 17: Which of the following routing protocols support the default...
- Question 18: In IPv6, interface IDs can be manually configured, automatic...
- Question 19: An engineer sets the CAPWAP heartbeat detection interval to ...
- Question 20: Link aggregation is a common network technology. Which of th...
- Question 21: After HSB is configured, the HSB channel fails to be establi...
- Question 22: Compared with STP, RSTP defines the different port states. W...
- Question 23: Which of the following statements regarding BGP route advert...
- Question 24: Preferences of routing protocols determine the sequence In w...
- Question 25: When two routers exchange LSDB information using DD packets,...
- Question 26: Which of the following statements is false about BFD?...
- Question 27: Which of the following statements about WLAN roaming are fal...
- Question 28: By default, some security zones are created when Huawei fire...
- Question 29: By default, some security zones are created when Huawei fire...
- Question 30: Which of the following statements regarding the MED value in...
- Question 31: A BGP device receives a route carrying an unknown attribute ...
- Question 32: BGP can select routes based on the AS_Path attribute. Theref...
- Question 33: A router performs a lookup in its FIB table for a packet. If...
- Question 34: Which of the following statements regarding OSPF is true?...
- Question 35: IPv6 defines multiple types of addresses. Which of the follo...
- Question 36: Which of the following methods is usually used by a network ...
- Question 37: In inter-AC roaming scenarios, an AC can function as the mob...
- Question 38: During routine maintenance, an enterprise administrator runs...
- Question 39: As shown in the following figure, a new AP is deployed In du...
- Question 40: As shown in the figure, data traffic is forwarded in tunnel ...
- Question 41: In IPv6, to communicate with a destination host, a host must...
- Question 42: There are various types of VPNs, which can be applied to dif...
- Question 43: When creating a single-hop BFD session for the first time, b...
- Question 44: Regarding the route-policy set-cost configuration below, whi...
- Question 45: IGMP group entries play an important role in multicast forwa...
- Question 46: During the DHCP interaction process, the DHCP server and cli...
- Question 47: VRF, also called VPN instance, is a network virtualization t...
- Question 48: Compared with RSTP, which of the following port roles are ad...
- Question 49: Which of the following statements regarding routing policy a...
- Question 50: BGP confederations are widely used because they can reduce t...
- Question 51: Which Of the following IEEE 802.11 standards is also known a...
- Question 52: BFD control packets are encapsulated in UDP packets for tran...
- Question 53: Which of the following statements regarding DR/BDR are false...
- Question 54: A wide area network (WAN) is a remote network that connects ...
- Question 55: OSPF supports area authentication and interface authenticati...
- Question 56: Which of the following PIM protocol packets have unicast des...
- Question 57: A monitoring plane usually comprises the monitoring units of...
- Question 58: On an OSPF network, if a router functions as an ABR, the rou...
- Question 59: A network entity title consists of an area address and a sys...
- Question 60: On a P2P IS-IS network, after a neighbor relationship is est...
- Question 61: Which of the following scenarios is not suitable for deployi...
- Question 62: BGP routes have multiple path attributes. When a router adve...
- Question 63: In BGP, the Origin attribute is used to identify the origin ...
- Question 64: As shown in the figure, SWA, SWB, and SWC run the Rapid Span...
- Question 65: Route attributes are specific descriptions of routes. BGP ro...
- Question 66: ASPF enables the firewall to support multi-channel protocols...
- Question 67: Drag the following VRRP states to the corresponding working ...
- Question 68: The native AC function allows an agile switch to integrate A...
- Question 69: On a network, some switches are enabled with RSTP and some s...
- Question 70: Which of the following statements regarding OSPF route summa...
- Question 71: A firewall receives a packet that PC1 sends to PC2. Which of...
- Question 72: A filter named si is configured on a device using the as-pat...
- Question 73: When a packet passes through a firewall, the firewall create...
- Question 74: Which of the following statements about WLAN roaming are tru...
- Question 75: On an OSPF network, an algorithm is used to prevent loops wi...
- Question 76: Which of the following is used as the destination port for s...
- Question 77: The typical characteristics of the AI era are that it focuse...
- Question 78: STAs stay on different subnets before and after Layer 3 roam...
- Question 79: When a BGP device sends an Open message to establish a peer ...
- Question 80: BGP is generally applied to complex networks where routes ch...
- Question 81: On an OSPF network, LSDBs are used to store LSAs. Common LSA...
- Question 82: During BGP route summarization configuration, the keyword ca...
- Question 83: Security policy is the core feature of firewalls. Only valid...
- Question 84: When an SSH client accesses an SSH server for the first time...
- Question 85: RSTP provides different functions in different scenarios. Wh...
- Question 86: On a broadcast IS-IS network, a DIS needs to be elected to c...
- Question 87: OSPF networks are classified into four types of networks by ...
- Question 88: Which of the following attributes cannot be directly referen...
- Question 89: ON a stateful inspection Firewall where there is no session ...
- Question 90: Similar to the OSPF DR, the IS-IS DIS needs to be elected on...
- Question 91: There are two BFD operating modes. In_______mode, the local ...
- Question 92: Which three transmission modes are supported for IPv4 packet...
- Question 93: When multiple access channels are set for the same access re...
- Question 94: On an STP network, the root bridge, root port, and designate...
- Question 95: IP multicast effectively conserves network bandwidth and red...
- Question 96: Which of the following statements about multicast packet for...
- Question 97: The Interface \P address and VRRP virtual IP address can be ...
- Question 98: An enterprise uses Huawei routers to deploy an IS-IS network...
- Question 99: STP ensures a loop-free network but has a slow network topol...
- Question 100: The following figure shows the OSPF network of an enterprise...
- Question 101: On the OSPF network shown in the figure, R1, R2, and R3 run ...
- Question 102: An edge port is a new port role added to RSTP to overcome th...
- Question 103: The VRID of the VRRP virtual router is 3 and the virtual IP ...
- Question 104: On the OSPF network shown in the figure, an adjacency has be...
- Question 105: See the network shown in the following figure. (Exhibit) R1 ...
- Question 106: In an IPv4 address space, Class D addresses are used for mul...
- Question 107: PBR is a mechanism for selecting routes based on user-define...


