Valid AB-Abdomen Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing AB-Abdomen Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest AB-Abdomen exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com AB-Abdomen exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com AB-Abdomen dumps with Test Engine here:
Access AB-Abdomen Dumps Premium Version
(165 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
Next Question >>
Question 1/76
Which condition is most consistent with this image of a postsurgical breast?
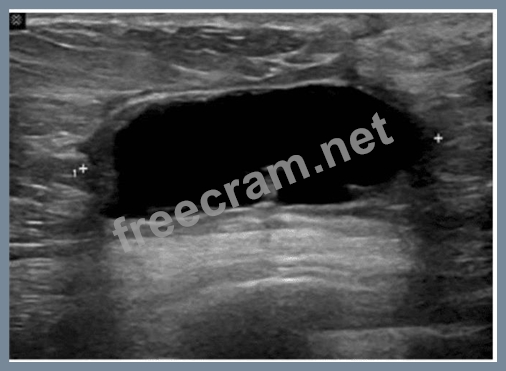

Correct Answer: D
The ultrasound image reveals a well-defined, anechoic (black), thin-walled fluid collection located in the subcutaneous or parenchymal plane of the breast. This is most consistent with a seroma, particularly in the context of recent breast surgery.
A seroma is a common postsurgical finding, representing a sterile collection of serous fluid that accumulates in the surgical bed. It typically appears:
* Anechoic (or hypoechoic if older)
* Well circumscribed
* Without internal septations or debris
* Lacking hyperemia or surrounding inflammatory changes
This contrasts with:
* A. Carcinoma - typically presents as an irregular, hypoechoic mass with angular margins, internal vascularity, and shadowing.
* B. Blood clot (hematoma) - often appears heterogeneous, with internal echoes and variable echotexture depending on the age of the clot.
* C. Abscess - appears as a complex fluid collection with thick walls, internal debris, septations, and surrounding hyperemia (often with clinical signs of infection).
D: Seroma - Correct. The described anechoic, clean-walled fluid collection is classic for a postoperative seroma.
References:
Mendelson EB, Bohm-Velez M, Berg WA.ACR BI-RADS Atlas: Ultrasound. American College of Radiology; 2013.
Stavros AT. Breast Ultrasound. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2004.
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound, 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
A seroma is a common postsurgical finding, representing a sterile collection of serous fluid that accumulates in the surgical bed. It typically appears:
* Anechoic (or hypoechoic if older)
* Well circumscribed
* Without internal septations or debris
* Lacking hyperemia or surrounding inflammatory changes
This contrasts with:
* A. Carcinoma - typically presents as an irregular, hypoechoic mass with angular margins, internal vascularity, and shadowing.
* B. Blood clot (hematoma) - often appears heterogeneous, with internal echoes and variable echotexture depending on the age of the clot.
* C. Abscess - appears as a complex fluid collection with thick walls, internal debris, septations, and surrounding hyperemia (often with clinical signs of infection).
D: Seroma - Correct. The described anechoic, clean-walled fluid collection is classic for a postoperative seroma.
References:
Mendelson EB, Bohm-Velez M, Berg WA.ACR BI-RADS Atlas: Ultrasound. American College of Radiology; 2013.
Stavros AT. Breast Ultrasound. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2004.
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound, 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
- Question List (76q)
- Question 1: Which condition is most consistent with this image of a post...
- Question 2: Which normal anatomical structure is also known as the acces...
- Question 3: Which of the following is the most common symptom of choleli...
- Question 4: Which condition is demonstrated in this image? (Exhibit)...
- Question 5: Which of the following is a possible early complication of a...
- Question 6: Which condition is associated with multiple pancreatic cysts...
- Question 7: Which imaging technique best demonstrates ureteral patency?...
- Question 8: Which condition is most likely depicted in this image? (Exhi...
- Question 9: Which type of choledochal cyst is the most common?...
- Question 10: Which thyroid condition is most likely caused by a viral inf...
- Question 11: Which condition is most consistent with the sonographic appe...
- Question 12: Which anatomical area of the male reproductive system is dem...
- Question 13: Which lymph node shape is concerning for malignancy in the p...
- Question 14: Beginning at the renal artery, what is the correct sequence ...
- Question 15: Which scanning approach was utilized to obtain this image? (...
- Question 16: Which condition is most likely the cause of claudication exp...
- Question 17: Which condition results in the vascular abnormality shown in...
- Question 18: Which finding is demonstrated in this image? (Exhibit)...
- Question 19: Which technique is used to demonstrate the finding in this v...
- Question 20: Which complication is of greatest concern with undescended t...
- Question 21: Which measurement is the upper limit for a normal gallbladde...
- Question 22: Which diagnosis is most consistent with this image from a pa...
- Question 23: Which sonographic appearance of the normal epididymis is the...
- Question 24: Which complication would be associated with retroperitoneal ...
- Question 25: Which sonographic finding is most consistent with scrotal in...
- Question 26: Which exam type would be most beneficial for evaluating an e...
- Question 27: Which condition is most consistent with the findings in the ...
- Question 28: Which laboratory value stays elevated longest and is conside...
- Question 29: Which condition is a common cause of biliary duct obstructio...
- Question 30: Which arterial branches lie at the base of the renal pyramid...
- Question 31: Which congenital disorder is most consistent with the findin...
- Question 32: Which best describes the Doppler waveform findings in this i...
- Question 33: Which hernia characteristic is demonstrated in these images?...
- Question 34: Which characteristic is associated with complex pleural effu...
- Question 35: Which finding is an indication for renal biopsy to assess fo...
- Question 36: Which change of the inferior vena cava spectral Doppler wave...
- Question 37: Which diagnosis is most accurate based on the findings in th...
- Question 38: Which finding is most likely demonstrated in these images of...
- Question 39: Identify the region where Doppler sampling should be perform...
- Question 40: Which foreign body is better visualized with sonography than...
- Question 41: What is the most common malignancy of the prostate?...
- Question 42: Which malignancy most commonly metastasizes to the testes?...
- Question 43: Which congenital anomaly is demonstrated in this image? (Exh...
- Question 44: Which disease process may cause numerous shadowing calcifica...
- Question 45: Which probe frequency is most appropriate for imaging of the...
- Question 46: Which condition is most likely associated with this image of...
- Question 47: Which gray scale artifact is caused by the oscillation of ga...
- Question 48: Which structure is indicated by the arrow on this image? (Ex...
- Question 49: Which common congenital anomaly is typically seen as a cysti...
- Question 50: Which condition is characterized by abnormal dilatation of v...
- Question 51: Which neoplasm is a benign tumor of the spleen?...
- Question 52: Which condition is most likely in a patient presenting with ...
- Question 53: Which sonographic finding distinguishes focal nodular hyperp...
- Question 54: What is the main purpose for performing focused abdominal so...
- Question 55: Which retroperitoneal finding is most likely associated with...
- Question 56: Which condition is most consistent with the findings in this...
- Question 57: What is the location of the left lobe of the thyroid gland?...
- Question 58: Which pancreatic condition is commonly associated with compl...
- Question 59: Which vascular condition is most likely associated with the ...
- Question 60: Which type of hernia is located medial to the inferior epiga...
- Question 61: Which sonographic finding is most consistent with this image...
- Question 62: Which arteries are the immediate branches of the celiac trun...
- Question 63: Identify the congenital anomaly. Using your mouse, place the...
- Question 64: A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency room, complainin...
- Question 65: Which structure is indicated by the arrow on this image? (Ex...
- Question 66: Which action should a sonographer take if the abdominal aort...
- Question 67: Which vessel is most likely to display hepatofugal flow in t...
- Question 68: Based on this image, which congenital anomaly should be susp...
- Question 69: Which clinical finding is most likely associated with the pa...
- Question 70: Which area of the spleen is not covered by visceral peritone...
- Question 71: Which condition is demonstrated in this image? (Exhibit)...
- Question 72: Which sonographic appearance of the bile ducts is demonstrat...
- Question 73: Elevation of alpha-fetoprotein levels is a characteristic fi...
- Question 74: What is the most common cause of nutcracker syndrome?...
- Question 75: How are portal veins differentiated from hepatic veins?...
- Question 76: Which abnormality is the most common adult adrenal tumor?...


