Valid TDA-C01 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing TDA-C01 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest TDA-C01 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com TDA-C01 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com TDA-C01 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access TDA-C01 Dumps Premium Version
(178 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 17/49
You have the following two datasets:
* A Microsoft Excel worksheet that has two columns named Employee Name and Department
* A Microsoft SQL Server table that has three columns named Employee Name. Pay Grade and Team Size.
You want to use Tableau Prep to join the two datasets.
Which three actions should you perform in order? (Place the three correct options in order.)

* A Microsoft Excel worksheet that has two columns named Employee Name and Department
* A Microsoft SQL Server table that has three columns named Employee Name. Pay Grade and Team Size.
You want to use Tableau Prep to join the two datasets.
Which three actions should you perform in order? (Place the three correct options in order.)

Correct Answer:
Explanation:
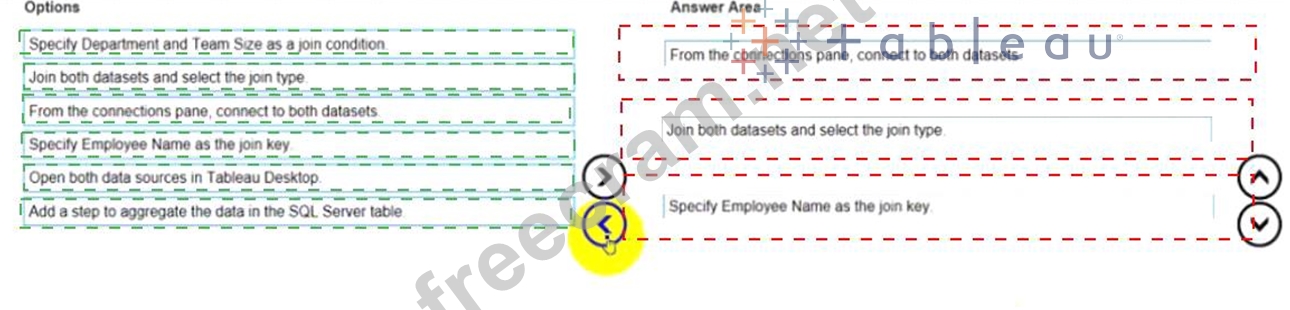
The correct order of the three actions is:
From the connections pane, connect to both data sources
Join both datasets and select the join type
Specify Employee Name as the join key
The first action is to connect to both data sources from the connections pane in Tableau Prep. The connections pane is where you can access and add data sources to your flow. You can connect to various types of data sources, such as Excel, SQL Server, or Tableau Server. In this case, you want to connect to an Excel worksheet and a SQL Server table.
The second action is to join both datasets and select the join type. A join is a way of combining data from two or more tables based on a common field. You can join datasets by dragging one table to the canvas and dropping it on top of another table. This will create a join step in your flow. You can select the join type from the drop-down list on the join step. The join type determines which rows are returned from the tables.
The third action is to specify Employee Name as the join key. A join key is a field that is used to match rows from different tables. You can specify the join key by clicking on the field name in each table and dragging it to the center of the join step. This will create a join clause that shows the field name and the operator. In this case, you want to use Employee Name as the join key, because it is a common field between the two datasets.
The other options are not relevant for this scenario. Specifying Department and Team Size as a join condition will not work, because they are not common fields between the two datasets. Opening both data sources in Tableau Desktop will not help you join them in Tableau Prep. Adding a step to aggregate the data in the SQL Server table will not affect the join, but it may change the level of detail of your data. References:
https://help.tableau.com/current/prep/en-us/prep_connect.htm
https://help.tableau.com/current/prep/en-us/prep_join.htm
https://help.tableau.com/current/prep/en-us/prep_join_types.htm
- Question List (49q)
- Question 1: You have the following table. (Exhibit) You need each record...
- Question 2: You are the owner of an alert. You receive an email notifica...
- Question 3: You have a dataset that contains daily sales by business seg...
- Question 4: You have the following dataset in Microsoft Excel. (Exhibit)...
- Question 5: You want to connect a Tableau workbook to a dataset in a Mic...
- Question 6: You connect to a database server by using Tableau Prep. The ...
- Question 7: You have the following box plot that shows the distribution ...
- Question 8: You create the following worksheet (Exhibit) The Pick Measur...
- Question 9: You have the following dataset (Exhibit) You need to create ...
- Question 10: You are developing a data source in Tableau Prep. You have t...
- Question 11: You want to create the following table in a view. (Exhibit) ...
- Question 12: Open the link to Book1 found on the desktop. Open the Movie ...
- Question 13: You have the following visualization. (Exhibit) You want the...
- Question 14: You have a dashboard that is configured for desktop browsers...
- Question 15: You have the following Map. (Exhibit) You need the map to ap...
- Question 16: You have the following dashboard that contains two sheets. (...
- Question 17: You have the following two datasets: * A Microsoft Excel wor...
- Question 18: You have the following visualization. (Exhibit) You Create a...
- Question 19: Open the link to Book1 found on the desktop. Use the Superst...
- Question 20: You have a dataset that has four fields named Category. Prof...
- Question 21: in which three formats can you export a worksheet from the W...
- Question 22: You have the following visualization. (Exhibit)...
- Question 23: You have the following chart that shows profits and discount...
- Question 24: You have a line chart on a worksheet. You want to add a comm...
- Question 25: You have a Tableau workbook. You want to make the workbook a...
- Question 26: You have a dataset that contains people and the awards they ...
- Question 27: You have a data source that contains data tor every city in ...
- Question 28: You have the following dataset. (Exhibit) You need to create...
- Question 29: You have a Tableau Prep flow that joins a dataset named Glob...
- Question 30: In a dataset, you have a string field named Name that contai...
- Question 31: Open the link to Book1 found on the desktop. Open the Histog...
- Question 32: Open the Link to Book1 found on the desktop. Open Map worksh...
- Question 33: You have the following primary data source that contains a d...
- Question 34: From Tableau Desktop you sign in lo a Tableau Server site. W...
- Question 35: You have the following dataset: (Exhibit) Which grouping opt...
- Question 36: A colleague provides you with access to a folder that contai...
- Question 37: You have two data sources that use the same schema One data ...
- Question 38: You have the following dataset. (Exhibit) When you use the d...
- Question 39: You want to create the following dashboard. (Exhibit) The da...
- Question 40: You have the following dataset. (Exhibit) Which formula calc...
- Question 41: You have the following dataset. (Exhibit) Which grouping opt...
- Question 42: You are creating a new dashboard. You need to add a button t...
- Question 43: You have a dataset that contains sates data. The following i...
- Question 44: You have the following line chart that shows the average sal...
- Question 45: Open the link to Book1 found on the desktop. Open Discipline...
- Question 46: You have the following worksheet. (Exhibit) You want to crea...
- Question 47: You have a blank dashboard. You want to add two sheets to th...
- Question 48: You have the following dataset: (Exhibit) You want to create...
- Question 49: You have the following tiled dashboard that has one sheet. (...


