Valid JN0-280 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing JN0-280 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest JN0-280 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com JN0-280 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com JN0-280 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access JN0-280 Dumps Premium Version
(187 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 57/85
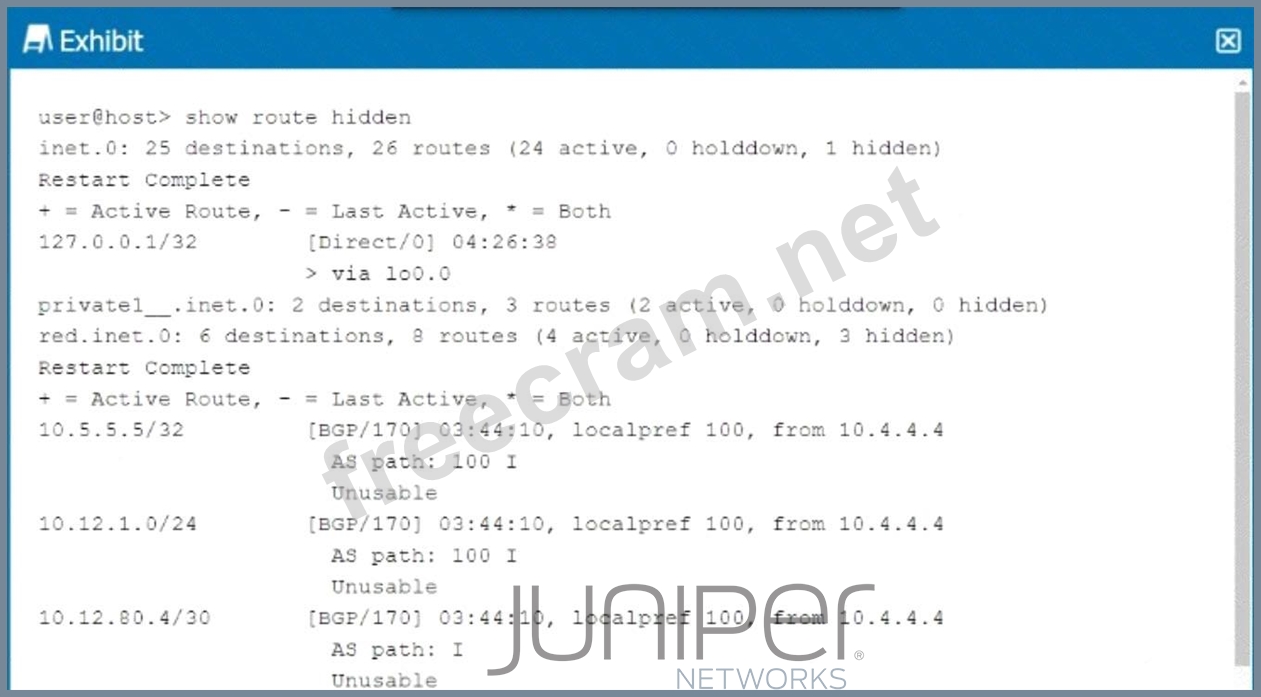
Referring to the exhibit, why are the BGP routes hidden?
Correct Answer: C
In the exhibit, the BGP routes are marked ashidden. This typically happens when the routes are not considered valid for use, but they remain in the routing table for reference. One common reason for BGP routes being hidden is that thenext hopfor these routes is unreachable.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
* BGP Next Hop:In BGP, when a route is received from a neighbor, thenext hopis the IP address that must be reachable for the route to be used. If the next hop is unreachable (i.e., the router cannot find a path to the next-hop IP), the route is marked as hidden.
* Analyzing the Exhibit:The exhibit shows that the BGP next hop for all hidden routes is 10.4.4.4. If this IP is unreachable, the BGP routes from that neighbor will not be considered valid, even though they appear in the routing table.
* Verification:
* Use the command show route 10.4.4.4 to check if the next-hop IP is reachable.
* If the next-hop is not reachable, the BGP routes will be hidden. Resolving the next-hop reachability issue (e.g., fixing an IGP route or an interface) will allow the BGP routes to become active.
Juniper Reference:
* Junos Command: show route hidden displays routes that are not considered for forwarding.
* Troubleshooting: Check the next hop reachability for hidden BGP routes using show route <next-hop>.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
* BGP Next Hop:In BGP, when a route is received from a neighbor, thenext hopis the IP address that must be reachable for the route to be used. If the next hop is unreachable (i.e., the router cannot find a path to the next-hop IP), the route is marked as hidden.
* Analyzing the Exhibit:The exhibit shows that the BGP next hop for all hidden routes is 10.4.4.4. If this IP is unreachable, the BGP routes from that neighbor will not be considered valid, even though they appear in the routing table.
* Verification:
* Use the command show route 10.4.4.4 to check if the next-hop IP is reachable.
* If the next-hop is not reachable, the BGP routes will be hidden. Resolving the next-hop reachability issue (e.g., fixing an IGP route or an interface) will allow the BGP routes to become active.
Juniper Reference:
* Junos Command: show route hidden displays routes that are not considered for forwarding.
* Troubleshooting: Check the next hop reachability for hidden BGP routes using show route <next-hop>.
- Question List (85q)
- Question 1: Which of the following are true regarding port modes in a VL...
- Question 2: Exhibit: (Exhibit) Referring to the exhibit, which statement...
- Question 3: Which statement is correct about OSPF?...
- Question 4: Which three actions are required to implement filter-based f...
- Question 5: Exhibit: (Exhibit) Referring to the exhibit, what is the rou...
- Question 6: Which two statements are correct about using LACP on a Junos...
- Question 7: Which OSPF troubleshooting tool is used to check the OSPF pr...
- Question 8: Exhibit: (Exhibit) R2 received an OSPF update from R1, and i...
- Question 9: What is the primary function of a VLAN?...
- Question 10: With regards to graceful restart, which two statements are t...
- Question 11: How does OSPF calculate the best path to a particular prefix...
- Question 12: Which statement is correct about a three-stage IP fabric und...
- Question 13: What is Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) primarily used...
- Question 14: What is the primary role of an IRB interface in a VLAN confi...
- Question 15: When evaluating BGP routes, what will be evaluated first?...
- Question 16: Which Junos operational mode command is used to troubleshoot...
- Question 17: What is the default route preference of a static route in th...
- Question 18: Which statement about switches is correct?...
- Question 19: Which BGP message type is used to establish peering sessions...
- Question 20: A generated route is configured under which hierarchy?...
- Question 21: Which three technologies improve high availability and conve...
- Question 22: What are two consequences of having all network devices in a...
- Question 23: You are creating an IP fabric underlay and want to use OSPF ...
- Question 24: Within your router, you want to verify that you are learning...
- Question 25: Which operation mode command will display the mapping betwee...
- Question 26: In OSPF, which command is commonly used to monitor neighbor ...
- Question 27: Which of the following BGP attributes is considered first in...
- Question 28: In configuring load balancing on a network router, which asp...
- Question 29: EVPN/VXLAN is primarily used in modern data centers to:...
- Question 30: Exhibit: (Exhibit) Referring to the exhibit, which next hop ...
- Question 31: Which statement is correct about per-flow load balancing?...
- Question 32: Which Junos OS routing table stores IPv6 addresses?...
- Question 33: In Ethernet switching, what is the primary function of a sto...
- Question 34: Which of the following are true about Layer 2 and Layer 3 st...
- Question 35: You want to minimize topology disruptions in your network wh...
- Question 36: What are two requirements for an IP fabric? (Choose two.)...
- Question 37: Which statement is correct about the OSPF link-state databas...
- Question 38: What are two reasons why you would deploy an IP fabric inste...
- Question 39: Which signaling protocol is used for EVPN?...
- Question 40: Referring to the exhibit, how many stages are in this IP fab...
- Question 41: In OSPF, which term refers to routers that have interfaces i...
- Question 42: What does VXLAN stand for in the context of EVPN/VXLAN?...
- Question 43: Which route is preferred by the Junos OS software routing ta...
- Question 44: What are two device roles in a five-member Virtual Chassis? ...
- Question 45: Which two statements are correct about VLAN tags? (Choose tw...
- Question 46: In the context of Ethernet bridging on Junos devices, what i...
- Question 47: What is the purpose of using route reflectors in BGP?...
- Question 48: In OSPF, how is the Router ID determined?...
- Question 49: Which two statement are correct about trunk ports? (Choose t...
- Question 50: VLANs help in reducing which of the following? (Choose two)...
- Question 51: Referring to the exhibit, how many milliseconds will pass be...
- Question 52: Which statement is correct about an IP fabric?...
- Question 53: Which two statements are correct about aggregate routes and ...
- Question 54: BGP is primarily used for which purpose in a network?...
- Question 55: You want to enable a Junos device to support aggregated Ethe...
- Question 56: What is the main advantage of using an Overlay Network in a ...
- Question 57: (Exhibit) Referring to the exhibit, why are the BGP routes h...
- Question 58: When configuring High Availability components, which of the ...
- Question 59: When configuring static routes, which command is typically u...
- Question 60: Referring to the exhibit, you notice that after committing t...
- Question 61: Which state in the adjacency process do OSPF routers check t...
- Question 62: Which type of route is used to represent a summary of multip...
- Question 63: Which two statements are correct about EVPN-VXLAN overlay ne...
- Question 64: Filter-based forwarding is typically used to:...
- Question 65: You are configuring OSPF in your network as shown in the exh...
- Question 66: Which of the following VLAN port modes exist in Junos OS? (C...
- Question 67: Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct a...
- Question 68: MACsec provides protection against which two types of threat...
- Question 69: What roles do the Designated Router (DR) and Backup Designat...
- Question 70: Leaf and spine data centers are used to better accommodate w...
- Question 71: When troubleshooting issues with static routes, what is a ke...
- Question 72: In the Junos OS, what is the default behavior of a switch wh...
- Question 73: Which of the following are functions of MACsec? (Choose two)...
- Question 74: Under which Junos hierarchy is a static route configured?...
- Question 75: During a BGP Graceful Restart, what happens to the routes le...
- Question 76: In networking, what is a RIB group primarily used for?...
- Question 77: Which EBGP feature must be used when peering to a non-direct...
- Question 78: Why is EVPN often used in conjunction with VXLAN in modern d...
- Question 79: What is the main purpose of Bidirectional Forwarding Detecti...
- Question 80: Which OSPF packet types are used to establish and maintain n...
- Question 81: In Junos, which command is used to display the status of all...
- Question 82: Exhibit: (Exhibit) How many stages are shown in the exhibit?...
- Question 83: What is a key characteristic of traditional multi-tier data ...
- Question 84: When using spine and leaf fabric architectures, what is the ...
- Question 85: Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are true? (Ch...


