Valid AZ-104 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing AZ-104 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest AZ-104 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com AZ-104 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com AZ-104 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access AZ-104 Dumps Premium Version
(815 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 106/146
Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles.
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure virtual network named VNet1. Each office has a site-to-site VPN connection to VNet1.
Each network uses the address spaces shown in the following table.
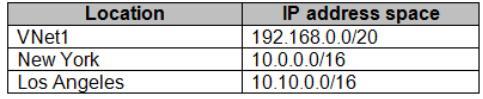
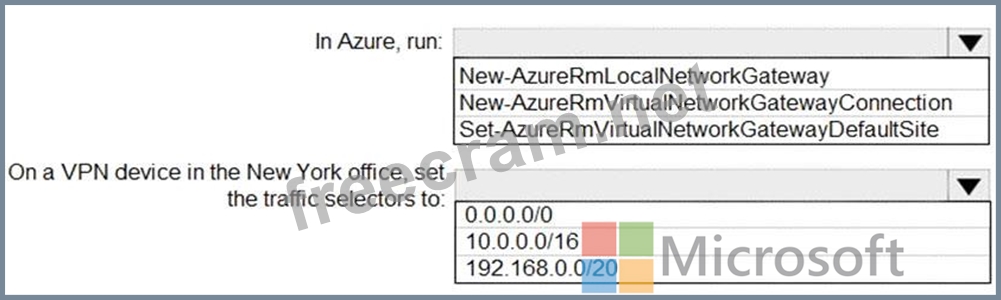
You need to ensure that all Internet-bound traffic from VNet1 is routed through the New York office.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure virtual network named VNet1. Each office has a site-to-site VPN connection to VNet1.
Each network uses the address spaces shown in the following table.

You need to ensure that all Internet-bound traffic from VNet1 is routed through the New York office.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Correct Answer:
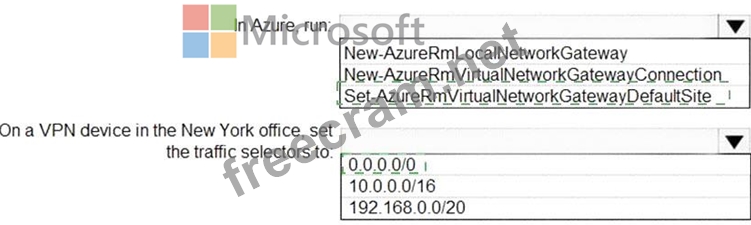
Explanation
Box 1 : Set-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayDefaultSite
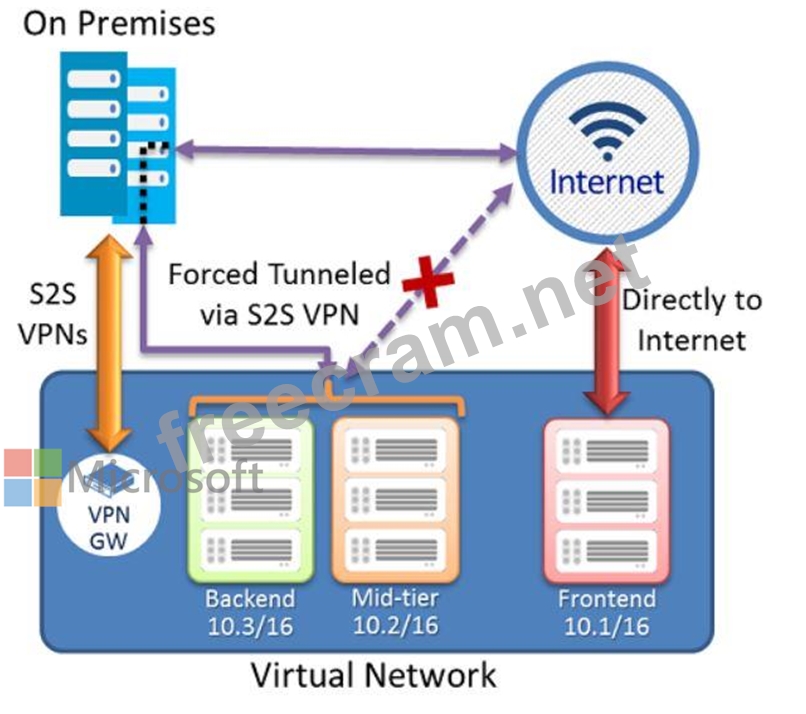
The Set-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayDefaultSite cmdlet assigns a forced tunneling default site to a virtual network gateway. Forced tunneling provides a way for you to redirect Internet-bound traffic from Azure virtual machines to your on-premises network; this enables you to inspect and audit traffic before releasing it. Forced tunneling is carried out by using a virtual private network (VPN) tunnel; this tunnel requires a default site, a local gateway where all the Azure Internet-bound traffic is redirected. Set-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayDefaultSite provides a way to change the default site assigned to a gateway.
Box 2 : 0.0.0.0/0
Forced tunneling must be associated with a VNet that has a route-based VPN gateway. You need to set a
"default site" among the cross-premises local sites connected to the virtual network. Also, the on-premises VPN device must be configured using 0.0.0.0/0 as traffic selectors.
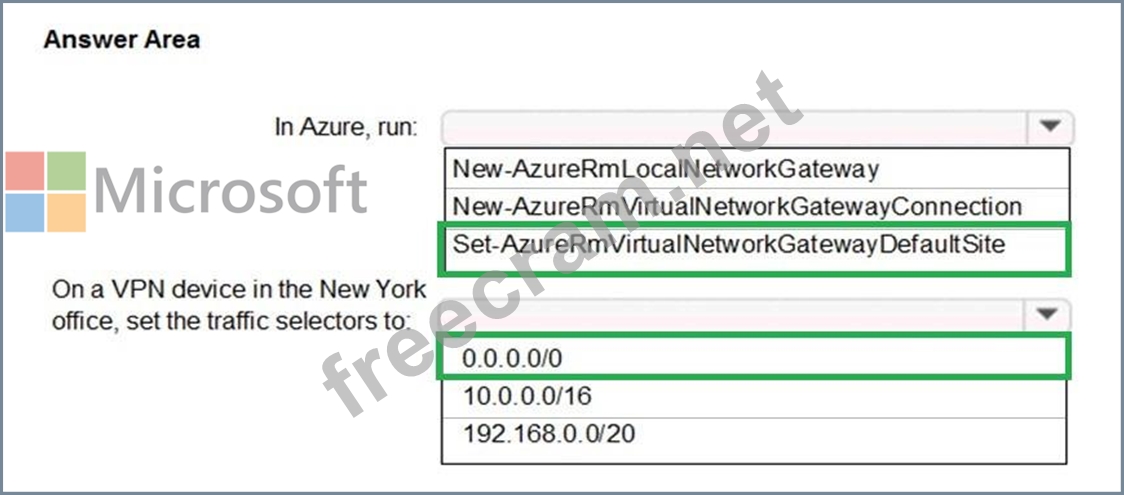
Forced Tunneling:
The following diagram illustrates how forced tunneling works
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/azurerm.network/set-azurermvirtualnetworkgatewaydefault
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-forced-tunneling-rm
- Question List (146q)
- Question 1: You create an Azure Migrate project named TestMig in a resou...
- Question 2: You plan to deploy five virtual machines to a virtual networ...
- Question 3: You have an on-premises network that contains a Hyper-V host...
- Question 4: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 5: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following u...
- Question 6: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources s...
- Question 7: You have an on-premises network that includes a Microsoft SQ...
- Question 8: You have a computer named Computer! that has a point-to site...
- Question 9: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- 1 commentQuestion 10: You have a .NET Core application running in Azure App Servic...
- Question 11: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- Question 12: You have an Azure web app named App1 that has two deployment...
- Question 13: You have an app named App1 that runs on an Azure web app nam...
- Question 14: Which blade should you instruct the finance department audit...
- Question 15: You create a virtual machine scale set named Scale1. Scale1 ...
- 1 commentQuestion 16: You have an Azure web app named App1 that streams video cont...
- Question 17: You have an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. You i...
- Question 18: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 19: You have an Azure subscription. The subscription includes a ...
- Question 20: You have two subscriptions named Subscription1 and Subscript...
- Question 21: You have an Azure virtual machine that runs Windows Server 2...
- Question 22: You have an Azure subscription that is used by four departme...
- Question 23: You have two Azure virtual networks named VNet1 and VNet2. V...
- Question 24: You are configuring serverless computing in Azure. You need ...
- Question 25: You create a Recovery Services vault backup policy named Pol...
- Question 26: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources s...
- Question 27: You have an Azure virtual machine that runs Windows Server 2...
- Question 28: You have an Azure subscription. You have an on-premises virt...
- Question 29: You have an Azure subscription named AZPT1 that contains the...
- Question 30: You have Azure subscription that includes following Azure fi...
- Question 31: You have an Azure subscription that contains the storage acc...
- Question 32: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 33: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 34: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 35: You have an Azure subscription that contains 10 virtual mach...
- Question 36: You have an Azure subscription that contains the public load...
- Question 37: You need to recommend a solution for App1. The solution must...
- Question 38: You have an Azure virtual network named VNet1 that contains ...
- Question 39: You recently created a new Azure subscription that contains ...
- Question 40: You need to define a custom domain name for Azure AD to supp...
- Question 41: VM1 is running and connects to NIC1 and Disk1. NIC1 connects...
- Question 42: You are creating an Azure load balancer. You need to add an ...
- Question 43: You create the following resources in an subscription: * An ...
- Question 44: You plan to deploy several Azure virtual machines that will ...
- 1 commentQuestion 45: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that ha...
- Question 46: You have an Azure Storage accounts as shown in the following...
- Question 47: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 48: You plan to create an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that w...
- Question 49: You have an Azure App Service plan that hosts an Azure App S...
- Question 50: You have a virtual network named VNet1 that has the configur...
- Question 51: You have an Azure subscription that contains a policy-based ...
- Question 52: You need to recommend a solution to automate the configurati...
- Question 53: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 54: You have Azure subscriptions named Subscription1 and Subscri...
- Question 55: You plan to deploy several Azure virtual machines that will ...
- 1 commentQuestion 56: You have a virtual network named VNET1 that contains the sub...
- Question 57: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 58: You have an Azure subscription that includes data in followi...
- Question 59: You have a resource group named RG1. RG1 contains an Azure S...
- Question 60: You have two Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenants named...
- Question 61: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 62: You have an Azure web app named webapp1. Users report that t...
- Question 63: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 64: You have an Azure subscription. You plan to use an Azure Res...
- Question 65: You have the Azure virtual machines shown in the following t...
- Question 66: You need to meet the user requirement for Admin1. What shoul...
- Question 67: Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain...
- Question 68: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 1 commentQuestion 69: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources s...
- Question 70: You have an Azure subscription that has a Recovery Services ...
- Question 71: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- 1 commentQuestion 72: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that has ...
- Question 73: You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following...
- Question 74: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual machi...
- Question 75: You need to implement Role1. Which command should you run be...
- Question 76: You create an Azure subscription named Subscription1 and an ...
- Question 77: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 78: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 79: You have an Azure Subscription named Subcription1.has Subcri...
- Question 80: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 81: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Active...
- Question 82: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 83: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- Question 84: You have an Azure Service Bus. You need to implement a Servi...
- Question 85: You have an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster named AKS...
- Question 86: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 87: You deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster named C...
- Question 88: You need to prepare the environment to ensure that the web a...
- Question 89: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 90: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- Question 91: You have an Azure Migrate project that has the following ass...
- Question 92: You need to use Azure Automation State Configuration to mana...
- Question 93: Note This question is part of a series of questions that pre...
- Question 94: You have an Active Directory domain named contoso.com that c...
- 1 commentQuestion 95: Your VMware vSphere on-premises infrastructure hosts 600 vir...
- Question 96: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 97: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 98: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named a...
- Question 99: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that you use for...
- Question 100: You have 100 Azure subscriptions. All the subscriptions are ...
- Question 101: You have two Azure virtual machines named VM1 and VM2. VM1 h...
- Question 102: You have an Azure subscription that contains a web app named...
- Question 103: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named C...
- Question 104: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 105: You have an azure subscription that contain a virtual named ...
- Question 106: Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles. You ha...
- Question 107: You have an Azure subscription that contains two virtual mac...
- Question 108: You are building a custom Azure function app to connect to A...
- Question 109: You have peering configured as shown in the following exhibi...
- Question 110: You have a Basic App Service plan named ASP1 that hosts an A...
- Question 111: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Active...
- Question 112: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 113: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 114: You have the App Service plans shown in the following table....
- Question 115: You have an Azure subscription that contains two virtual net...
- Question 116: You have an Azure subscription. You create the Azure Storage...
- Question 117: You have an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster named AKS...
- Question 118: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 119: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 120: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 121: You are the global administrator for an Azure Active Directo...
- Question 122: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 123: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 124: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 125: A web developer creates a web application that you plan to d...
- Question 126: You have an azure subscription named Subscription that conta...
- Question 127: You need to the appropriate sizes for the Azure virtual for ...
- Question 128: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 129: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 130: You have an Azure subscription named Subcription1 that conta...
- Question 131: You have an Azure Storage account named storage1. You plan t...
- Question 132: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 133: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 134: You have an Azure policy as shown in the following exhibit. ...
- Question 135: You have an Azure Active Directory tenant named Contoso.com ...
- Question 136: You have a Microsoft SQL Server Always On availability group...
- Question 137: You need to move the blueprint files to Azure. What should y...
- Question 138: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 139: You have an on-premises network that you plan to connect to ...
- Question 140: You have an Azure subscription that contains a resource grou...
- Question 141: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant. You ne...
- Question 142: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. You have...
- Question 143: You have a sync group named Sync1 that has a cloud endpoint....
- Question 144: You need to resolve the licensing issue before you attempt t...
- Question 145: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- Question 146: You are configuring Azure Active Directory (AD) Privileged I...


