<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 28/42
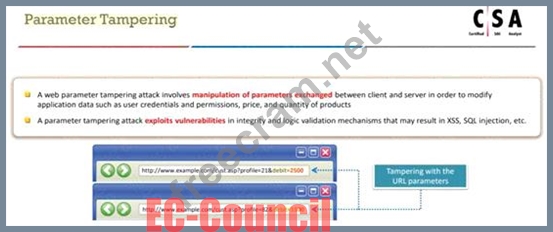
An attacker exploits the logic validation mechanisms of an e-commerce website. He successfully purchases a product worth $100 for $10 by modifying the URL exchanged between the client and the server.
Original
URL: http://www.buyonline.com/product.aspx?profile=12
&debit=100
Modified URL: http://www.buyonline.com/product.aspx?profile=12
&debit=10
Identify the attack depicted in the above scenario.
Original
URL: http://www.buyonline.com/product.aspx?profile=12
&debit=100
Modified URL: http://www.buyonline.com/product.aspx?profile=12
&debit=10
Identify the attack depicted in the above scenario.