Valid SK0-005 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing SK0-005 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest SK0-005 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com SK0-005 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com SK0-005 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access SK0-005 Dumps Premium Version
(492 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 53/154
A security analyst completed a port scan of the corporate production-server network. Results of the scan were then provided to a systems administrator for immediate action. The following table represents the requested changes:
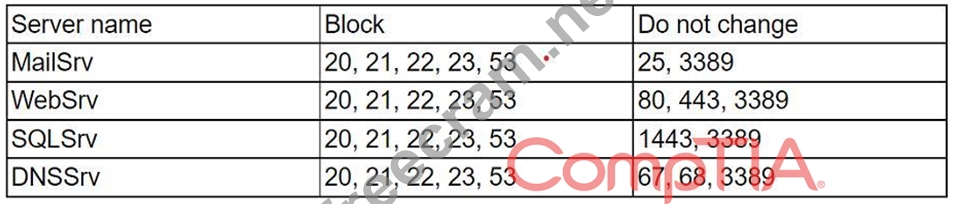
The systems administrator created local firewall rules to block the ports indicated above. Immediately, the service desk began receiving calls about the internet being down. The systems administrator then reversed the changes, and the internet became available again. Which of the following ports on DNSSrv must remain open when the firewall rules are reapplied?

The systems administrator created local firewall rules to block the ports indicated above. Immediately, the service desk began receiving calls about the internet being down. The systems administrator then reversed the changes, and the internet became available again. Which of the following ports on DNSSrv must remain open when the firewall rules are reapplied?
Correct Answer: E
Explanation
Port 53 is the standard port for DNS (Domain Name System) queries and responses. DNS is a service that translates domain names (such as www.example.com) into IP addresses (such as 192.0.2.1) and vice versa. DNS is essential for internet connectivity, as it allows users and applications to access websites and other online resources by using human-readable names instead of numerical addresses1.
The DNSSrv server is a DNS server that provides name resolution for the corporate network. If port 53 is blocked on this server, it will not be able to communicate with other DNS servers or clients, and the name resolution will fail. This will prevent users from accessing any websites or online services that rely on domain names, such as web browsers, email clients, or cloud applications. Therefore, port 53 must remain open on DNSSrv to allow DNS traffic to flow.
Port 53 is the standard port for DNS (Domain Name System) queries and responses. DNS is a service that translates domain names (such as www.example.com) into IP addresses (such as 192.0.2.1) and vice versa. DNS is essential for internet connectivity, as it allows users and applications to access websites and other online resources by using human-readable names instead of numerical addresses1.
The DNSSrv server is a DNS server that provides name resolution for the corporate network. If port 53 is blocked on this server, it will not be able to communicate with other DNS servers or clients, and the name resolution will fail. This will prevent users from accessing any websites or online services that rely on domain names, such as web browsers, email clients, or cloud applications. Therefore, port 53 must remain open on DNSSrv to allow DNS traffic to flow.
- Question List (154q)
- Question 1: The management team at a healthcare organization is concerne...
- Question 2: Which of the following physical security concepts would most...
- Question 3: A server technician is configuring the IP address on a newly...
- Question 4: Which of the following is the MOST secure method to access s...
- Question 5: An organization is donating its outdated server equipment to...
- Question 6: A server administrator is installing a new server that uses ...
- Question 7: Following a recent power outage, a server in the data center...
- Question 8: An administrator is deploying a new secure web server. The o...
- Question 9: A server administrator needs to harden a server by only allo...
- Question 10: Due to a recent application migration, a company's current s...
- Question 11: A new application server has been configured in the cloud to...
- Question 12: A technician is laying out a filesystem on a new Linux serve...
- Question 13: An administrator has been asked to deploy a database server ...
- Question 14: A company is implementing a check-in desk to heighten physic...
- Question 15: Which of the following testing exercises for disaster recove...
- Question 16: Which of the following DR testing scenarios is described as ...
- Question 17: An administrator is researching the upcoming licensing softw...
- Question 18: A server that recently received hardware upgrades has begun ...
- Question 19: When configuring networking on a VM, which of the following ...
- Question 20: A server technician is installing a Windows server OS on a p...
- Question 21: A server technician downloaded new firmware from the manufac...
- Question 22: A technician is connecting a Linux server to a share on a NA...
- Question 23: A technician is creating a network snare that will be used a...
- Question 24: An administrator discovers a Bash script file has the follow...
- Question 25: Due to a disaster incident on a primary site, corporate user...
- Question 26: An administrator is working on improving the security of a n...
- Question 27: A server administrator wants to run a performance monitor fo...
- Question 28: Which of the following technologies would allow an administr...
- Question 29: An application server's power cord was accidentally unplugge...
- Question 30: Which of the following ensures a secondary network path is a...
- Question 31: A systems administrator is attempting to install a package o...
- Question 32: A server has experienced several component failures. To mini...
- Question 33: A company is reviewing options for its current disaster reco...
- Question 34: A server administrator has been creating new VMs one by one....
- Question 35: A technician recently applied a critical OS patch to a worki...
- Question 36: Which of the following open ports should be closed to secure...
- Question 37: A server administrator is using remote access to update a se...
- Question 38: A technician has been asked to check on a SAN. Upon arrival,...
- Question 39: A system administrator has been alerted to a zero-day vulner...
- Question 40: Which of the following BEST describes a warm site?...
- Question 41: Which of the following policies would be BEST to deter a bru...
- Question 42: Corporate policy mandates that logs from all servers be avai...
- Question 43: An administrator is configuring the storage for a new databa...
- Question 44: A technician re working on a Linux server and re trying to a...
- Question 45: An administrator is configuring a server that will host a hi...
- Question 46: An administrator needs to perform bare-metal maintenance on ...
- Question 47: A server administrator mounted a new hard disk on a Linux sy...
- Question 48: An application needs 10GB of RAID 1 for log files, 20GB of R...
- Question 49: Users in an office lost access to a file server following a ...
- Question 50: A technician is configuring a server that requires secure re...
- Question 51: An administrator is troubleshooting a RAID issue in a failed...
- Question 52: A server administrator is implementing an authentication pol...
- Question 53: A security analyst completed a port scan of the corporate pr...
- Question 54: An administrator is troubleshooting a failed NIC in an appli...
- Question 55: A security administrator ran a port scanning tool against a ...
- Question 56: Which of the following would MOST likely be part of the user...
- Question 57: An upper management team is investigating a security breach ...
- Question 58: An administrator has deployed a new virtual server from a te...
- Question 59: Which of the following is an architectural reinforcement tha...
- Question 60: Which of the following would a systems administrator most li...
- Question 61: An administrator has been asked to verify that all traffic e...
- Question 62: A technician runs top on a dual-core server and notes the fo...
- Question 63: A server administrator notices the /var/log/audit/audit.log ...
- Question 64: A newly hired systems administrator is concerned about files...
- Question 65: Which of the following attacks is the most difficult to miti...
- Question 66: The HIDS logs on a server indicate a significant number of u...
- Question 67: A server technician notices a server is very low on disk spa...
- Question 68: A user can successfully connect to a database server from a ...
- Question 69: Which of the following types of asset management documentati...
- Question 70: After configuring IP networking on a newly commissioned serv...
- Question 71: An administrator is troubleshooting an application performan...
- Question 72: Which of the following licensing models is MOST appropriate ...
- Question 73: A server administrator is trying to determine the cause of a...
- Question 74: A systems administrator needs to configure a new server and ...
- Question 75: A server administrator has a system requirement lo install t...
- Question 76: A technician has received multiple reports of issues with a ...
- Question 77: A technician learns users are unable to tog in to a Linux se...
- Question 78: A company needs to increase the security controls on its ser...
- Question 79: A systems administrator is trying to determine why users in ...
- Question 80: A server administrator is installing an OS on a new server. ...
- Question 81: A technician is troubleshooting a server issue. The technici...
- Question 82: A server administrator is completing an OS installation for ...
- Question 83: The accounting department needs more storage and wants to re...
- Question 84: Which of the following BEST describes overprovisioning in a ...
- Question 85: Which of me following is the BEST action to perform before a...
- Question 86: A server shut down after an extended power outage. When powe...
- Question 87: An administrator is troubleshooting a failure in the data ce...
- Question 88: A company needs a media server set up that provides the high...
- Question 89: An administrator is able to ping the default gateway and int...
- Question 90: A server administrator is connecting a new storage array to ...
- Question 91: A server administrator needs to keep a copy of an important ...
- Question 92: A server administrator made a change in a server's BIOS in a...
- Question 93: A server administrator receives the following output when tr...
- Question 94: A technician has several possible solutions to a reported se...
- Question 95: Which of the following describes a configuration in winch bo...
- Question 96: Which of the following concepts is in use when dual power su...
- Question 97: A change in policy requires a complete backup of the account...
- Question 98: A server administrator is creating a new server that will be...
- Question 99: A technician is configuring a point-to-point heartbeat conne...
- Question 100: Which of the following must a server administrator do to ens...
- Question 101: Which of the following would be BEST to help protect an orga...
- Question 102: A company's security team has noticed employees seem to be b...
- Question 103: A data center has 4U rack servers that need to be replaced u...
- Question 104: A server administrator needs to ensure all Window-based serv...
- Question 105: A server administrator is instating a new server in a data c...
- Question 106: The Chief Information Officer (CIO) of a datacenter is conce...
- Question 107: An administrator needs to disable root login over SSH. Which...
- Question 108: A systems administrator is preparing to install two servers ...
- Question 109: Which of me following BEST describes a disaster recovery sit...
- Question 110: Which of the following backup methods protects all the chang...
- Question 111: Which of the following actions should a server administrator...
- Question 112: A storage administrator needs to implement SAN-based shared ...
- Question 113: A systems administrator is performing maintenance on 12 Wind...
- Question 114: Which of the following security risks provides unauthorized ...
- Question 115: Which of the following BEST measures now much downtime an or...
- Question 116: A systems administrator has noticed performance degradation ...
- Question 117: A company deploys antivirus, anti-malware, and firewalls tha...
- Question 118: A security analyst suspects a remote server is running vulne...
- Question 119: An administrator has been asked to disable CPU hyperthreadin...
- Question 120: A Linux server was recently updated. Now, the server stops d...
- Question 121: An administrator restores several database files without err...
- Question 122: A server technician has been asked to upload a few files fro...
- Question 123: An administrator needs to increase the size of an existing R...
- Question 124: A server administrator is swapping out the GPU card inside a...
- Question 125: A server technician has received reports of database update ...
- Question 126: A technician is attempting to log in to a Linux server as ro...
- Question 127: A server technician is installing a new server OS on legacy ...
- Question 128: The network's IDS is giving multiple alerts that unauthorize...
- Question 129: A server technician installs a new NIC on a server and confi...
- Question 130: A server administrator needs to check remotely for unnecessa...
- Question 131: A user has been unable to authenticate to the company's exte...
- Question 132: Which of the following is an example of load balancing?...
- Question 133: Which of the following is a method that is used to prevent m...
- Question 134: A security manager is concerned that a rogue employee could ...
- Question 135: A server administrator is currently working on an incident. ...
- Question 136: Which of the following licensing concepts is based on the nu...
- Question 137: A technician has beer tasked to install a new CPU. Prior to ...
- Question 138: An administrator gave Ann modify permissions to a shared fol...
- Question 139: A technician needs to install a Type 1 hypervisor on a serve...
- Question 140: (Exhibit) Which of the following actions should the server a...
- Question 141: The Chief Information Officer of a data center is concerned ...
- Question 142: An administrator is deploying a new secure web server. The o...
- Question 143: A technician set up a new multifunction printer. After addin...
- Question 144: A server administrator encounters some issues with the serve...
- Question 145: The management team has mandated the use of data-at-rest enc...
- Question 146: A server administrator is building a pair of new storage ser...
- Question 147: A global organization keeps personnel application servers th...
- Question 148: Users ate experiencing issues when trying to access resource...
- Question 149: A snapshot is a feature that can be used in hypervisors to:...
- Question 150: A technician needs maximum power redundancy while configurin...
- Question 151: A server administrator has configured a web server. Which of...
- Question 152: A human resources analyst is attempting to email the records...
- Question 153: Which of the following access control methodologies can be d...
- Question 154: Which of the following concepts refers to prioritizing a con...


