- Home
- Cisco
- Performing CyberOps Using Cisco Security Technologies
- Cisco.350-201.v2025-02-19.q68
- Question 10
Valid 350-201 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 350-201 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 350-201 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 350-201 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 350-201 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 350-201 Dumps Premium Version
(141 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 10/68
Refer to the exhibit.
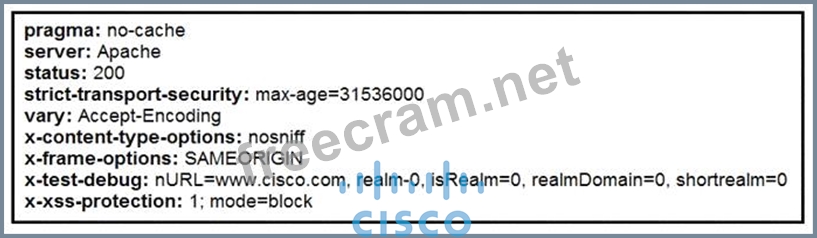
Where does it signify that a page will be stopped from loading when a scripting attack is detected?

Where does it signify that a page will be stopped from loading when a scripting attack is detected?
Correct Answer: C
The HTTP response header that signifies a page will be stopped from loading when a scripting attack is detected is the x-xss-protection header. When configured with the value "1; mode=block", it instructs the browser to block the entire page from loading if a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack is detected, rather than attempting to sanitize the potentially malicious script. This header is a browser-side measure to prevent the execution of scripts if an XSS attack is suspected.
The other headers listed serve different purposes:
* x-frame-options: Controls whether a browser should be allowed to render a page in a <frame>, <iframe>, <embed>, or <object>.
* x-content-type-options: Prevents the browser from interpreting files as a different MIME type to what is specified in the Content-Type HTTP header.
* x-test-debug: This is not a standard response header and does not relate to XSS protection.
It's important to configure web servers and applications with the appropriate security headers to mitigate various types of web-based attacks.
The other headers listed serve different purposes:
* x-frame-options: Controls whether a browser should be allowed to render a page in a <frame>, <iframe>, <embed>, or <object>.
* x-content-type-options: Prevents the browser from interpreting files as a different MIME type to what is specified in the Content-Type HTTP header.
* x-test-debug: This is not a standard response header and does not relate to XSS protection.
It's important to configure web servers and applications with the appropriate security headers to mitigate various types of web-based attacks.
- Question List (68q)
- Question 1: A customer is using a central device to manage network devic...
- Question 2: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Rapid Threat Containment usi...
- Question 3: Drag and drop the threat from the left onto the scenario tha...
- Question 4: A cloud engineer needs a solution to deploy applications on ...
- Question 5: A security architect in an automotive factory is working on ...
- Question 6: What is idempotence?
- Question 7: Which command does an engineer use to set read/write/execute...
- Question 8: A threat actor attacked an organization's Active Directory s...
- Question 9: A company recently completed an internal audit and discovere...
- Question 10: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Where does it signify that a...
- Question 11: A security expert is investigating a breach that resulted in...
- Question 12: A SOC team receives multiple alerts by a rule that detects r...
- Question 13: An organization had several cyberattacks over the last 6 mon...
- Question 14: An engineer notices that every Sunday night, there is a two-...
- Question 15: A threat actor has crafted and sent a spear-phishing email w...
- Question 16: An organization suffered a security breach in which the atta...
- Question 17: A payroll administrator noticed unexpected changes within a ...
- Question 18: Drag and drop the function on the left onto the mechanism on...
- Question 19: A European-based advertisement company collects tracking inf...
- Question 20: A SIEM tool fires an alert about a VPN connection attempt fr...
- Question 21: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) An engineer is investigating...
- Question 22: Drag and drop the phases to evaluate the security posture of...
- Question 23: An analyst wants to upload an infected file containing sensi...
- Question 24: An engineer wants to review the packet overviews of SNORT al...
- Question 25: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which code snippet will pars...
- Question 26: After a recent malware incident, the forensic investigator i...
- Question 27: What is the difference between process orchestration and aut...
- Question 28: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) What is the connection statu...
- Question 29: Drag and drop the actions below the image onto the boxes in ...
- Question 30: A SOC team is investigating a recent, targeted social engine...
- Question 31: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) An employee is a victim of a...
- Question 32: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Where are the browser page r...
- Question 33: How does Wireshark decrypt TLS network traffic?...
- Question 34: The SIEM tool informs a SOC team of a suspicious file. The t...
- Question 35: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) An engineer is reverse engin...
- Question 36: An engineer received an incident ticket of a malware outbrea...
- Question 37: An engineer notices that unauthorized software was installed...
- Question 38: A company's web server availability was breached by a DDoS a...
- Question 39: A SOC analyst detected a ransomware outbreak in the organiza...
- Question 40: A security manager received an email from an anomaly detecti...
- Question 41: Employees receive an email from an executive within the orga...
- Question 42: An engineer receives an incident ticket with hundreds of int...
- Question 43: A SOC team is informed that a UK-based user will be travelin...
- Question 44: A SOC analyst is investigating a recent email delivered to a...
- Question 45: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) An engineer must tune the Ci...
- Question 46: An audit is assessing a small business that is selling autom...
- Question 47: A patient views information that is not theirs when they sig...
- Question 48: A Mac laptop user notices that several files have disappeare...
- Question 49: Drag and drop the components from the left onto the phases o...
- Question 50: Where do threat intelligence tools search for data to identi...
- Question 51: An engineer is analyzing a possible compromise that happened...
- Question 52: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Cisco Advanced Malware Prote...
- Question 53: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Cisco Advanced Malware Prote...
- Question 54: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which asset has the highest ...
- Question 55: How is a SIEM tool used?
- Question 56: The physical security department received a report that an u...
- Question 57: An engineer received an alert of a zero-day vulnerability af...
- Question 58: An organization lost connectivity to critical servers, and u...
- Question 59: An engineer returned to work and realized that payments that...
- Question 60: An analyst is alerted for a malicious file hash. After analy...
- Question 61: A company launched an e-commerce website with multiple point...
- Question 62: A SOC analyst is notified by the network monitoring tool tha...
- Question 63: A security engineer discovers that a spreadsheet containing ...
- Question 64: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) An engineer is performing a ...
- Question 65: Which bash command will print all lines from the "colors.txt...
- Question 66: What is a principle of Infrastructure as Code?...
- Question 67: An engineer is investigating several cases of increased inco...
- Question 68: A company recently started accepting credit card payments in...


