Valid 1Z0-804 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 1Z0-804 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 1Z0-804 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 1Z0-804 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 1Z0-804 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 1Z0-804 Dumps Premium Version
(150 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 8/150
Given:
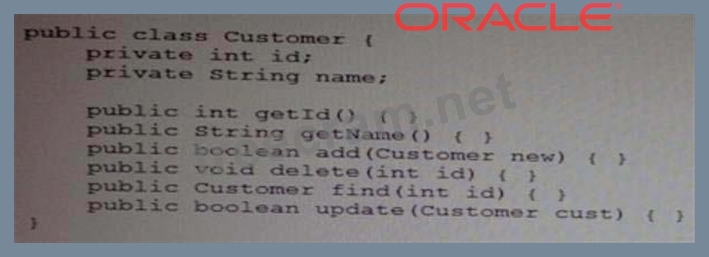
What two changes should you make to apply the DAO pattern to this class?

What two changes should you make to apply the DAO pattern to this class?
Correct Answer: C,D
Explanation/Reference:
Explanation:
C:The methods related directly to the entity Customer is moved to a new class.
D: Example (here Customer is the main entity):
public class Customer {
private final String id;
private String contactName;
private String phone;
public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; }
102
public String getId() { return this.id; }
public void setContactName(String cn) { this.contactName = cn;} public String getContactName() { return
this.contactName; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } public String getPhone()
{ return this.phone; }
}
public interface CustomerDAO {
public void addCustomer(Customer c) throws DataAccessException; public Customer getCustomer(String
id) throws DataAccessException; public List getCustomers() throws DataAccessException; public void
removeCustomer(String id) throws DataAccessException; public void modifyCustomer(Customer c) throws
DataAccessException; }
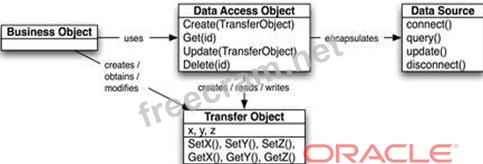
Note: DAO Design Pattern
*Abstracts and encapsulates all access to a data source *Manages the connection to the data source to
obtain and store data *Makes the code independent of the data sources and data vendors (e.g. plain-text,
xml, LDAP,
MySQL, Oracle, DB2)
Explanation:
C:The methods related directly to the entity Customer is moved to a new class.
D: Example (here Customer is the main entity):
public class Customer {
private final String id;
private String contactName;
private String phone;
public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; }
102
public String getId() { return this.id; }
public void setContactName(String cn) { this.contactName = cn;} public String getContactName() { return
this.contactName; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } public String getPhone()
{ return this.phone; }
}
public interface CustomerDAO {
public void addCustomer(Customer c) throws DataAccessException; public Customer getCustomer(String
id) throws DataAccessException; public List getCustomers() throws DataAccessException; public void
removeCustomer(String id) throws DataAccessException; public void modifyCustomer(Customer c) throws
DataAccessException; }
Note: DAO Design Pattern
*Abstracts and encapsulates all access to a data source *Manages the connection to the data source to
obtain and store data *Makes the code independent of the data sources and data vendors (e.g. plain-text,
xml, LDAP,
MySQL, Oracle, DB2)

- Question List (150q)
- Question 1: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 2: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 3: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 4: Given: (Exhibit) What is the most likely result?...
- Question 5: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) And a DOS-based file syst...
- Question 6: Given: (Exhibit) From what threading problem does the progra...
- Question 7: Which code fragment correctly appends "Java 7" to the end of...
- Question 8: Given: (Exhibit) What two changes should you make to apply t...
- Question 9: Given: (Exhibit) Which two are true?...
- Question 10: Given the directory structure that contains three directorie...
- Question 11: You have been asked to create a ResourceBundle file to local...
- Question 12: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 13: Given: String s = new String("3"); System.out.print(1 + 2 + ...
- Question 14: Which statement creates a low overhead, low-contention rando...
- Question 15: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 16: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Which two try statements,...
- Question 17: ITEM Table * ID, INTEGER: PK * DESCRIP, VARCHAR(100) * PRICE...
- Question 18: Given these facts about Java types in an application: - Type...
- Question 19: Which four are syntactically correct?...
- Question 20: Which represents part of a DAO design pattern?...
- Question 21: Assuming the port statements are correct, which two (three?)...
- Question 22: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 23: Given the code fragment: SimpleDataFormat sdf; Which code fr...
- Question 24: Given a language code of fr and a country code of FR, which ...
- Question 25: Given that myfile.txt contains: (Exhibit) What is the result...
- Question 26: Given the Greetings.properties file, containing: (Exhibit) W...
- Question 27: Which two forms of abstraction can a programmer use in Java?...
- Question 28: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 29: An application is waiting for notification of changes to a t...
- Question 30: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Assume that the SQL queri...
- Question 31: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What change should you ma...
- Question 32: Given: public class Main { public static void main(String......
- Question 33: Which class(es) safely protects the doIt () method from conc...
- Question 34: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result of the...
- Question 35: Which two actions can be used in registering a JDBC 3.0 driv...
- Question 36: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 37: Given the following code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the res...
- Question 38: A valid reason to declare a class as abstract is to:...
- Question 39: Given: (Exhibit) Which two are true about the lines labeled ...
- Question 40: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 41: Which two demonstrate the valid usage of the keyword synchro...
- Question 42: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 43: Which code fragment is required to load a JDBC 3.0 driver?...
- Question 44: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result, if th...
- Question 45: Given the database table: (Exhibit) And given this class: (E...
- Question 46: Which two properly implement a Singleton pattern?...
- Question 47: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result, if th...
- Question 48: For which three objects must a vendor provide implementation...
- Question 49: Which type of ExecutorService supports the execution of task...
- Question 50: How many Threads are created when passing task to an Executo...
- Question 51: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 52: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 53: Given: (Exhibit) Which three statements concerning the OO co...
- Question 54: When using the default file system provider with a JVM runni...
- Question 55: Given the fragment: (Exhibit) Which two valid alternatives t...
- Question 56: Given: ConcurrentMap <String, String> PartList = new C...
- Question 57: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 58: Given three resources bundles with these values set for menu...
- Question 59: Given the classes: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 60: What will the following class print when run? (Exhibit)...
- Question 61: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Assume that the SQL query...
- Question 62: Given: (Exhibit) Which two are true?...
- Question 63: Given: (Exhibit) Which statement will iterate through Direct...
- Question 64: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result when t...
- Question 65: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 66: Given the following files in doc directory: - Index.htm - Se...
- Question 67: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 68: Which four are true about enums?...
- Question 69: Given: (Exhibit) Which statement, inserted at line 8, enable...
- Question 70: The default file system includes a logFiles directory that c...
- Question 71: Which two statements are true about RowSet subinterfaces?...
- Question 72: Given: (Exhibit) Which statement is true?...
- Question 73: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 74: Given the fragment: (Exhibit) If thread a and thread b are r...
- Question 75: Which two are true about Singletons?...
- Question 76: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 77: Given this error message when running your application: Exce...
- Question 78: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 79: Which two compile?
- Question 80: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 81: Given: (Exhibit) Which two classes correctly override the ge...
- Question 82: Given the class? (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 83: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 84: Which code fragment demonstrates the proper way to handle JD...
- Question 85: Given: (Exhibit) Which two statements are true about the wri...
- Question 86: Which method would you supply to a class implementing the Ca...
- Question 87: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Which two try statements,...
- Question 88: Given the integer implements comparable: (Exhibit) What is t...
- Question 89: Which two codes correctly represent a standard language loca...
- Question 90: Given: (Exhibit) What two changes, made independently, will ...
- Question 91: Given: (Exhibit) Which two statements concerning the OO conc...
- Question 92: Which two are valid initialization statements?...
- Question 93: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 94: Given the incomplete pseudo-code for a fork/join framework a...
- Question 95: Given: (Exhibit) Which two statements, inserted independentl...
- Question 96: Given that myFile.txt contains: (Exhibit) What is the result...
- Question 97: Which three are true?
- Question 98: Given: (Exhibit) Which group of method is moved to a new cla...
- Question 99: Given: import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; pub...
- Question 100: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 101: Which concept allows generic collections to interoperate wit...
- Question 102: Given: (Exhibit) Which three are true?...
- Question 103: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Which three are true?...
- Question 104: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result of invoking Car's scop m...
- Question 105: To provide meaningful output for: System.out.print( new Item...
- Question 106: Which is a key aspect of composition?...
- Question 107: Given: (Exhibit) And the command-line invocation: Java Track...
- Question 108: Given the cache class: (Exhibit)...
- Question 109: Given the following code fragment: 10. p1 = paths.get("repor...
- Question 110: Given the code format: SimpleDateFormat sdf; Which code stat...
- Question 111: Which statement declares a generic class?...
- Question 112: Given: (Exhibit) What is the most likely result?...
- Question 113: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 114: Given: (Exhibit) And the commands: javac Test.java java ea T...
- Question 115: What are two differences between Callable and Runnable?...
- Question 116: Given the existing destination file, a source file only 1000...
- Question 117: Sam has designed an application. It segregates tasks that ar...
- Question 118: Given the code fragment: DateFormat df; Which statement defi...
- Question 119: Given two classes in separate files: (Exhibit) Which two imp...
- Question 120: Given this code fragment: (Exhibit) Assume that the SQL quer...
- Question 121: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 122: Which is a factory method from the java.text.NumberFormat cl...
- Question 123: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 124: Which three statements are correct about thread's sleep meth...
- Question 125: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) If the file userguide.txt...
- Question 126: Given: (Exhibit) And the commands: javac Counter.java java e...
- Question 127: Give: (Exhibit) Which is correct?...
- Question 128: Given: (Exhibit) Which fragment, inserted in the Books inter...
- Question 129: Give: (Exhibit) What is the likely result?...
- Question 130: View the exhibit: (Exhibit) Given the code fragment: (Exhibi...
- Question 131: Give: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 132: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 133: Given the interface: Public interface Idgenerator { int getN...
- Question 134: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Assume the method printNu...
- Question 135: The two methods of code reuse that aggregate the features lo...
- Question 136: Given: (Exhibit) Which three values will appear in the outpu...
- Question 137: Given these facts about Java classes in an application: - Cl...
- Question 138: Given the following incorrect program: (Exhibit) Which two c...
- Question 139: Given the two Java classes: (Exhibit) Which two code snippet...
- Question 140: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 141: Given: StringBuffer b = new StringBuffer("3"); System.out.pr...
- Question 142: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result when i...
- Question 143: Given: (Exhibit) Which of the four are valid modifications t...
- Question 144: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Why is there no output wh...
- Question 145: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 146: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 147: Select four examples that initialize a NumberFormat referenc...
- Question 148: Given the code fragment: (Exhibit) Which code fragment inser...
- Question 149: Given: (Exhibit) What is the result?...
- Question 150: Which two code blocks correctly initialize a Locale variable...


