Valid AZ-104 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing AZ-104 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest AZ-104 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com AZ-104 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com AZ-104 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access AZ-104 Dumps Premium Version
(428 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 206/441
You manage two Azure subscriptions named Subscription1 and Subscription2.
Subscription1 has following virtual networks:
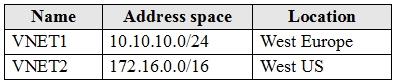
The virtual networks contain the following subnets:
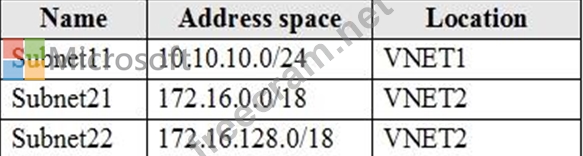
Subscription2 contains the following virtual network:
* Name: VNETA
* Address space: 10.10.128.0/17
* Location: Canada Central
VNETA contains the following subnets:
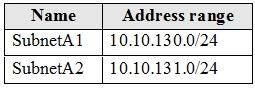
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Subscription1 has following virtual networks:

The virtual networks contain the following subnets:

Subscription2 contains the following virtual network:
* Name: VNETA
* Address space: 10.10.128.0/17
* Location: Canada Central
VNETA contains the following subnets:

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Correct Answer:

Explanation

Box 1: Yes
With VNet-to-VNet you can connect Virtual Networks in Azure across Different regions.
Box 2: Yes
Azure supports the following types of peering:
Virtual network peering: Connect virtual networks within the same Azure region.
Global virtual network peering: Connecting virtual networks across Azure regions.
Box 3: No
The virtual networks you peer must have non-overlapping IP address spaces.
References:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/vnet-to-vnet-connecting-virtual-networks-in-azure-across-different-region
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-network-manage-peering#requirements-and-const
- Question List (441q)
- Question 1: You have an app named App1 that runs on an Azure web app nam...
- Question 2: You have an Azure subscription that contains several virtual...
- Question 3: You have an Azure Storage account named storage1. You have a...
- Question 4: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources s...
- Question 5: You have an Azure subscription. You plan to use Azure Resour...
- Question 6: You deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster that ha...
- Question 7: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 8: You need to meet the connection requirements for the New Yor...
- Question 9: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 10: You have an Azure Linux virtual machine that is protected by...
- Question 11: You have the Azure management groups shown in the following ...
- 1 commentQuestion 12: You have an Azure subscription that contains two om-premises...
- Question 13: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 14: You have an Azure subscription You need to receive an email ...
- Question 15: You have two subscriptions named Subscription1 and Subscript...
- Question 16: You download an Azure Resource Manager template based on an ...
- 1 commentQuestion 17: You have an Azure subscription named Subcription1 that conta...
- Question 18: You have two Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenants named...
- 1 commentQuestion 19: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Availa...
- Question 20: You have an Azure subscription. You need to deploy a virtual...
- Question 21: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 22: You have an Azure subscription that contains a resource grou...
- Question 23: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- 1 commentQuestion 24: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. In Subsc...
- 1 commentQuestion 25: You have an Azure subscription. You plan to use Azure Resour...
- Question 26: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Servic...
- Question 27: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- Question 28: You need to recommend a solution to automate the configurati...
- Question 29: You have an Azure Storage accounts as shown in the following...
- Question 30: You are configuring serverless computing in Azure. You need ...
- 2 commentQuestion 31: You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage accou...
- Question 32: You plan to use Azure Network Watcher to perform the followi...
- Question 33: You have an Azure subscription named Sub1. You plan to deplo...
- Question 34: You have an Azure subscription. You deploy a virtual machine...
- 2 commentQuestion 35: You have the App Service plan shown in the following exhibit...
- Question 36: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 37: You have a pay-as-you-go Azure subscription that contains th...
- Question 38: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- Question 39: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named a...
- Question 40: You have an Azure subscription. The subscription contains a ...
- Question 41: You have an Azure subscription. Users access the resources i...
- Question 42: You have Azure virtual machines that run Windows Server 2019...
- Question 43: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. You have...
- Question 44: You have an Azure subscription that contains a resource grou...
- 2 commentQuestion 45: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- 1 commentQuestion 46: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 47: You need to ensure that User1 can create initiative definiti...
- Question 48: You plan to create a new Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) r...
- Question 49: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 50: You need to use Azure Automation State Configuration to mana...
- 1 commentQuestion 51: You have an Azure web app named webapp! You have a virtual n...
- Question 52: You plan to deploy an Azure container instance by using the ...
- Question 53: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 54: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 55: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 56: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 57: You plan to create an Azure Storage account in the Azure reg...
- Question 58: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 59: You have an Azure Storage accounts as shown in the following...
- Question 60: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 61: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 62: You have an Azure subscription that is used by four departme...
- Question 63: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 64: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 65: You have an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster named AKS...
- Question 66: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 67: You have a virtual network named VNet1 that has the configur...
- Question 68: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 69: Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles. You ha...
- Question 70: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 71: You have an Azure Storage account named storage1. You have a...
- Question 72: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- 1 commentQuestion 73: You have two Azure virtual machines as shown in the followin...
- Question 74: You have an Azure subscription that contains two virtual net...
- Question 75: You have an Azure subscription. The subscription includes a ...
- Question 76: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 77: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 78: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following r...
- Question 79: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 and a Recovery S...
- 1 commentQuestion 80: You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage accou...
- Question 81: You have an Azure web app named WebApp1 that runs in an Azur...
- Question 82: You need to implement Role1. Which command should you run be...
- Question 83: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 84: You download an Azure Resource Manager template based on an ...
- 2 commentQuestion 85: You have several Azure virtual machines on a virtual network...
- Question 86: You need to deploy two Azure web apps named WebApp1 and WebA...
- Question 87: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that ha...
- 1 commentQuestion 88: VM1 is running and connects to NIC1 and Disk1. NIC1 connects...
- Question 89: Case Study 1 - Humongous Insurance Overview Humongous Insura...
- Question 90: You have an Azure subscription that contains two virtual net...
- Question 91: You recently created a new Azure subscription that contains ...
- 1 commentQuestion 92: You have peering configured as shown in the following exhibi...
- Question 93: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 94: You have an existing Azure subscription that contains 10 vir...
- 1 commentQuestion 95: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- 2 commentQuestion 96: You have an Azure subscription that contains the hierarchy s...
- Question 97: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 98: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 99: You need to use Azure Automation State Configuration to mana...
- Question 100: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Availa...
- Question 101: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. You plan...
- Question 102: You have an Azure web app named App1. App1 has the deploymen...
- Question 103: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- 2 commentQuestion 104: You have web app in the West US, Central US and East US Azur...
- Question 105: You have an Azure subscription. You enable multi-factor auth...
- Question 106: You have an Azure Resource Manager template named Template1 ...
- Question 107: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- Question 108: You have an Azure subscription that contains two virtual net...
- Question 109: You have an Azure subscription that contains the public load...
- 2 commentQuestion 110: You need to define a custom domain name for Azure AD to supp...
- Question 111: You need to create an Azure Storage account that meets the f...
- 1 commentQuestion 112: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 113: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- Question 114: Case Study 3 - Contoso, Ltd Overview Contoso, Ltd. is a cons...
- Question 115: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 1 commentQuestion 116: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- 1 commentQuestion 117: You have the Azure management groups shown in the following ...
- Question 118: Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles. You ha...
- Question 119: You have an Azure subscription named Subscroption1. In Subsc...
- Question 120: You need to create container1 and share1. Which storage acco...
- Question 121: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 122: You have an Azure subscription that contains the Azure virtu...
- 1 commentQuestion 123: You have an Azure subscription that contains the Azure virtu...
- Question 124: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 125: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that runs Window...
- 1 commentQuestion 126: You have a network security group (NSG) named NSG1 that has ...
- Question 127: You have an Azure web app named App1 that has two deployment...
- Question 128: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. In Subsc...
- Question 129: You have an A2ure virtual machine named VMV The network inte...
- Question 130: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named a...
- Question 131: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 132: Your network contains an on-premises Active Directory forest...
- Question 133: From Azure Active Directory (AD) Privileged Identify Managem...
- Question 134: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 135: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 136: You purchase a new Azure subscription named Subscription1. Y...
- Question 137: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. In Subsc...
- Question 138: You have an app named App1 that runs on two Azure virtual ma...
- Question 139: A web developer creates a web application that you plan to d...
- Question 140: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. You plan...
- Question 141: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 142: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- Question 143: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 144: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1. You use Azure B...
- Question 145: You plan to create a new Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) r...
- Question 146: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- 1 commentQuestion 147: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 1 commentQuestion 148: You deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster that ha...
- Question 149: Your network is configured as shown in the following exhibit...
- 1 commentQuestion 150: You have an Azure subscription that contains the hierarchy s...
- Question 151: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 2 commentQuestion 152: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- 2 commentQuestion 153: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- 2 commentQuestion 154: You create an Azure file sync group named Sync 1 and perform...
- 1 commentQuestion 155: You have an Azure virtual network named VNet1 that connects ...
- 1 commentQuestion 156: You are evaluating the connectivity between the virtual mach...
- Question 157: Your company has a main office in London that contains 100 c...
- Question 158: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 159: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- 1 commentQuestion 160: You need to configure the alerts for VM1 and VM2 to meet the...
- Question 161: You have an Azure web app named App1 that has two deployment...
- 1 commentQuestion 162: You manage two Azure subscriptions named Subscription1 and S...
- Question 163: You have an Azure subscription named Subcription1 that conta...
- Question 164: You are the global administrator for an Azure Active Directo...
- Question 165: You have an Azure subscription named Sub1. You plan to deplo...
- Question 166: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 167: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named C...
- Question 168: SIMULATION Overview The following section of the exam is a l...
- Question 169: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Servic...
- Question 170: You have Azure virtual machines that run Windows Server 2019...
- Question 171: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 172: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure virtua...
- Question 173: You need to identify the storage requirements for Contoso. F...
- Question 174: You create an Azure Migrate project named TestMig in a resou...
- Question 175: Peering for VNET2 is configured as shown in the following ex...
- Question 176: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following u...
- 2 commentQuestion 177: You have an Azure subscription. You deploy a virtual machine...
- Question 178: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- Question 179: You have an Azure web app named WebApp1 that runs in an Azur...
- Question 180: You have an Azure Subscription named Subcription1.has Subcri...
- Question 181: You have an Azure Storage accounts as shown in the following...
- 1 commentQuestion 182: You have two Azure virtual machines as shown in the followin...
- 2 commentQuestion 183: You have an Azure virtual machine mat runs Windows Server 20...
- Question 184: You discover that VM3 does NOT meet the technical requiremen...
- Question 185: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 1 commentQuestion 186: You have an Azure subscription. You are deploying an Azure K...
- Question 187: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following r...
- Question 188: You need to identify the storage requirements for Contoso. F...
- Question 189: You have a virtual network named VNet1 as shown in the exhib...
- Question 190: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that connects to...
- 2 commentQuestion 191: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that sy...
- Question 192: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- Question 193: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following u...
- Question 194: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- 1 commentQuestion 195: You have an Azure subscription named Sub1 that contains the ...
- Question 196: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- Question 197: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 198: You have an Azure subscription that contains the hierarchy s...
- Question 199: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 200: Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain...
- Question 201: You have an Azure subscription. You need to implement a cust...
- Question 202: You have a Microsoft SQL Server Always On availability group...
- Question 203: You have an Azure Active Directory tenant named Contoso.com ...
- 1 commentQuestion 204: You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following...
- Question 205: You plan to deploy an Azure container instance by using the ...
- 1 commentQuestion 206: You manage two Azure subscriptions named Subscription1 and S...
- Question 207: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 208: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. In Subsc...
- 1 commentQuestion 209: You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following...
- Question 210: You deploy a load balancer that has the following configurat...
- Question 211: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named a...
- Question 212: You need to the appropriate sizes for the Azure virtual for ...
- Question 213: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 214: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 215: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 216: You need to prepare the environment to meet the authenticati...
- Question 217: You have an Azure web app named webapp1. You have a virtual ...
- Question 218: You create an Azure Migrate project named TestMig in a resou...
- Question 219: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that has ...
- Question 220: Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles. You ha...
- Question 221: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual netwo...
- Question 222: You have an Azure subscription that contains the public load...
- Question 223: You create an Azure file sync group named Sync 1 and perform...
- 1 commentQuestion 224: You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage accou...
- Question 225: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. In Subsc...
- Question 226: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 227: You have an Azure App Service plan that hosts an Azure App S...
- Question 228: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 229: HOTSPOT You plan to use Azure Network Watcher to perform the...
- 1 commentQuestion 230: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- Question 231: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 1 commentQuestion 232: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. You depl...
- Question 233: You have an Azure Active Directory tenant named Contoso.com ...
- 1 commentQuestion 234: You create a Recovery Services vault backup policy named Pol...
- Question 235: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 236: You plan to deploy an Azure container instance by using the ...
- Question 237: You have two Azure virtual machines named VM1 and VM2. VM1 h...
- 2 commentQuestion 238: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- 1 commentQuestion 239: You have the App Service plan shown in the following exhibit...
- 1 commentQuestion 240: You have an Azure Subscription that contains the virtual net...
- 1 commentQuestion 241: You need to configure the alerts for VM1 and VM2 to meet the...
- 1 commentQuestion 242: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that connects to...
- Question 243: Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles. You ha...
- Question 244: You are evaluating the name resolution for the virtual machi...
- 1 commentQuestion 245: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 246: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 247: You have an availability set named AS1 that contains three v...
- 3 commentQuestion 248: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 249: You have an Azure subscription that contains the Azure virtu...
- Question 250: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources s...
- Question 251: You have a sync group named Sync1 that has a cloud endpoint....
- Question 252: You need to use Azure Automation State Configuration to mana...
- Question 253: You have an Azure subscription that contains several virtual...
- Question 254: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 255: Your network is configured as shown in the following exhibit...
- 1 commentQuestion 256: You have peering configured as shown in the following exhibi...
- Question 257: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 1 commentQuestion 258: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following s...
- 1 commentQuestion 259: You need to prepare the environment to meet the authenticati...
- Question 260: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 261: Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles. You ha...
- Question 262: You are troubleshooting a performance issue for an Azure App...
- Question 263: You create an Azure Migrate project named TestMig in a resou...
- 1 commentQuestion 264: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure virtua...
- Question 265: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1. The network int...
- 1 commentQuestion 266: Your company registers a domain name of contoso.com. You cre...
- Question 267: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 268: You have an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster named AKS...
- Question 269: You have an Azure App Service plan that hosts an Azure App S...
- Question 270: You have a sync group named Sync1 that has a cloud endpoint....
- Question 271: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 272: You create a Recovery Services vault backup policy named Pol...
- Question 273: You have a hybrid infrastructure that contains an Azure Acti...
- Question 274: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following r...
- Question 275: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 276: You have an Azure subscription. You plan to use Azure Resour...
- Question 277: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 that runs Window...
- Question 278: You have a public load balancer that balances ports 80 and 4...
- Question 279: You have a virtual network named VNET1 that contains the sub...
- 1 commentQuestion 280: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that co...
- Question 281: Case Study 4 - ADatum Overview ADatum Corporation is a finan...
- Question 282: You have an on-premises network that contains a Hyper-V host...
- Question 283: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 284: You have a sync group named Sync1 that has a cloud endpoint....
- 1 commentQuestion 285: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 286: You deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster that ha...
- Question 287: You have the Azure virtual machines shown in the following t...
- Question 288: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named T...
- Question 289: You have Azure virtual machines that run Windows Server 2019...
- Question 290: You have Azure subscriptions named Subscription1 and Subscri...
- Question 291: You need to meet the connection requirements for the New Yor...
- Question 292: You have an Azure subscription that contains the Azure virtu...
- Question 293: You have an Azure subscription that contains 10 virtual mach...
- Question 294: You have a pay-as-you-go Azure subscription that contains th...
- Question 295: You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage accou...
- 1 commentQuestion 296: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that co...
- Question 297: Peering for VNET2 is configured as shown in the following ex...
- 1 commentQuestion 298: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Availa...
- 1 commentQuestion 299: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that has ...
- Question 300: From Azure Active Directory (AD) Privileged Identify Managem...
- Question 301: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- Question 302: You have an Azure subscription that contains the following u...
- 1 commentQuestion 303: You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual machi...
- Question 304: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 305: You create an App Service plan named App1 and an Azure web a...
- 1 commentQuestion 306: You need to resolve the licensing issue before you attempt t...
- Question 307: You create a Recovery Services vault backup policy named Pol...
- 1 commentQuestion 308: Your on-premises network contains a VPN gateway. You have an...
- 1 commentQuestion 309: You need to identify which storage account to use for the fl...
- Question 310: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 311: You have an Azure subscription that contains the Azure virtu...
- 2 commentQuestion 312: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Direct...
- Question 313: You have a hybrid deployment of Azure Active Directory (Azur...
- Question 314: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 315: You create a Recovery Services vault backup policy named Pol...
- Question 316: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 317: You need to deploy two Azure web apps named WebApp1 and WebA...
- 2 commentQuestion 318: You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named c...
- Question 319: You are creating an Azure load balancer. You need to add an ...
- Question 320: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 321: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources i...
- Question 322: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that has ...
- Question 323: You are evaluating the name resolution for the virtual machi...
- Question 324: Hotspot Question You have an Azure Migrate project that has ...
- 1 commentQuestion 325: You have an Azure subscription named Sub1 that contains the ...
- Question 326: You need to create an Azure Storage account that meets the f...
- Question 327: You need to implement Role1. Which command should you run be...
- Question 328: HOTSPOT You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtu...
- Question 329: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 330: You plan to create the Azure web apps shown in the following...
- Question 331: You have an Azure Migrate project that has the following ass...
- Question 332: You have the App Service plans shown in the following table....
- Question 333: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 334: You have peering configured as shown in the following exhibi...
- Question 335: You create an Azure Storage account named contosostorage. Yo...
- 1 commentQuestion 336: You have the Azure virtual networks shown in the following t...
- Question 337: You have peering configured as shown in the following exhibi...
- Question 338: Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatu...
- Question 339: You need to resolve the Active Directory issue. What should ...
- Question 340: You have the App Service plans shown in the following table....
- Question 341: You have an Azure virtual machine named VM1 and a Recovery S...
- Question 342: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. You crea...
- 1 commentQuestion 343: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Direct...
- Question 344: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 345: You have the Azure virtual network named VNet1 that contains...
- Question 346: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 347: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 348: You have an Azure virtual machine that runs Windows Server 2...
- Question 349: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure virtua...
- Question 350: You are evaluating the name resolution for the virtual machi...
- Question 351: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 352: You download an Azure Resource Manager template based on an ...
- Question 353: You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage accou...
- Question 354: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Active...
- Question 355: You have Azure virtual machines that run Windows Server 2019...
- Question 356: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. You have...
- Question 357: You have an Azure Subscription named Subcription1.has Subcri...
- 2 commentQuestion 358: You need to prepare the environment to meet the authenticati...
- Question 359: You have an Azure subscription. You need to implement a cust...
- Question 360: You have an Azure subscription. You need to implement a cust...
- Question 361: You have an Azure web app named App1. App1 has the deploymen...
- Question 362: This question is part of a series of questions that present ...
- 1 commentQuestion 363: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual net...
- Question 364: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 365: You have a Recovery Service vault that you use to test backu...
- Question 366: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 367: You need to prepare the environment to ensure that the web a...
- 2 commentQuestion 368: You have an on premises data center and an Azure subscriptio...
- Question 369: You need to configure the Device settings to meet the techni...
- Question 370: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 371: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 372: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that has ...
- Question 373: You create an Azure web app named WebApp1. WebApp1 has the a...
- Question 374: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- Question 375: You have an Azure subscription that contains a storage accou...
- Question 376: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 377: You have an Azure subscription named Sub1. You plan to deplo...
- Question 378: You have an Azure Storage account named storage1. You have a...
- Question 379: You are developing an Azure web app named WebApp1. WebApp1 u...
- Question 380: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- Question 381: You have an Azure subscription. You are deploying an Azure K...
- Question 382: You have an Azure subscription. The subscription includes a ...
- 1 commentQuestion 383: You have Azure subscription that includes following Azure fi...
- Question 384: You have an Azure web app named WebApp1 that runs in an Azur...
- Question 385: You have three offices and an Azure subscription that contai...
- Question 386: You have an azure subscription that contain a virtual named ...
- Question 387: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- 1 commentQuestion 388: You have an Azure virtual network named VNet1 that connects ...
- Question 389: You have an Azure subscription. You create the Azure Storage...
- 2 commentQuestion 390: You need to meet the technical requirement for VM4. What sho...
- Question 391: You create a Recovery Services vault backup policy named Pol...
- Question 392: You are creating an Azure load balancer. You need to add an ...
- Question 393: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 394: You have an Azure subscription named Subcription1 that conta...
- Question 395: You are creating an Azure load balancer. You need to add an ...
- Question 396: You have an Azure subscription. You deploy a virtual machine...
- Question 397: You have a Recovery Service vault that you use to test backu...
- Question 398: You plan to deploy 20 Azure virtual machines by using an Azu...
- 1 commentQuestion 399: You have the App Service plan shown in the following exhibit...
- Question 400: You are creating an Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS) cluster ...
- 1 commentQuestion 401: You need to recommend a solution for App1. The solution must...
- Question 402: You are evaluating the connectivity between the virtual mach...
- Question 403: You have an Azure subscription. You have an on-premises virt...
- Question 404: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 405: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 406: You are evaluating the connectivity between the virtual mach...
- 2 commentQuestion 407: You create a virtual machine scale set named Scale1. Scale1 ...
- Question 408: You have an Azure virtual machine that runs Windows Server 2...
- Question 409: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resource gr...
- Question 410: You recently created a new Azure subscription that contains ...
- 1 commentQuestion 411: You need to meet the technical requirement for VM4. What sho...
- Question 412: You have a Microsoft SQL Server Always On availability group...
- Question 413: You have an Azure subscription that contains the storage acc...
- Question 414: Hotspot Question You have an Azure subscription that contain...
- Question 415: You need to configure the Device settings to meet the techni...
- Question 416: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 417: You create the following resources in an Azure subscription:...
- 1 commentQuestion 418: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Availa...
- Question 419: You have an Azure subscription. You need to implement a cust...
- 2 commentQuestion 420: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual net...
- Question 421: You have an Azure subscription that contains a user named Us...
- Question 422: You have an Azure subscription that contains the virtual mac...
- Question 423: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 424: You have an Azure web app named WebApp1. You need to provide...
- 2 commentQuestion 425: You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources s...
- Question 426: Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain...
- Question 427: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storag...
- Question 428: HOTSPOT You have an Azure virtual machine that runs Windows ...
- Question 429: You have an on-premises network that includes a Microsoft SQ...
- Question 430: You are evaluating the name resolution for the virtual machi...
- 1 commentQuestion 431: You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Direct...
- Question 432: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscrip...
- Question 433: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- Question 434: You have an azure subscription that contain a virtual named ...
- Question 435: Note This question is part of a series of questions that pre...
- Question 436: You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that cont...
- 1 commentQuestion 437: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 438: You have the App Service plan shown in the following exhibit...
- Question 439: You download an Azure Resource Manager template based on an ...
- 1 commentQuestion 440: You have the web apps shown in the following table (Exhibit)...
- 1 commentQuestion 441: VM1 is running and connects to NIC1 and Disk1. NIC1 connects...



Recent Comments (The most recent comments are at the top.)
VNET1: 10.10.10.0 - 10.10.10.255
VNET2: 172.16.0.0 - 172.16.255.255
VNETA: 10.10.128.0 - 10.10.255.255
Box 1: No
To create a VNet to VNet VPN you need to have a special Gateway Subnet. Here, the VNet has no sufficient address space to create a Gateway Subnet and thus to establish a VNet to VNet VPN connection.
Box 2: Yes
For VNet peering the only consideration is that the VNets do not overlap. VNET1 and VNET2 do not overlap.
Box 3: Yes
For VNet peering the only consideration is that the VNets do not overlap. VNET1 and VNETA do not overlap.