Valid 70-765 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 70-765 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 70-765 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 70-765 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 70-765 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 70-765 Dumps Premium Version
(268 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 78/110
HOTSPOT
Background
You manage the Microsoft SQL Server environment for a company that manufactures and sells automobile parts.
The environment includes the following servers: SRV1 and SRV2. SRV1 has 16 logical cores and hosts a SQL Server instance that supports a mission-critical application. The application has approximately 30,000 concurrent users and relies heavily on the use of temporary tables.
The environment also includes the following databases: DB1, DB2, and Reporting. The Reporting database is protected with Transparent Data Encryption (TDE). You plan to migrate this database to a new server. You detach the database and copy it to the new server.
You are performing tuning on a SQL Server database instance. The application which uses the database was written using an object relationship mapping (ORM) tool which maps tables as objects within the application code. There are 30 stored procedures that are regularly used by the application.
Exhibit
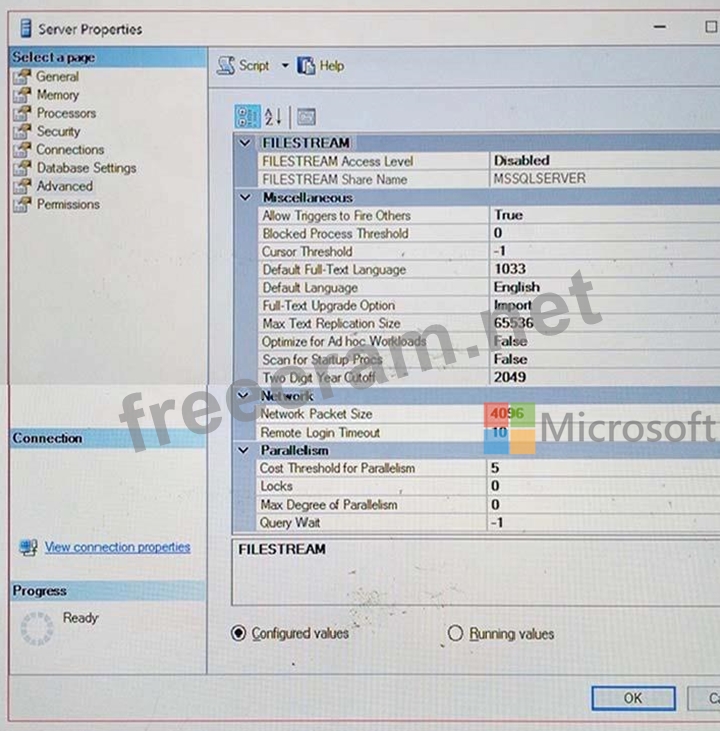
You need to optimize SRV1.
What configuration changes should you implement? To answer, select the appropriate option from each list in the answer area.
Hot Area:
Background
You manage the Microsoft SQL Server environment for a company that manufactures and sells automobile parts.
The environment includes the following servers: SRV1 and SRV2. SRV1 has 16 logical cores and hosts a SQL Server instance that supports a mission-critical application. The application has approximately 30,000 concurrent users and relies heavily on the use of temporary tables.
The environment also includes the following databases: DB1, DB2, and Reporting. The Reporting database is protected with Transparent Data Encryption (TDE). You plan to migrate this database to a new server. You detach the database and copy it to the new server.
You are performing tuning on a SQL Server database instance. The application which uses the database was written using an object relationship mapping (ORM) tool which maps tables as objects within the application code. There are 30 stored procedures that are regularly used by the application.
Exhibit

You need to optimize SRV1.
What configuration changes should you implement? To answer, select the appropriate option from each list in the answer area.
Hot Area:

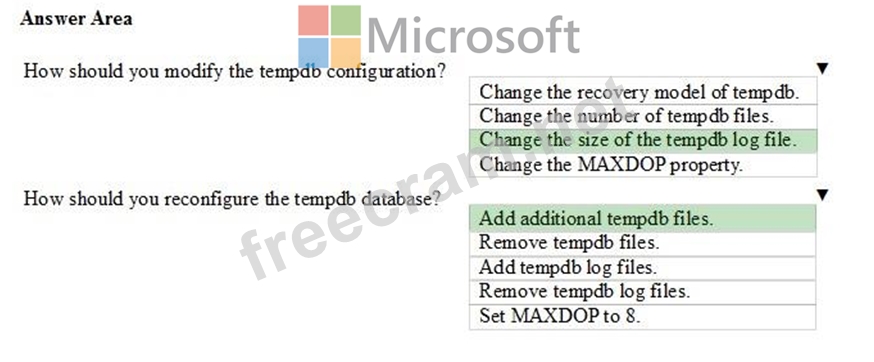
Correct Answer:
Explanation/Reference:
Explanation:
From the scenario: SRV1 has 16 logical cores and hosts a SQL Server instance that supports a mission- critical application. The application has approximately 30,000 concurrent users and relies heavily on the use of temporary tables.
Box 1: Change the sisze of the tempdb log file.
The size and physical placement of the tempdb database can affect the performance of a system. For example, if the size that is defined for tempdb is too small, part of the system-processing load may be taken up with autogrowing tempdb to the size required to support the workload every time you restart the instance of SQL Server. You can avoid this overhead by increasing the sizes of the tempdb data and log file.
Box 2: Add additional tempdb files.
Create as many files as needed to maximize disk bandwidth. Using multiple files reduces tempdb storage contention and yields significantly better scalability. However, do not create too many files because this can reduce performance and increase management overhead. As a general guideline, create one data file for each CPU on the server (accounting for any affinity mask settings) and then adjust the number of files up or down as necessary.
Incorrect Answers:
Not MAXDOP:
The MAXDOP setting is fine. From the exhibit we see that MAXDOP is set to 0. This is the default setting, which enables the server to determine the maximum degree of parallelism.
Note: When an instance of SQL Server runs on a computer that has more than one microprocessor or CPU, it detects the best degree of parallelism, that is, the number of processors employed to run a single statement, for each parallel plan execution. You can use the max degree of parallelism option to limit the number of processors to use in parallel plan execution.
References: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms175527(v=sql.105).aspx
- Question List (110q)
- Question 1: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. You nee...
- Question 2: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 3: You plan to deploy an on-premises SQL Server 2014 database t...
- Question 4: You administer two Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers named P...
- Question 5: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012. A process that n...
- Question 6: DRAG DROP Background You manage a Microsoft SQL Server envir...
- Question 7: HOTSPOT Background You manage a Microsoft SQL Server environ...
- Question 8: You have Microsoft SQL server on a Microsoft Azure virtual m...
- Question 9: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 10: You administer a SQL Server 2012 server that contains a data...
- Question 11: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 12: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. After a...
- Question 13: You are designing a Windows Azure SQL Database for an order ...
- Question 14: You have a server named Serverl that is hosted in an Azure v...
- Question 15: HOTSPOT You are building the database platform for a multi-t...
- Question 16: You develop a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that contai...
- Question 17: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 18: HOTSPOT Database DB1 must use two CPU cores. Queries that we...
- Question 19: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You nee...
- Question 20: You have a server named server1-contoso.database.windows.net...
- Question 21: You plan to install a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. Th...
- Question 22: You administer a SQL 2012 server that contains a database na...
- Question 23: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that con...
- Question 24: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You hav...
- Question 25: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 26: You administer two Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers. Each s...
- Question 27: You are the administrator of a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 ser...
- Question 28: You use a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that contains t...
- Question 29: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance named SQ...
- Question 30: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You con...
- Question 31: You are a database administrator for a Microsoft SQL Server ...
- Question 32: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that con...
- Question 33: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. The ins...
- Question 34: You are the database administrator in your company. You plan...
- Question 35: You have been hired as a Database Consultant by ABC.com to d...
- Question 36: You are a database developer for an application hosted on a ...
- Question 37: HOTSPOT Background You manage the Microsoft SQL Server envir...
- Question 38: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. You plan ...
- Question 39: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 40: You are a database administrator for a Microsoft SQL Server ...
- Question 41: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 42: You are a database developer of a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 ...
- Question 43: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Enterprise Editio...
- Question 44: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 45: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 46: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 47: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 48: You have a SQL Server 2016 database named DB1. You plan to i...
- Question 49: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 50: Your database contains a table named Purchases. The table in...
- Question 51: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance named SQ...
- Question 52: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Or...
- Question 53: Note: This questions is part of a series of questions that u...
- Question 54: You administer a SQL Server 2012 database instance. You need...
- Question 55: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. The MSSQL...
- Question 56: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 failover cluster....
- Question 57: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 58: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. Users r...
- Question 59: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database named Sales. ...
- Question 60: You create an availability group that has replicas named HA/...
- Question 61: You administer a Windows Azure SQL Database database named O...
- Question 62: DRAG DROP Background You manage the Microsoft SQL Server env...
- Question 63: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 64: DRAG DROP You deploy a new Microsoft Azure SQL Database inst...
- Question 65: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that has...
- Question 66: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 67: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database instance...
- Question 68: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 environment. One ...
- Question 69: You administer two instances of Microsoft SQL Server 2012. Y...
- Question 70: You administer a Windows 2008 server hosting an instance of ...
- Question 71: You are deploying a Microsoft SQL Server database that will ...
- Question 72: You manage an on-premises, multi-tier application that has t...
- Question 73: You plan to install Microsoft SQL Server 2012 for a web host...
- Question 74: HOTSPOT Background You are the database administrator for Co...
- Question 75: You have Microsoft SQL Server on a DS-series Microsoft Azure...
- Question 76: HOTSPOT Background You are the database administrator for Co...
- Question 77: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 failover cluster ...
- Question 78: HOTSPOT Background You manage the Microsoft SQL Server envir...
- Question 79: You are the administrator for a SQL Server 2016 instance tha...
- Question 80: You are using dynamic management views to monitor an SQL Ser...
- Question 81: Note: This questions is part of a series of questions that u...
- Question 82: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database instance...
- Question 83: A company has an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server 2014 envir...
- Question 84: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that inc...
- Question 85: You have an on-premises server that runs Windows Server 2012...
- Question 86: You administer all the deployments of Microsoft SQL Server 2...
- Question 87: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 88: You administer a SQL Server 2012 server that contains a data...
- Question 89: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 90: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 91: DRAG DROP A new Azure Active Directory security principal na...
- Question 92: You administer a SQL Server 2012 server that contains a data...
- Question 93: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that has...
- Question 94: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 95: HOTSPOT Background You manage a Microsoft SQL Server environ...
- Question 96: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. One of th...
- Question 97: You use a contained database named ContosoDb within a domain...
- Question 98: You administer a single server that contains a Microsoft SQL...
- Question 99: You use Microsoft SQL Server 2012 to develop a database appl...
- Question 100: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 101: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 102: HOTSPOT Background You manage the Microsoft SQL Server envir...
- Question 103: You are the database administrator for your company. Your co...
- Question 104: You use Microsoft SQL Server 2012 to develop a database appl...
- Question 105: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You wan...
- Question 106: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- Question 107: HOTSPOT Background You manage a Microsoft SQL Server environ...
- Question 108: You administer a Windows Azure SQL Database database named I...
- Question 109: You administer a Windows Azure SQL Database database named H...
- Question 110: Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...


