- Home
- Microsoft
- Implementing a Data Warehouse with Microsoft SQL Server 2012/2014
- Microsoft.70-463.v2018-04-15.q230
- Question 84
Valid 70-463 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 70-463 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 70-463 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 70-463 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 70-463 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 70-463 Dumps Premium Version
(267 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 84/230
HOTSPOT
You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package.
The package must run a parameterized query against a Windows Azure SQL Database database.
You need to use the least amount of development effort to meet the package requirement.
Which task should you use? (To answer, select the appropriate task in the answer area.)
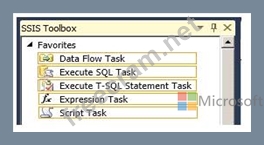
You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package.
The package must run a parameterized query against a Windows Azure SQL Database database.
You need to use the least amount of development effort to meet the package requirement.
Which task should you use? (To answer, select the appropriate task in the answer area.)

Correct Answer:
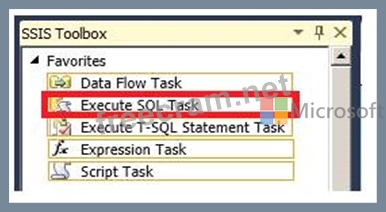
Running Parameterized SQL Commands
SQL statements and stored procedures frequently use input parameters, output parameters, and return codes. The
Execute SQL task supports the Input, Output, and ReturnValue parameter types. You use the Input type for input
parameters, Output for output parameters, and ReturnValue for return codes.
Ref: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms141003.aspx
In SSIS there are two tasks than can be used to execute SQL statements: Execute T-SQL Statement and Execute SQL.
What is the difference between the two?
The Execute T-SQL Statement task tasks less memory, parse time, and CPU time than the Execute SQL task, but is not
as flexible. If you need to run parameterized queries, save the query results to variables, or use property expressions,
you should use the Execute SQL task instead of the Execute T-SQL Statement task.
Ref: http://www.sqlservercentral.com/blogs/jamesserra/2012/11/08/ssis-execute-sql-task-vs-execute-t-sql-
statement-task/
- Question List (230q)
- Question 1: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) s...
- Question 2: You are creating a SQL Server Master Data Services (MDS) mod...
- Question 3: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 4: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 5: DRAG DROP You are designing an extract, transform, load (ETL...
- Question 6: To facilitate the troubleshooting of SQL Server Integration ...
- Question 7: You are creating a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) pa...
- Question 8: You are completing the installation of the Data Quality Serv...
- Question 9: DRAG DROP You are editing a SQL Server Integration Services ...
- Question 10: You develop and deploy a SQL Server Integration Services (SS...
- Question 11: CORRECT TEXT You are designing a package control flow. The p...
- Question 12: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) project...
- Question 13: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 14: You are creating a Data Quality Services (DQS) solution. You...
- Question 15: HOTSPOT You are the Master Data Services (MDS) administrator...
- Question 16: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 17: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) d...
- Question 18: Your team is creating SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)...
- Question 19: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package...
- Question 20: HOTSPOT You are the Master Data Services (MDS) administrator...
- Question 21: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) p...
- Question 22: You are using a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) proje...
- Question 23: You are designing an Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) solut...
- Question 24: You have a secured database that contains all of the custome...
- Question 25: A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package on a comput...
- Question 26: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 27: You are designing an enterprise star schema that will consol...
- Question 28: DRAG DROP A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package n...
- Question 29: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 30: DRAG DROP You are the administrator for a Data Quality Serve...
- Question 31: Occasionally a job that executes an existing SQL Server Inte...
- Question 32: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 33: You are installing SQL Server Data Quality Services (DQS). Y...
- Question 34: You are reviewing the design of a customer dimension table i...
- Question 35: You are reviewing the design of an existing fact table named...
- Question 36: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 37: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 38: You are designing a data warehouse with two fact tables. The...
- Question 39: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 40: You are creating a SQL Server Master Data Services (MDS) mod...
- Question 41: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that has S...
- Question 42: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 43: You are the data steward for a Business Intelligence project...
- Question 44: You are designing a data warehouse that contains a product d...
- Question 45: You are designing a data warehouse with two fact tables. The...
- Question 46: You are developing a data flow transformation to merge two d...
- Question 47: You are editing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) pac...
- Question 48: You manage a SQL Server Master Data Services (MDS) environme...
- Question 49: You are implementing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS...
- Question 50: You are creating a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) pa...
- Question 51: You are editing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) pac...
- Question 52: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 53: You are troubleshooting an existing SQL Server Integration S...
- Question 54: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 55: You are creating a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) pa...
- Question 56: HOTSPOT You are the data steward at your company. Duplicate ...
- Question 57: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 58: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package...
- Question 59: HOTSPOT You have a data warehouse that is hosted in a SQL Se...
- Question 60: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 61: You are developing a project that contains multiple SQL Serv...
- Question 62: You have Master Data Services (MDS) in a SQL Server deployme...
- Question 63: You are adding a new capability to several dozen SQL Server ...
- Question 64: You are a database developer of a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 ...
- Question 65: You are implementing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS...
- Question 66: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package...
- Question 67: HOTSPOT You are a data warehouse developer responsible for d...
- Question 68: Your company has several line-of-business applications. The ...
- Question 69: HOTSPOT You are editing a SQL Server Integration Services (S...
- Question 70: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 71: To ease the debugging of packages, you standardize the SQL S...
- Question 72: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 73: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) d...
- Question 74: DRAG DROP A Data Flow task in a SQL Server Integration Servi...
- Question 75: You maintain a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packag...
- Question 76: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 77: HOTSPOT You are developing a data flow to load sales data in...
- Question 78: You are completing the installation of the Data Quality Serv...
- Question 79: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package...
- Question 80: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) d...
- Question 81: A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) 2012 package curren...
- Question 82: You maintain a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packag...
- Question 83: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 84: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 85: DRAG DROP You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database. Yo...
- Question 86: DRAG DROP You are designing a SQL Server Integration Service...
- Question 87: DRAG DROP You are building a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 88: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 89: You are reviewing the design of a student dimension table in...
- Question 90: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 91: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 92: You are designing an extract, transform, and load (ETL) solu...
- Question 93: DRAG DROP A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) project h...
- Question 94: You are performance tuning a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 95: You are deploying a project to the SQL Server Integration Se...
- Question 96: You are deploying a new SQL Server Integration Services (SSI...
- Question 97: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 98: You are using the Knowledge Discovery feature of the Data Qu...
- Question 99: DRAG DROP You are maintaining a SQL Server Integration Servi...
- Question 100: You are designing a data warehouse for a fresh food distribu...
- Question 101: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 102: You are using a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) proje...
- Question 103: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) d...
- Question 104: HOTSPOT You are editing a SQL Server Integration Services (S...
- Question 105: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) 2...
- Question 106: You have a SQL server integration Services (SSIS) package na...
- Question 107: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 108: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package...
- Question 109: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) s...
- Question 110: To support the implementation of new reports, Active Directo...
- Question 111: You are designing a data warehouse that contains a customer ...
- Question 112: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 113: You have a server named SQL1 that has SQL Server Integration...
- Question 114: DRAG DROP You are designing a SQL Server Integration Service...
- Question 115: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 116: You maintain a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packag...
- Question 117: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 118: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 119: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 120: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package...
- Question 121: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 122: You are reviewing the design of an existing fact table named...
- Question 123: You are implementing a new SQL Server Integration Services (...
- Question 124: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 125: DRAG DROP You need to design a data load strategy for a data...
- Question 126: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 127: You are designing a data warehouse with two fact tables. The...
- Question 128: DRAG DROP Your company is evaluating the data cleansing capa...
- Question 129: DRAG DROP You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSI...
- Question 130: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 131: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 132: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 133: DRAG DROP You are editing a SQL Server Integration Services ...
- Question 134: DRAG DROP You are validating whether a SQL Server Integratio...
- Question 135: You are designing a fact table in a SQL Server database. The...
- Question 136: You are installing the Data Quality Server component of Data...
- Question 137: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 138: You are maintaining a Data Quality Services (DQS) environmen...
- Question 139: You are designing a data warehouse that uses SQL Server 2012...
- Question 140: You are designing a partitioning strategy for a large fact t...
- Question 141: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 142: A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package was deploye...
- Question 143: DRAG DROP A new dedicated server is used to execute resource...
- Question 144: HOTSPOT You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services ...
- Question 145: You are administering SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)...
- Question 146: You are implementing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS...
- Question 147: You are designing an enterprise star schema that will consol...
- Question 148: DRAG DROP You are creating a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 149: You are designing a data warehouse for a software distributi...
- Question 150: You are creating a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) pa...
- Question 151: You are implementing the indexing strategy for a fact table ...
- Question 152: To support the implementation of new reports, Active Directo...
- Question 153: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 154: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 155: DRAG DROP You are loading a dataset into SQL Server. The dat...
- Question 156: You are preparing to install SQL Server 2012 Master Data Ser...
- Question 157: You manage a SQL Server Master Data Services (MDS) environme...
- Question 158: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 159: You are developing a project that contains multiple SQL Serv...
- Question 160: You are using SQL Server Data Tools to develop a SQL Server ...
- Question 161: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 162: You are installing SQL Server Data Quality Services (DQS). Y...
- Question 163: You are completing the installation of the Data Quality Serv...
- Question 164: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 165: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 166: DRAG DROP A new SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) proje...
- Question 167: HOTSPOT A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package is ...
- Question 168: You are designing a data warehouse that uses SQL Server 2012...
- Question 169: You are completing the installation of the Data Quality Serv...
- Question 170: DRAG DROP You are creating a sales data warehouse. When a pr...
- Question 171: You administer a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) solu...
- Question 172: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 173: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Service ...
- Question 174: You develop a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package...
- Question 175: You are developing a data flow transformation to merge two d...
- Question 176: You install a SQL Server 2012 database engine instance on a ...
- Question 177: DRAG DROP A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) project h...
- Question 178: You are installing the Data Quality Server component of Data...
- Question 179: You are performance tuning a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 180: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) d...
- Question 181: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) 2...
- Question 182: You are the administrator of a server that hosts Data Qualit...
- Question 183: DRAG DROP You plan to deploy a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 184: DRAG DROP You use SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) for...
- Question 185: CORRECT TEXT You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 data...
- Question 186: You are designing a data warehouse that uses SQL Server 2012...
- Question 187: You are the data steward for a Business Intelligence project...
- Question 188: You are designing a data warehouse hosted on SQL Azure. The ...
- Question 189: You are deploying a new SQL Server Integration Services (SSI...
- Question 190: You are designing a data warehouse with two fact tables. The...
- Question 191: You are creating a SQL Server Master Data Services (MDS) mod...
- Question 192: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 193: DRAG DROP You are building a fact table in a data warehouse....
- Question 194: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 195: Your company uses a proprietary encryption algorithm to secu...
- Question 196: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 197: CORRECT TEXT You are designing a package control flow. The p...
- Question 198: You are preparing to install SQL Server 2012 Master Data Ser...
- Question 199: DRAG DROP You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database. Se...
- Question 200: You are designing a data warehouse hosted on Windows Azure S...
- Question 201: DRAG DROP You are building a fact table in a data warehouse....
- Question 202: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) p...
- Question 203: You install a SQL Server 2012 database engine instance on a ...
- Question 204: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) p...
- Question 205: HOTSPOT You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 206: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) s...
- Question 207: You are designing a complex SQL Server Integration Services ...
- Question 208: You are writing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) pac...
- Question 209: DRAG DROP You are building a SQL Server Integration Services...
- Question 210: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 211: HOTSPOT You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services ...
- Question 212: You are administering SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)...
- Question 213: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 214: You are deploying a new SQL Server Integration Services (SSI...
- Question 215: You are implementing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS...
- Question 216: DRAG DROP You administer a large and complex SQL Server Inte...
- Question 217: You are installing the Data Quality Client on user desktops....
- Question 218: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 219: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 220: HOTSPOT You are using the Master Data Services (MDS) Add-in ...
- Question 221: You are creating a Data Quality Services (DQS) solution. You...
- Question 222: You are using SQL Server Data Tools to develop a SQL Server ...
- Question 223: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SS1S) p...
- Question 224: You maintain a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packag...
- Question 225: DRAG DROP You are developing a SQL Server Integration Servic...
- Question 226: You are developing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) ...
- Question 227: You are designing a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) p...
- Question 228: A SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package imports dai...
- Question 229: You are designing an extract, transform, load (ETL) process ...
- Question 230: You are using the Knowledge Discovery feature of the Data Qu...


