- Home
- Microsoft
- Administering Microsoft SQL Server 2012/2014 Databases
- Microsoft.70-462.v2018-04-17.q140
- Question 121
Valid 70-462 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 70-462 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 70-462 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 70-462 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 70-462 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 70-462 Dumps Premium Version
(305 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 121/140
You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that hosts a transactional database and a reporting database. The transactional database is updated through a web application and is operational throughout the day. The reporting database is only updated from the transactional database.
The recovery model and backup schedule are configured as shown in the following table:
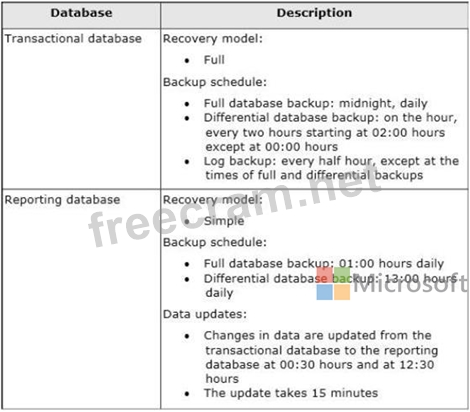
At 16:20 hours, you discover that pages 17, 137, and 205 on one of the database files are corrupted on the transactional database.
You need to ensure that the transactional database is restored.
You also need to ensure that data loss is minimal.
What should you do?
The recovery model and backup schedule are configured as shown in the following table:

At 16:20 hours, you discover that pages 17, 137, and 205 on one of the database files are corrupted on the transactional database.
You need to ensure that the transactional database is restored.
You also need to ensure that data loss is minimal.
What should you do?
Correct Answer: F
Explanation/Reference:
Requirements for Restoring Pages
A page restore is subject to the following requirements:
The databases must be using the full or bulk-logged recovery model. Some issues exist if you are using

the bulk-logged model. For more information, see the following section.
Pages in read-only filegroups cannot be restored. Trying to make a filegroup read-only will fail if there is

a page restore going on at the same time in the filegroup.
The restore sequence must start with a full, file, or filegroup backup.

A page restore requires an unbroken chain of log backups up to the current log file, and they must all

be applied so that the page is brought up to date with the current log file.
As in a file-restore sequence, in each restore step, you can add more pages to the roll forward set.

A database backup and page restore cannot be run at the same time.

Bulk-logged Recovery Model and Page Restore
For a database that uses the bulk-logged recovery model, page restore has the following additional

conditions:
Backing up while filegroup or page data is offline is problematic for bulk-logged data, because the

offline data is not recorded in the log. Any offline page can prevent backing up the log. In this cases, consider using
DBCC REPAIR, because this might cause less data loss than restoring to the most recent backup.

If a log backup of a bulk-logged database encounters a bad page, it fails unless WITH

CONTINUE_AFTER_ERROR is specified.

Page restore generally does not work with bulk-logged recovery.

A best practice for performing page restore is to set the database to the full recovery model, and try a

log backup. If the log backup works, you can continue with the page restore. If the log backup fails, you either have to lose work since the previous log backup or you have to try running DBCC must be run with the REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS option.
Requirements for Restoring Pages
A page restore is subject to the following requirements:
The databases must be using the full or bulk-logged recovery model. Some issues exist if you are using

the bulk-logged model. For more information, see the following section.
Pages in read-only filegroups cannot be restored. Trying to make a filegroup read-only will fail if there is

a page restore going on at the same time in the filegroup.
The restore sequence must start with a full, file, or filegroup backup.

A page restore requires an unbroken chain of log backups up to the current log file, and they must all

be applied so that the page is brought up to date with the current log file.
As in a file-restore sequence, in each restore step, you can add more pages to the roll forward set.

A database backup and page restore cannot be run at the same time.

Bulk-logged Recovery Model and Page Restore
For a database that uses the bulk-logged recovery model, page restore has the following additional

conditions:
Backing up while filegroup or page data is offline is problematic for bulk-logged data, because the

offline data is not recorded in the log. Any offline page can prevent backing up the log. In this cases, consider using
DBCC REPAIR, because this might cause less data loss than restoring to the most recent backup.

If a log backup of a bulk-logged database encounters a bad page, it fails unless WITH

CONTINUE_AFTER_ERROR is specified.

Page restore generally does not work with bulk-logged recovery.

A best practice for performing page restore is to set the database to the full recovery model, and try a

log backup. If the log backup works, you can continue with the page restore. If the log backup fails, you either have to lose work since the previous log backup or you have to try running DBCC must be run with the REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS option.
- Question List (140q)
- Question 1: You administer several Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers. Yo...
- Question 2: You are a database administrator for a Microsoft SQL Server ...
- Question 3: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database named Sales. ...
- Question 4: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 failover cluster ...
- Question 5: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. An appl...
- Question 6: You maintain several databases on a 32-bit Microsoft SQL Ser...
- Question 7: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. You nee...
- Question 8: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that has m...
- Question 9: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 10: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 11: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 12: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 13: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database instance...
- Question 14: You administer a SQL Server 2012 server that contains a data...
- Question 15: You are a database administrator for a Microsoft SQL Server ...
- Question 16: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You con...
- Question 17: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Enterprise Editio...
- Question 18: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. When tran...
- Question 19: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database instance...
- Question 20: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 21: You are implementing a SQL Server 2012 four-node failover cl...
- Question 22: You administer a Windows Azure SQL Database database named H...
- Question 23: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. You dis...
- Question 24: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that con...
- Question 25: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that hosts...
- Question 26: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. A variety...
- Question 27: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 28: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database called H...
- Question 29: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 30: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. One of th...
- Question 31: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You cre...
- Question 32: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance named SQ...
- Question 33: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 clustered instanc...
- Question 34: You administer all the deployments of Microsoft SQL Server 2...
- Question 35: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You pro...
- Question 36: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You con...
- Question 37: You install Microsoft SQL Server 2012 on a new server. After...
- Question 38: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012. A process that n...
- Question 39: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 40: You administer all the deployments of Microsoft SQL Server 2...
- Question 41: You administer several Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers. Yo...
- Question 42: You administer two instances of Microsoft SQL Server 2012. Y...
- Question 43: You are the lead database administrator (DBA) of a Microsoft...
- Question 44: You use Microsoft SQL Server 2012 to write code for a transa...
- Question 45: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. Users r...
- Question 46: You administer two Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers. Each s...
- Question 47: You plan to install a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. Th...
- Question 48: You are migrating a database named Orders to a new server th...
- Question 49: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database instance...
- Question 50: You administer three Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers named...
- Question 51: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 52: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 53: You administer three Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 instances....
- Question 54: You administer a SQL Server 2012 server that contains a data...
- Question 55: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You hav...
- Question 56: You administer a single Microsoft SQL Server instance on a t...
- Question 57: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 58: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. The ins...
- Question 59: You administer all the deployments of Microsoft SQL Server 2...
- Question 60: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 61: You use a contained database named ContosoDb within a domain...
- Question 62: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Or...
- Question 63: You administer a Windows Azure SQL Database database named I...
- Question 64: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. You plan ...
- Question 65: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 66: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You wan...
- Question 67: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that inc...
- Question 68: You administer two Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers named S...
- Question 69: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You hav...
- Question 70: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that has...
- Question 71: You administer all the deployments of Microsoft SQL Server 2...
- Question 72: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You nee...
- Question 73: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 74: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that has...
- Question 75: You use a contained database named ContosoDb within a domain...
- Question 76: You administer a Windows Azure SQL Database database used fo...
- Question 77: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that inc...
- Question 78: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 79: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that hosts...
- Question 80: You install a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. The instan...
- Question 81: You administer all the deployments of Microsoft SQL Server 2...
- Question 82: You administer a single server that contains a Microsoft SQL...
- Question 83: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. You nee...
- Question 84: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 failover cluster....
- Question 85: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You nee...
- Question 86: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. You use...
- Question 87: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database that is used ...
- Question 88: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database. You want to ...
- Question 89: You create an availability group that has replicas named HA/...
- Question 90: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. All dat...
- Question 91: You administer several Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database se...
- Question 92: You administer a Windows Azure SQL Database database named O...
- Question 93: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance named SQ...
- Question 94: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that has...
- Question 95: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 environment that ...
- Question 96: You are a database administrator for a Microsoft SQL Server ...
- Question 97: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 98: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Co...
- Question 99: You are a database administrator of a Microsoft SQL Server 2...
- Question 100:
- Question 101: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 102: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that has a...
- Question 103: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that con...
- Question 104: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database instance...
- Question 105: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database. The database...
- Question 106: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. You nee...
- Question 107: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 environment. One ...
- Question 108: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server database. Service acco...
- Question 109: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. Users r...
- Question 110: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that has S...
- Question 111: You administer a SQL Server 2012 server that contains a data...
- Question 112: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. The MSSQL...
- Question 113: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance. After a...
- Question 114: You plan to install Microsoft SQL Server 2012 for a web host...
- Question 115: You administer a single server that contains a Microsoft SQL...
- Question 116: You are the administrator of a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 ser...
- Question 117: You administer two Microsoft SQL Server 2012 servers named P...
- Question 118: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server. You need ...
- Question 119: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database named Or...
- Question 120: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that has...
- Question 121: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that hosts...
- Question 122: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that hosts...
- Question 123: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server along with...
- Question 124: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database that has...
- Question 125: You administer a SQL Server 2012 database instance. You need...
- Question 126: You are creating an application that will connect to the Age...
- Question 127: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. Your da...
- Question 128: You are migrating an OLTP database from Windows Azure SQL Da...
- Question 129: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 130: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server environment. You purch...
- Question 131: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Enterprise Editio...
- Question 132: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 133: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 server that has a...
- Question 134: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 default instance....
- Question 135: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 instance that con...
- Question 136: You create an availability group named HaContoso that has re...
- Question 137: You administer two Microsoft SQL Server 2012 databases named...
- Question 138: You administer a Microsoft SQL Server 2012 database. The dat...
- Question 139: You are a database administrator for a Microsoft SQL Server ...
- Question 140: You administer a SQL Server 2012 database instance. You need...


