Valid 70-345 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 70-345 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 70-345 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 70-345 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 70-345 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 70-345 Dumps Premium Version
(168 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 29/72
DRAG DROP
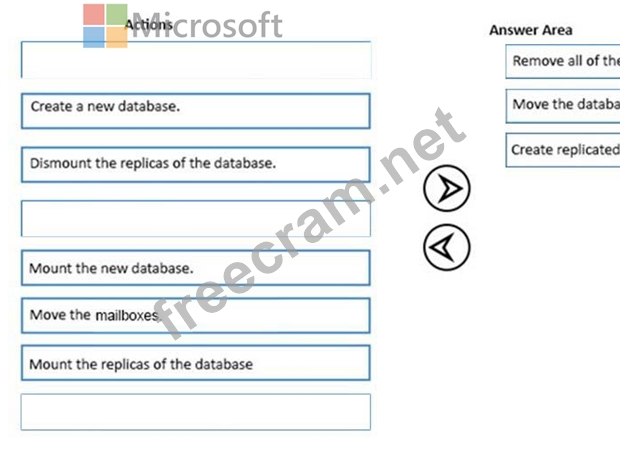
You have an Exchange Server 2016 organization. The organization contains two Mailbox servers.
You have a database that is replicated to both servers. The database contains 500 mailboxes.
You add new volumes to the Mailbox servers.
You need to move all of the mailbox data to the new volumes. The solution must meet the following requirements:
Ensure that multiple copies of the mailbox data are available at all times.

Minimize downtime for the mailbox users.

Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
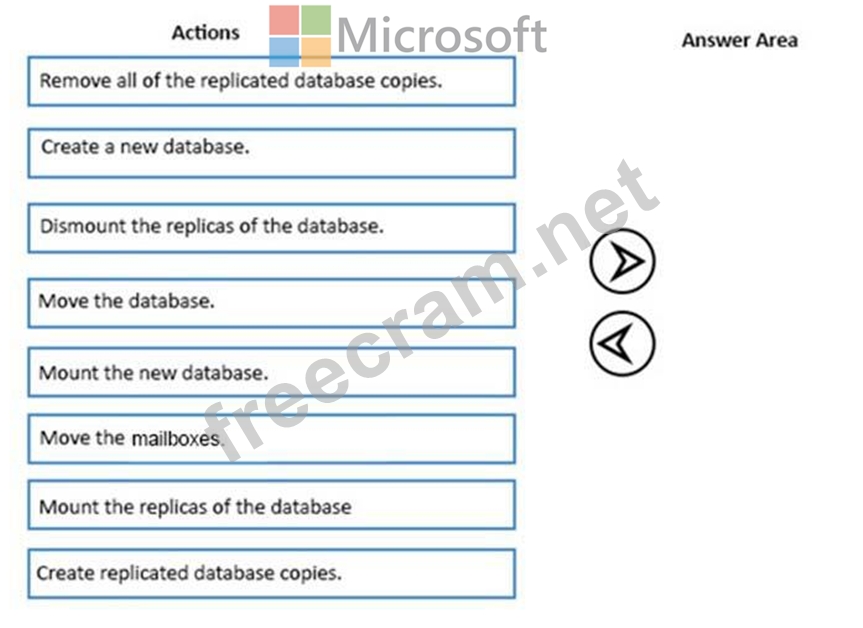
You have an Exchange Server 2016 organization. The organization contains two Mailbox servers.
You have a database that is replicated to both servers. The database contains 500 mailboxes.
You add new volumes to the Mailbox servers.
You need to move all of the mailbox data to the new volumes. The solution must meet the following requirements:
Ensure that multiple copies of the mailbox data are available at all times.

Minimize downtime for the mailbox users.

Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place: