- Home
- Microsoft
- Core Solutions of Microsoft Exchange Server 2013
- Microsoft.70-341.v2018-05-22.q85
- Question 25
Valid 70-341 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 70-341 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 70-341 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 70-341 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 70-341 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 70-341 Dumps Premium Version
(241 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 25/85
HOTSPOT
You need to recommend which configurations must be set for each network.
Which configurations should you recommend?
To answer, select the appropriate configurations for each network in the answer area.
Hot Area:
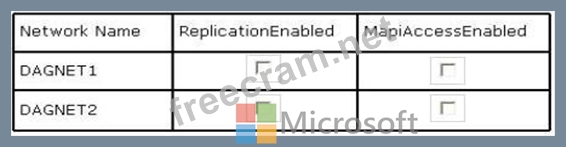
You need to recommend which configurations must be set for each network.
Which configurations should you recommend?
To answer, select the appropriate configurations for each network in the answer area.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:

Explanation/Reference:
Explanation:
A DAG network is a collection of one or more subnets used for either replication traffic or MAPI traffic.
Each DAG contains a maximum of one MAPI network and zero or more replication networks.
In a single network adapter configuration, the network is used for both MAPI and replication traffic.
In a two-network configuration, one network is typically dedicated for replication traffic, and the other network is used primarily for MAPI traffic. You can also add network adapters to each DAG member and configure additional DAG networks as replication networks. A two-network configuration is the recommended configuration.
There are several items to keep in mind when configuring DAG networks:
There must be one MAPI network. If there is not going to be a replication network, the MAPI network

will be used for replication.
Replication networks are optional. There can be multiple replication networks. If the replication network

fails, the DAG will fail back to the MAPI network for replication.
If you want to utilize a replication network, it must reside on a different subnet than the MAPI network.

This often makes it difficult to use a replication network when building a DAG across multiple locations.
The reason being that multiple WAN connections would be needed in order to separate the MAPI traffic from the replication traffic.
Each server within a DAG must have the same number of replication networks. This means that you

cannot use a replication network between two local Mailbox servers and not use a replication network for a server that is a member of the same DAG located across a WAN connection.
STEPS
DAGNET1 must be ReplicationEnabled
DAGNET2 must be MapiAccessEnabled to fulfill the requirements
References:http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd298065(v=exchg.150).aspx
- Question List (85q)
- Question 1: HOTSPOT You need to recommend a solution to meet the technic...
- Question 2: You need to recommend which tasks must be performed to deliv...
- Question 3: DRAG DROP You need to identify which commands must be run to...
- Question 4: Your company has a main office site and a disaster recovery ...
- Question 5: HOTSPOT You are evaluating a DAG design for the New York and...
- Question 6: DRAG DROP Your network contains an internal network and a pe...
- Question 7: You need to recommend a solution to resolve the issue of dom...
- Question 8: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You plan to d...
- Question 9: DRAG DROP You need to recommend a solution to resolve the us...
- Question 10: HOTSPOT You need to ensure that the help desk application ca...
- Question 11: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You need to e...
- Question 12: You need to recommend a solution to resolve the issue for th...
- Question 13: HOTSPOT You need to recommend a solution to meet the busines...
- Question 14: DRAG DROP You need to recommend a solution to meet the mailb...
- Question 15: DRAG DROP You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that...
- Question 16: DRAG DROP You are evaluating the implementation of the addre...
- Question 17: You need to recommend which tasks must be performed to meet ...
- Question 18: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains ...
- Question 19: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains ...
- Question 20: You need to recommend which type of group must be used to cr...
- Question 21: DRAG DROP You need to recommend to a solution to deploy the ...
- Question 22: HOTSPOT You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that c...
- Question 23: Your company has offices in Miami, Singapore and Montreal. A...
- Question 24: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization named for Cont...
- Question 25: HOTSPOT You need to recommend which configurations must be s...
- Question 26: You deploy a server that has the Exchange Server 2013 Mailbo...
- Question 27: DRAG DROP You are evaluating the implementation of a second ...
- Question 28: You need to recommend a solution to resolve the issue of the...
- Question 29: Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest...
- Question 30: You need to recommend which actions must be performed to mee...
- Question 31: You need to recommend which task is required to prepare Acti...
- Question 32: HOTSPOT You create a workload management policy named EX4. Y...
- Question 33: DRAG DROP You are evaluating the planned deployment of the a...
- Question 34: An administrator recommends removing EDGE1 from the implemen...
- Question 35: You need to prevent several users in the Miami office from e...
- Question 36: You need to ensure that if a volume fails on EX2 again, a ma...
- Question 37: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains ...
- Question 38: You plan to deploy an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You...
- Question 39: You need to recommend a design that meets the technical requ...
- Question 40: HOTSPOT You need to recommend a solution to resolve the issu...
- Question 41: You are testing the planned implementation of Exchange Serve...
- Question 42: Refer to the Exhibit. You create a mailbox named ConfRoom1 a...
- Question 43: HOTSPOT You need to recommend a solution to meet the technic...
- Question 44: You need to recommend a solution to resolve the issue of ema...
- Question 45: You are evaluating the deployment of the additional Exchange...
- Question 46: You need to ensure that all of the email messages sent from ...
- Question 47: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains ...
- Question 48: DRAG DROP You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization name...
- Question 49: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You create tw...
- Question 50: HOTSPOT You need to identify which names must be used as the...
- Question 51: DRAG DROP You are planning the upgrade to Exchange Server 20...
- Question 52: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization named adatum.c...
- Question 53: You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains ...
- Question 54: You are evaluating the planned deployment of the additional ...
- Question 55: DRAG DROP You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that...
- Question 56: DRAG DROP You need to recommend to a solution to deploy the ...
- Question 57: HOTSPOT Your company has an Exchange Server 2013 organizatio...
- Question 58: You are implementing a solution to meet the security require...
- Question 59: You need to identify which business requirement will be met ...
- Question 60: DRAG DROP You need to identify which external namespaces mus...
- Question 61: HOTSPOT You discover that one of the Client Access servers i...
- Question 62: HOTSPOT You need to recommend which script the administrator...
- Question 63: HOTSPOT You are attempting to resolve the database activatio...
- Question 64: You have an Exchange Server 2010 organization. All users con...
- Question 65: Your company named Contoso, Ltd., has an Exchange Server 201...
- Question 66: You need to recommend a temporary solution to reroute all of...
- Question 67: DRAG DROP You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that...
- Question 68: HOTSPOT You need to recommend a solution to resolve the Auto...
- Question 69: You need to recommend which recovery solution will restore a...
- Question 70: DRAG DROP You need to create and configure a hierarchical ad...
- Question 71: You need to recommend a solution for the New York office tha...
- Question 72: You need to configure the address books to meet the business...
- Question 73: You need to resolve the search issue reported by the users i...
- Question 74: You need to ensure that users can create new public folders ...
- Question 75: HOTSPOT You need to implement the SCL configurations to supp...
- Question 76: HOTSPOT You need to recommend a solution to meet the technic...
- Question 77: DRAG DROP Your network contains four servers. The servers ar...
- Question 78: You need to recommend a solution to resolve the load balanci...
- Question 79: You are testing the planned implementation of Domain Securit...
- Question 80: DRAG DROP You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that...
- Question 81: HOTSPOT You need to recommend which command must be run to r...
- Question 82: DRAG DROP Your company plans to deploy an Exchange Server 20...
- Question 83: HOTSPOT Your company has two offices. The offices are config...
- Question 84: Your network contains an Active Directory forest named conto...
- Question 85: Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest...


