Valid H12-891_V1.0 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing H12-891_V1.0 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest H12-891_V1.0 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com H12-891_V1.0 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com H12-891_V1.0 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access H12-891_V1.0 Dumps Premium Version
(276 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question
Question 85/85
The figure shows a packet that contains three label headers. Select the values (in decimal notation) of the X, Y, and Z fields, respectively.
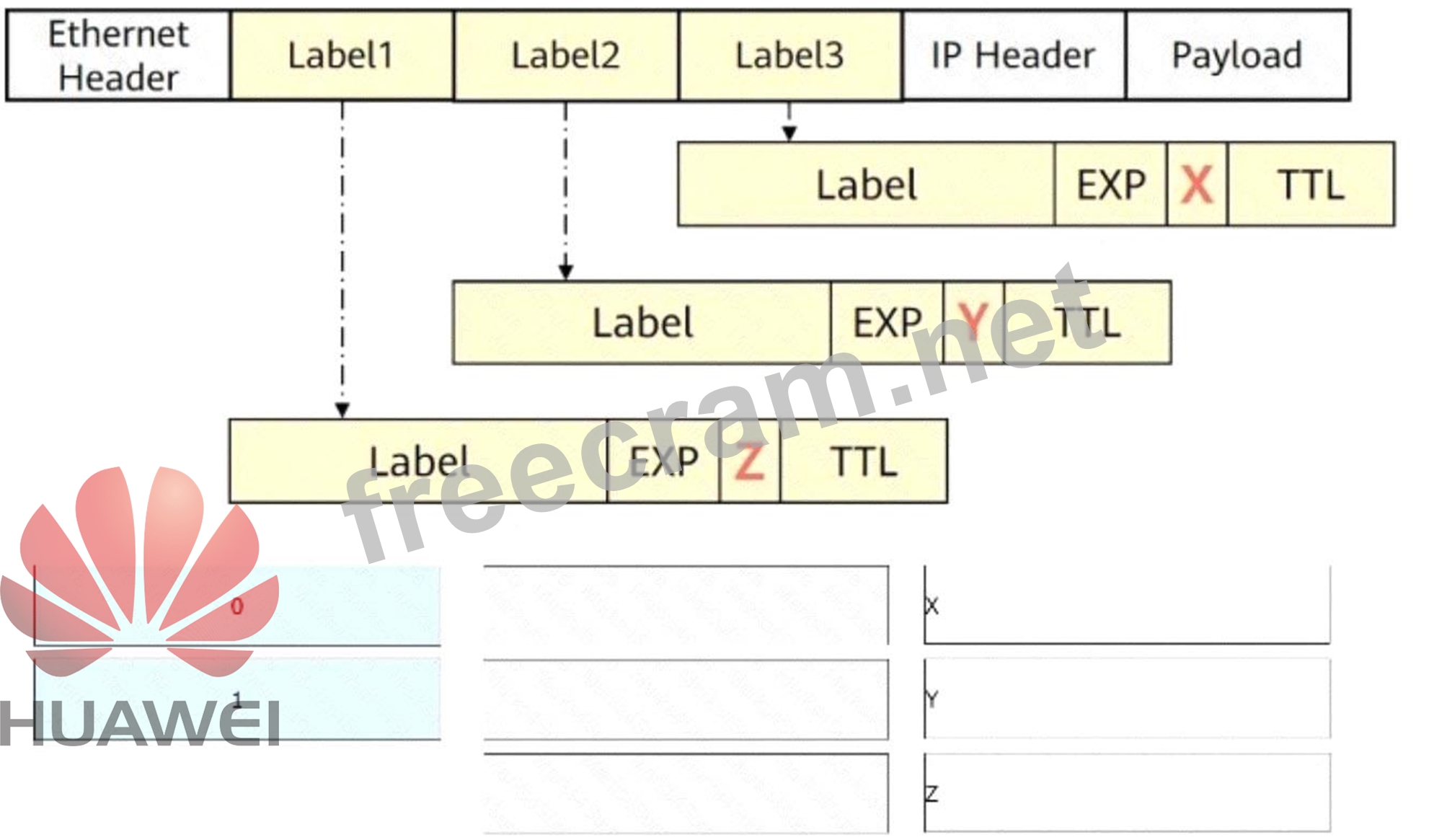

Correct Answer:
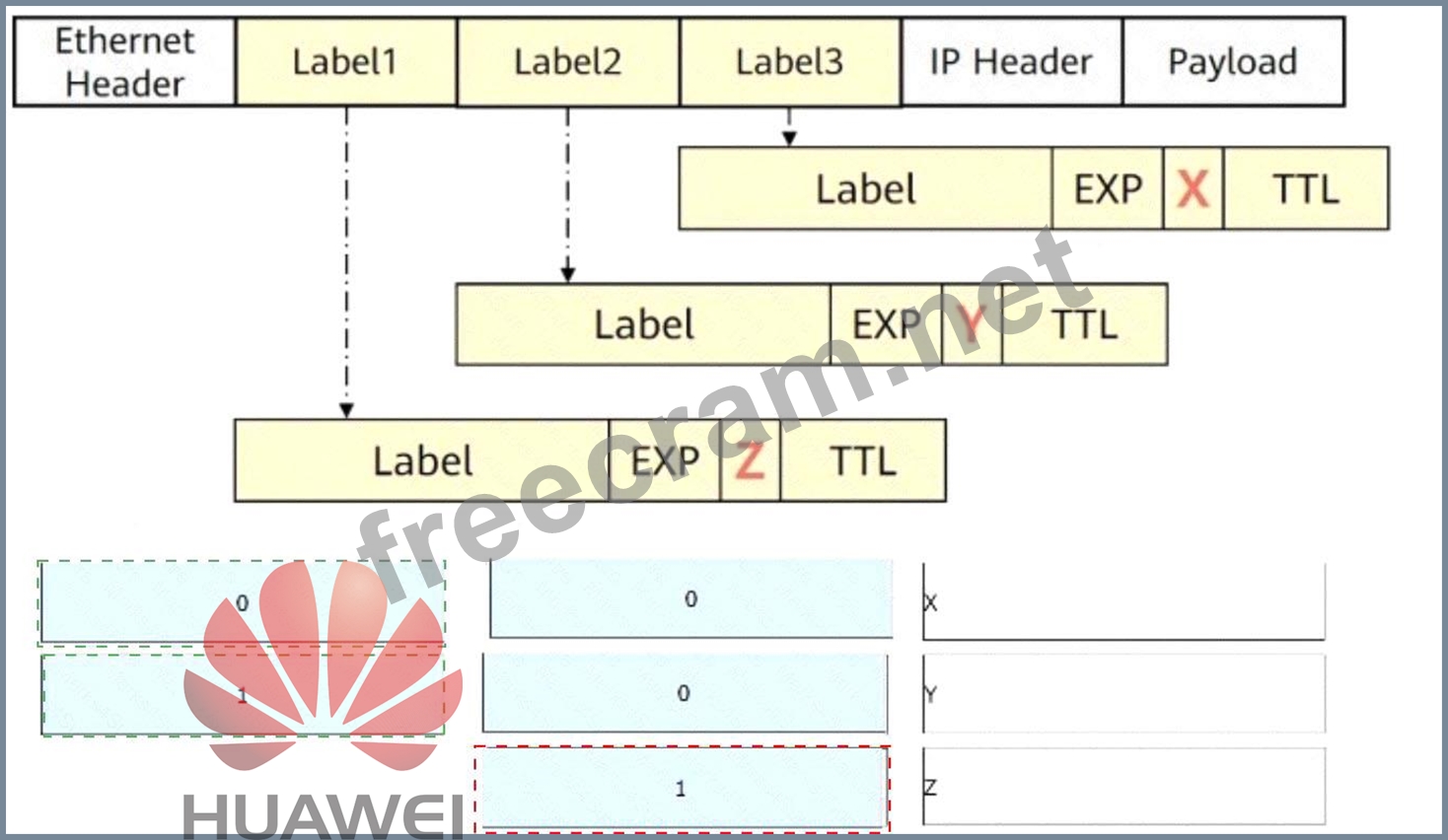
Explanation:
* X = 0
* Y = 0
* Z = 1
Understanding MPLS Label Headers
# What is MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)?
* MPLS is a high-performance forwarding technology that replaces IP lookups with label switching.
* Packets are forwarded based on labels instead of destination IP addresses.
* MPLS labels are stacked when passing through multiple hops.
# MPLS Label Stack StructureEach MPLS label has four fields:
* Label - 20-bit identifier used for forwarding.
* EXP (Experimental Bits / Traffic Class) - 3-bit field used for QoS (Quality of Service).
* S (Bottom of Stack) - 1-bit flag that indicates whether this is the last (bottom) label in the stack.
* TTL (Time-To-Live) - 8-bit field to prevent loops.
Understanding the EXP Fields (X, Y, Z) in the Figure
* The image shows a packet with three MPLS labels.
* Each label has an EXP field (X, Y, Z) representing the QoS bits.
* By default, MPLS EXP bits are copied from the top label to lower labels unless modified by QoS policies.
* If no QoS policy modifies the EXP bits, they remain the default value of 0.
* The bottom label in the stack (Label 3) often has an EXP value of 1 to indicate specific QoS policies.
Why Are the Answers X = 0, Y = 0, Z = 1?
# X = 0 (Default EXP for Label 1, the top label in the stack).# Y = 0 (EXP for Label 2, unchanged from the default value).# Z = 1 (EXP for Label 3, indicating a QoS setting applied to the bottom label).
Real-World Application:
* MPLS QoS (Quality of Service): EXP values determine packet priority in Service Provider networks.
* Traffic Engineering (TE): MPLS labels guide packets through optimized paths, ensuring low-latency services.
* Enterprise WAN Optimization: MPLS traffic is prioritized for critical applications like VoIP, Video Conferencing, and Cloud Services.
# Reference: Huawei HCIE-Datacom Guide - MPLS Label Stack and QoS EXP Field Processing
- Question List (85q)
- Question 1: Which of the following intelligent traffic steering policies...
- Question 2: Prefix segments and adjacency segments are globally visible ...
- Question 3: Which of the following statements is incorrect about the use...
- Question 4: gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call) is a language-neutral, p...
- Question 5: Portal authentication is recommended for scenarios with high...
- Question 6: What can be determined from the following figure? <R1>...
- Question 7: Which of the following types of EVPN routes does not carry M...
- Question 8: In the firewall hot standby scenario, which of the following...
- Question 9: In the figure, SR-MPLS is enabled on R1, R2, and R3. The SRG...
- Question 10: In the firewall hot standby scenario, in which of the follow...
- Question 11: IPsec SAs can be established in either manual mode or IKE au...
- Question 12: The ingress VTEP performs both Layer 2 and Layer 3 table loo...
- Question 13: What can be determined from the following IS-IS peer output?...
- Question 14: Which of the following are carried in an HTTP/1.1 response?...
- Question 15: An engineer often remotely logs in to the device to check th...
- Question 16: (Exhibit) As shown in the following figure, an engineer test...
- Question 17: In the Huawei SD-WAN Solution, the topologies of different V...
- Question 18: Flavors are additional behaviors defined to enhance the End ...
- Question 19: The following figure shows the inter-AS MPLS L3VPN Option C ...
- Question 20: In the following figure, all routers are running OSPF. Given...
- Question 21: (Exhibit) Refer to the configuration in the figure. Which qu...
- Question 22: In a scenario where a VXLAN tunnel is dynamically establishe...
- Question 23: In the SD-WAN Solution, which routing protocols can be used ...
- Question 24: IPsec uses an asymmetric encryption algorithm to encrypt the...
- Question 25: On a CloudCampus virtualized campus network, virtual network...
- Question 26: In a scenario where a VXLAN tunnel is dynamically establishe...
- Question 27: When an SSH client logs in to an SSH server that is configur...
- Question 28: Congestion management technology can be used to discard data...
- Question 29: After the reset isis all command is run, the specified IS-IS...
- Question 30: In Huawei Open Programmability System (OPS), /ifm/interfaces...
- Question 31: Which of the following statements about BGP EVPN principles ...
- Question 32: Which of the following is the drop probability of packets ex...
- Question 33: An HTTP request line consists of three fields. Select the fi...
- Question 34: Which of the following is the purpose of configuring IS-IS f...
- Question 35: Which of the following statements regarding OSPF neighbor re...
- Question 36: Exhibit: (Exhibit) The following figure shows the inter-AS M...
- Question 37: Huawei CloudCampus Solution has multiple application scenari...
- Question 38: Before connecting an SSH client to an SSH server in public k...
- Question 39: An SRv6 Policy can be either statically configured on a devi...
- Question 40: An SRLB is a set of user-specified local labels reserved for...
- Question 41: In a scenario where a VXLAN tunnel is dynamically establishe...
- Question 42: In DU label advertisement mode, if the liberal label retenti...
- Question 43: Exhibit: (Exhibit) A loop occurs because Spanning Tree Proto...
- Question 44: To allow only authorized users (users who obtain IP addresse...
- Question 45: A network administrator runs the display telemetry subscript...
- Question 46: Man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM) or IP/MAC Spoofing attacks ...
- Question 47: Which of the following functions can be provided by iMaster ...
- Question 48: A VGMP packet is encapsulated with a UDP header and a VGMP h...
- Question 49: OSPFv2 is an IGP running on IPv4 networks, whereas OSPFv3 is...
- Question 50: What can be determined from the following figure? (Exhibit)...
- Question 51: Which of the following items are included in static informat...
- Question 52: To deploy a virtual campus network using iMaster NCE-Campus,...
- Question 53: OSPF is a mature protocol and is unlikely to have route comp...
- Question 54: As shown in the figure, PE1 establishes an EVPN peer relatio...
- Question 55: The display current-configuration command displays the runni...
- Question 56: Which of the following roles is NOT a core role in Huawei's ...
- Question 57: In OSPFv3, which of the following types of LSAs can be flood...
- Question 58: As shown in the figure, what is known about the default rout...
- Question 59: Which of the following statements is incorrect about intrane...
- Question 60: Network administrator A wants to use an IP prefix-list to ma...
- Question 61: In a scenario where a VXLAN tunnel is dynamically establishe...
- Question 62: In the small and midsize campus network design based on the ...
- Question 63: When a client invokes the iMaster NCE-Campus RESTful API, it...
- Question 64: Which of the following are carried in the HTTP/1.1 response ...
- Question 65: iMaster NCE-Campus provides the terminal identification func...
- Question 66: In a VXLAN scenario, which of the following features can be ...
- Question 67: MPLS supports forwarding equivalence class (FEC). Which of t...
- Question 68: Which of the following statements about VXLAN principles is ...
- Question 69: Collecting information before a cutover helps you determine ...
- Question 70: Huawei Open Programmability System (OPS) uses standard HTTP ...
- Question 71: Which MPLS label will be used by PE2 for forwarding traffic ...
- Question 72: Which of the following commands is used to adjust the cost o...
- Question 73: BGP Link State (BGP-LS) introduces a new NLRI into BGP. The ...
- Question 74: Refer to the figure. (Exhibit) Which of the following steps ...
- Question 75: The channelized sub-interface and FlexE technologies both ca...
- Question 76: In addition to indicating priority, the DSCP value can also ...
- Question 77: On a router, SRv6 is enabled, and the configurations shown b...
- Question 78: On a campus network, iMaster NCE-Campus is used to deploy tw...
- Question 79: In the following figure, OSPF is enabled on all router inter...
- Question 80: Which of the following inter-AS MPLS L3VPN solutions needs A...
- Question 81: Huawei Open Programmability System (OPS) uses HTTP methods t...
- Question 82: Which of the following number sequences can be matched by th...
- Question 83: BFD can implement millisecond-level link status detection....
- Question 84: In the CloudCampus public cloud scenario, if deployment thro...
- Question 85: The figure shows a packet that contains three label headers....


