- Home
- Curam Software
- CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+) Certification Exam
- CuramSoftware.CS0-003.v2025-08-30.q175
- Question 44
Valid CS0-003 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing CS0-003 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest CS0-003 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com CS0-003 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com CS0-003 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access CS0-003 Dumps Premium Version
(622 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 44/175
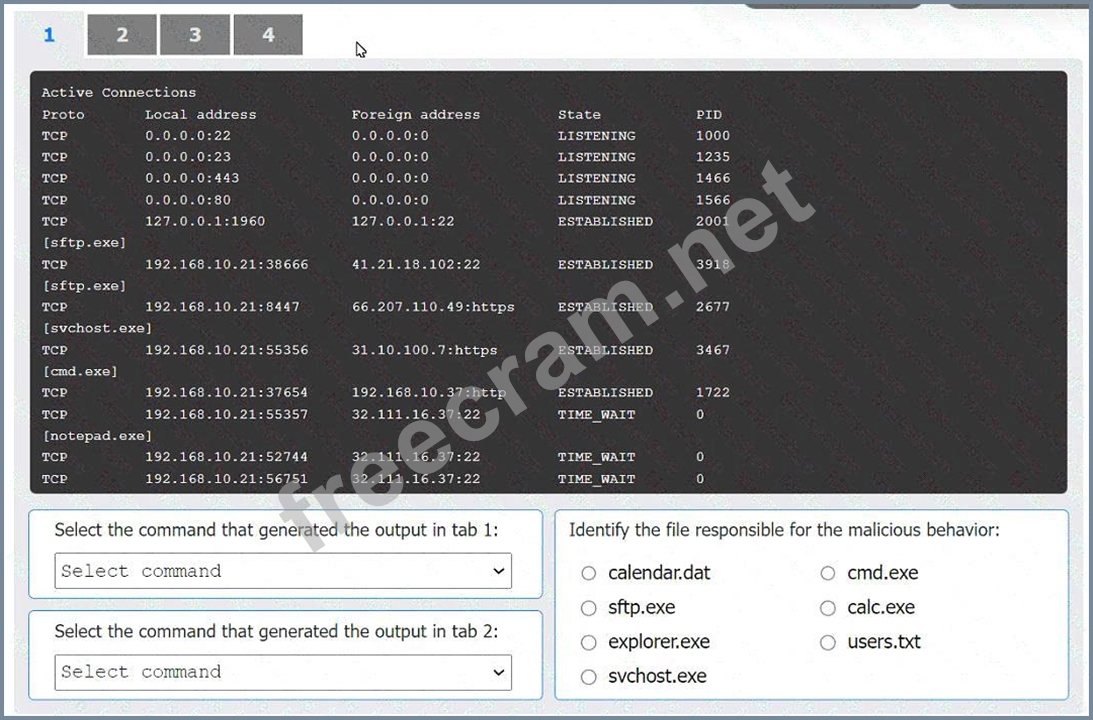
An organization has noticed large amounts of data are being sent out of its network. An analyst is identifying the cause of the data exfiltration.
INSTRUCTIONS
Select the command that generated the output in tabs 1 and 2.
Review the output text in all tabs and identify the file responsible for the malicious behavior.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
INSTRUCTIONS
Select the command that generated the output in tabs 1 and 2.
Review the output text in all tabs and identify the file responsible for the malicious behavior.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.







Correct Answer:
Explanation:
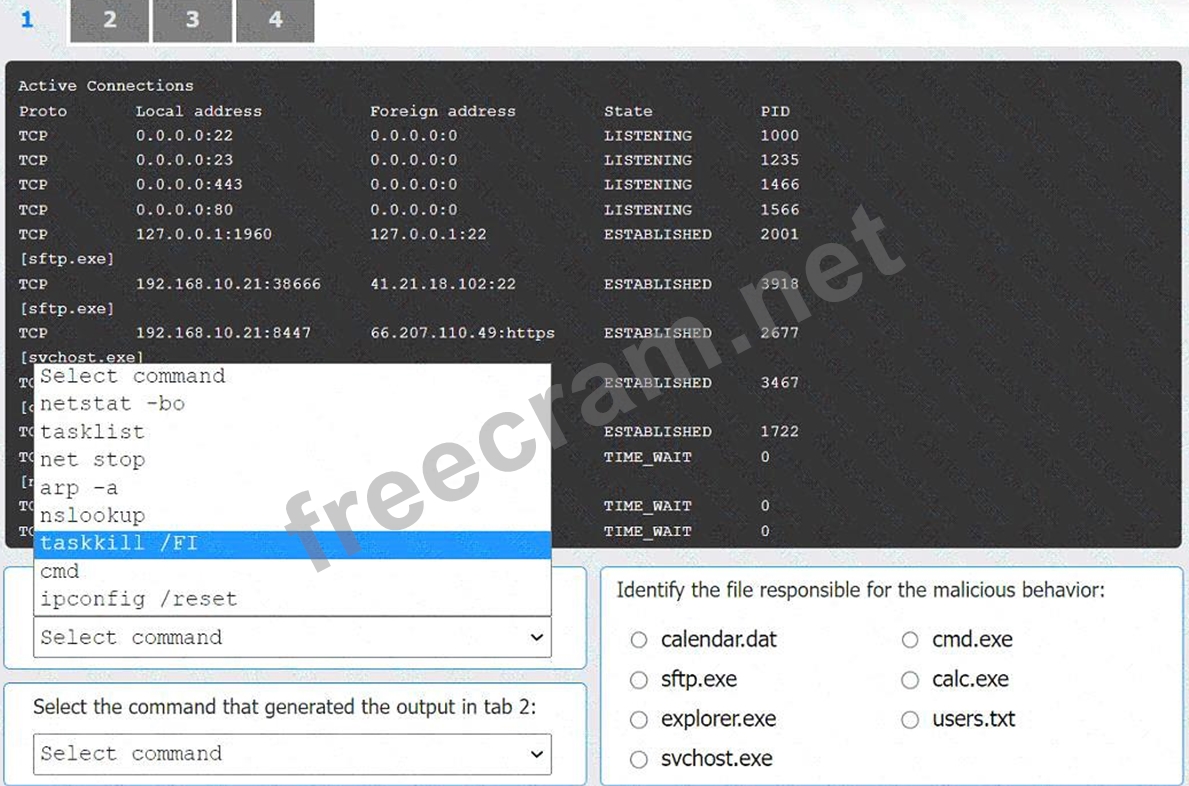
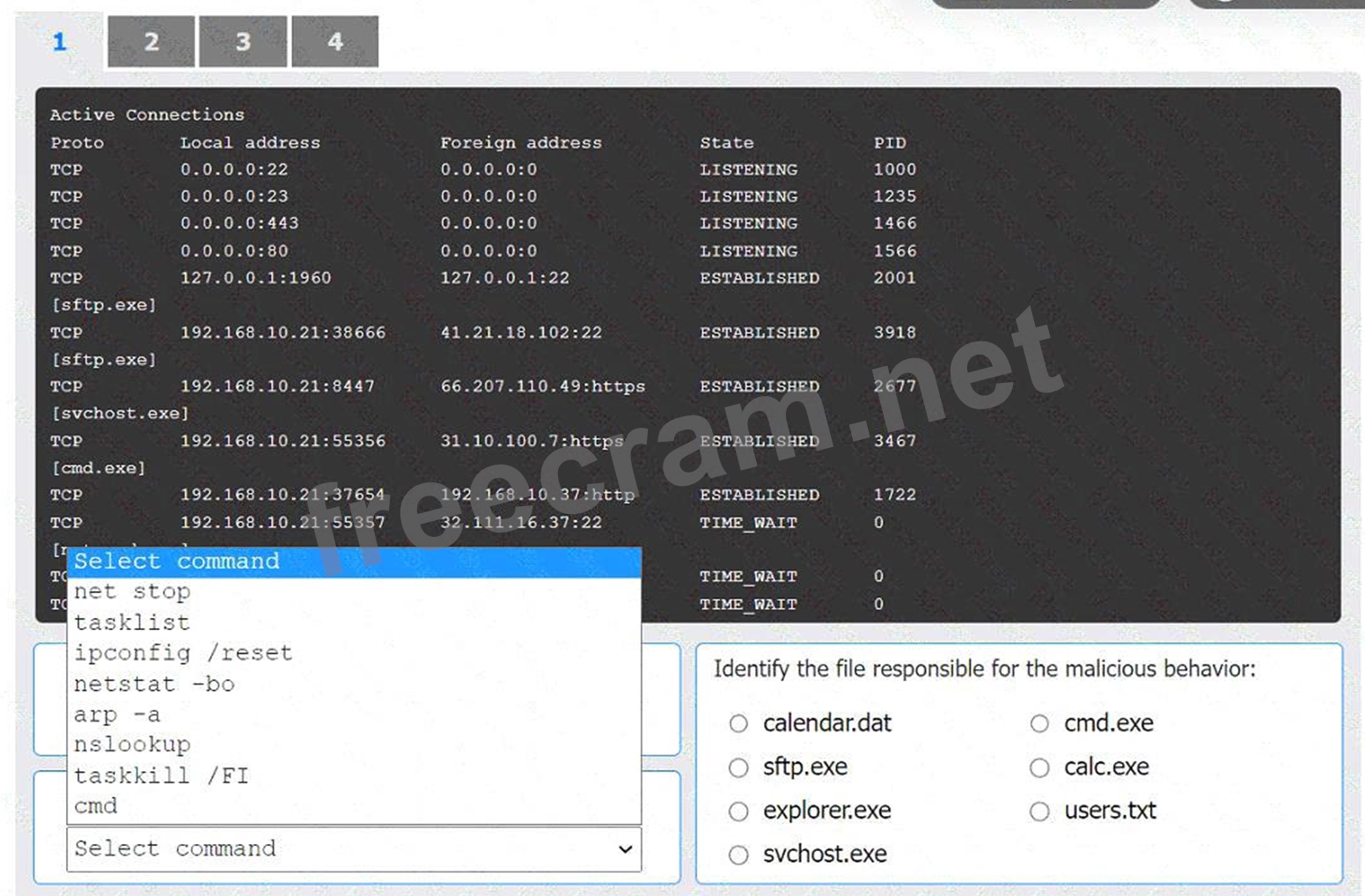
Select the command that generated the output in tab 1:
* netstat -bo
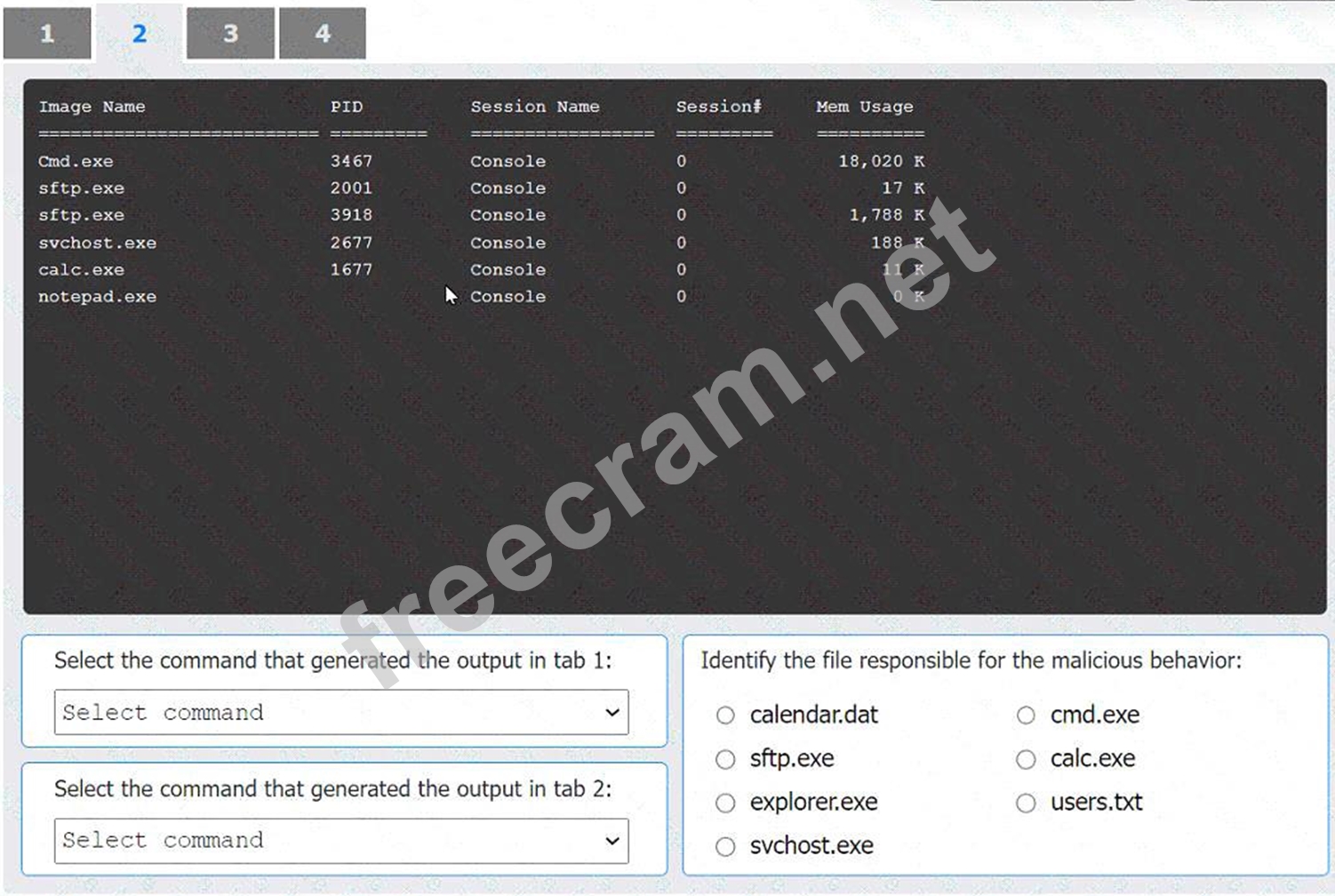
Select the command that generated the output in tab 2:
* tasklist
Identify the file responsible for the malicious behavior:
* cmd.exe
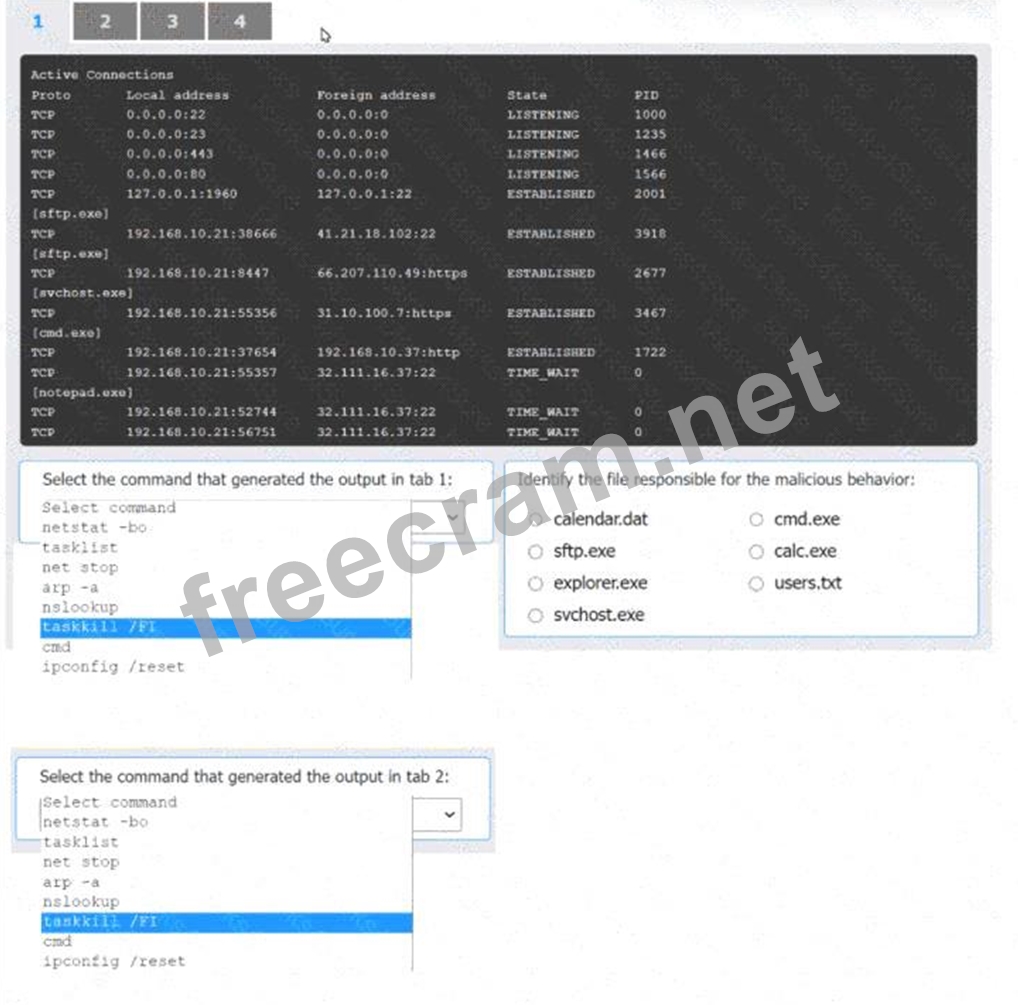
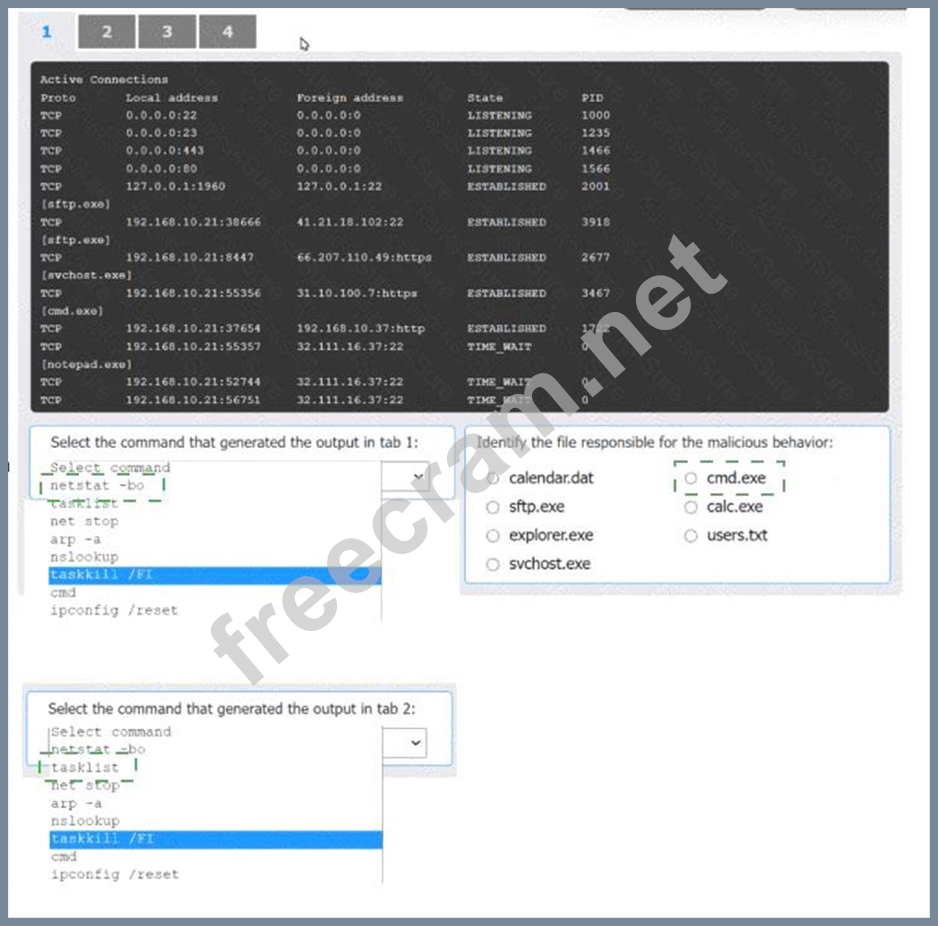
Select the command that generated the output in tab 1: The output in tab 1 displays active network connections, which can be generated using the netstat command with options to display the owning process ID.
Select the command that generated the output in tab 1:
* netstat -bo
Select the command that generated the output in tab 2: The output in tab 2 lists the running processes with their PIDs and memory usage, which can be generated using the tasklist command.
Select the command that generated the output in tab 2:
* tasklist
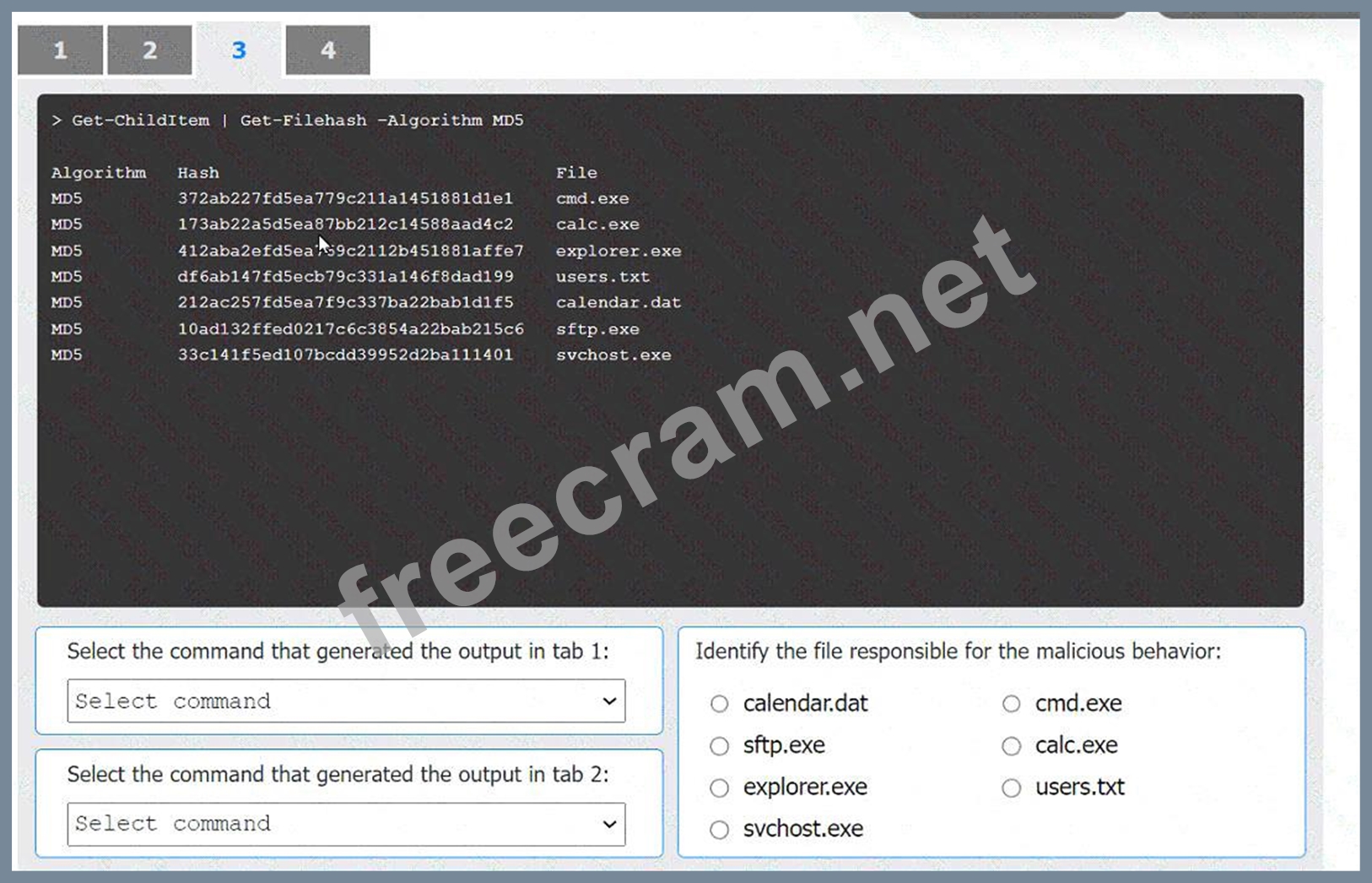
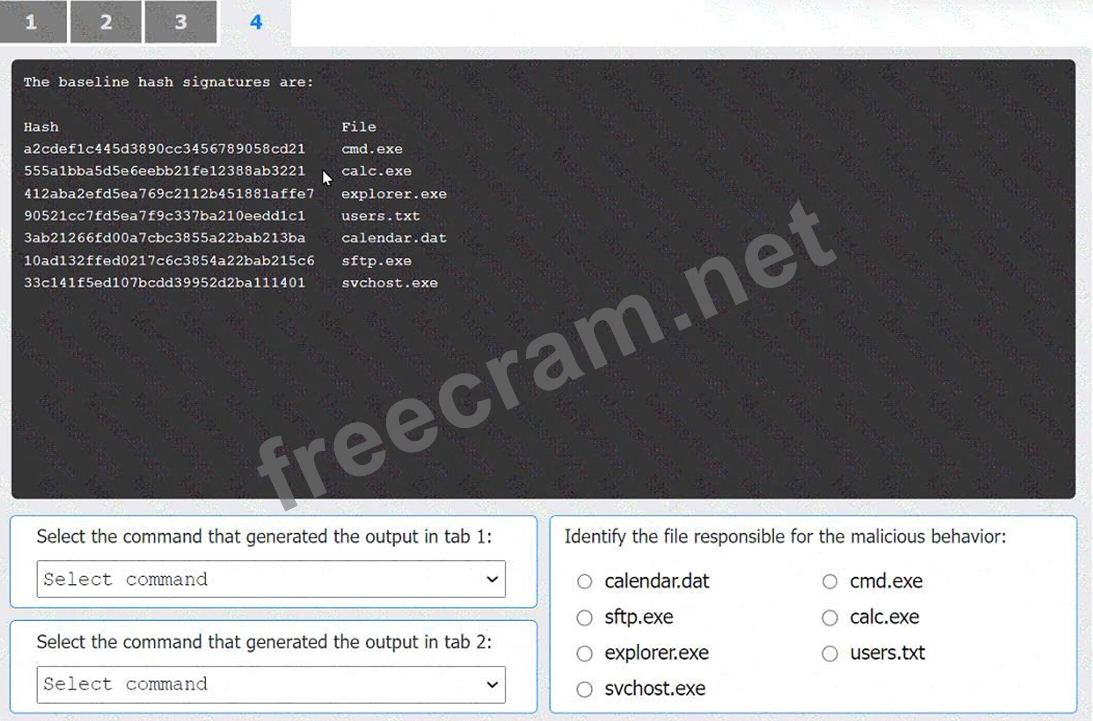
Identify the file responsible for the malicious behavior: To identify the malicious file, we compare the hashes of the current files against the baseline hashes. From the provided data:
* The hash for cmd.exe in the current state (tab 3) is 372ab227fd5ea779c211a1451881d1e1.
* The baseline hash for cmd.exe (tab 4) is a2cdef1c445d3890cc3456789058cd21.
Since these hashes do not match, cmd.exe is the file responsible for the malicious behavior.
- Question List (175q)
- Question 1: Which of the following is the appropriate phase in the incid...
- Question 2: An analyst is conducting routine vulnerability assessments o...
- Question 3: During a scan of a web server in the perimeter network, a vu...
- Question 4: A company has decided to expose several systems to the inter...
- Question 5: An analyst is imaging a hard drive that was obtained from th...
- Question 6: A cryptocurrency service company is primarily concerned with...
- Question 7: An XSS vulnerability was reported on one of the public websi...
- Question 8: After an incident, a security analyst needs to perform a for...
- Question 9: An end-of-life date was announced for a widely used OS. A bu...
- Question 10: A penetration tester is conducting a test on an organization...
- Question 11: A cybersecurity analyst is tasked with scanning a web applic...
- Question 12: An organization has activated the CSIRT. A security analyst ...
- Question 13: A zero-day command injection vulnerability was published. A ...
- Question 14: Which of the following is a benefit of the Diamond Model of ...
- Question 15: A security analyst needs to secure digital evidence related ...
- Question 16: Which of the following ensures that a team receives simulate...
- Question 17: A company has a primary control in place to restrict access ...
- Question 18: A security analyst must assist the IT department with creati...
- Question 19: An analyst reviews a recent government alert on new zero-day...
- Question 20: A company is implementing a vulnerability management program...
- Question 21: A company's internet-facing web application has been comprom...
- Question 22: The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) has notified that a confid...
- Question 23: An analyst is reviewing a vulnerability report for a server ...
- Question 24: Which of the following concepts is using an API to insert bu...
- Question 25: A security analyst is reviewing a recent vulnerability scan ...
- Question 26: An employee received a phishing email that contained malware...
- Question 27: A company's security team is updating a section of the repor...
- Question 28: A vulnerability management team found four major vulnerabili...
- Question 29: A security alert was triggered when an end user tried to acc...
- Question 30: A security team identified several rogue Wi-Fi access points...
- Question 31: During an incident, a security analyst discovers a large amo...
- Question 32: Which of the following security operations tasks are ideal f...
- Question 33: A vulnerability scan of a web server that is exposed to the ...
- Question 34: The vulnerability analyst reviews threat intelligence regard...
- Question 35: Which of the following best explains the importance of commu...
- Question 36: The security operations team is required to consolidate seve...
- Question 37: A security analyst is performing an investigation involving ...
- Question 38: A company is concerned with finding sensitive file storage l...
- Question 39: An incident response analyst notices multiple emails travers...
- Question 40: Which of the following is the best metric for an organizatio...
- Question 41: When undertaking a cloud migration of multiple SaaS applicat...
- Question 42: An analyst investigated a website and produced the following...
- Question 43: A company's user accounts have been compromised. Users are a...
- Question 44: An organization has noticed large amounts of data are being ...
- Question 45: After updating the email client to the latest patch, only ab...
- Question 46: A security analyst is working on a server patch management p...
- Question 47: Which of the following best describes the goal of a tabletop...
- Question 48: A security program was able to achieve a 30% improvement in ...
- Question 49: Which of the following will most likely cause severe issues ...
- Question 50: An incident response team finished responding to a significa...
- Question 51: When starting an investigation, which of the following must ...
- Question 52: While performing a dynamic analysis of a malicious file, a s...
- Question 53: Which of the following describes how a CSIRT lead determines...
- Question 54: An analyst is suddenly unable to enrich data from the firewa...
- Question 55: An organization utilizes multiple vendors, each with its own...
- Question 56: A Chief Information Security Officer wants to map all the at...
- Question 57: A recent penetration test discovered that several employees ...
- Question 58: While reviewing web server logs, an analyst notices several ...
- Question 59: When investigating a potentially compromised host, an analys...
- Question 60: An analyst notices there is an internal device sending HTTPS...
- Question 61: An email hosting provider added a new data center with new p...
- Question 62: A security analyst reviews the following results of a Nikto ...
- Question 63: A systems administrator receives reports of an internet-acce...
- Question 64: A security administrator needs to import Pll data records fr...
- Question 65: Patches for two highly exploited vulnerabilities were releas...
- Question 66: Which of the following best explains the importance of netwo...
- Question 67: A team of analysts is developing a new internal system that ...
- Question 68: An incident response analyst is investigating the root cause...
- Question 69: A company patches its servers using automation software. Rem...
- Question 70: A security analyst reviews a packet capture and identifies t...
- Question 71: A security analyst has prepared a vulnerability scan that co...
- Question 72: A security analyst is validating a particular finding that w...
- Question 73: A security analyst identifies a device on which different ma...
- Question 74: While configuring a SIEM for an organization, a security ana...
- Question 75: Which of the following should be updated after a lessons-lea...
- Question 76: During a tabletop exercise, engineers discovered that an ICS...
- Question 77: Which of the following would eliminate the need for differen...
- Question 78: A security analyst reviews the latest vulnerability scans an...
- Question 79: A SOC manager receives a phone call from an upset customer. ...
- Question 80: A SOC receives several alerts indicating user accounts are c...
- Question 81: The analyst reviews the following endpoint log entry: (Exhib...
- Question 82: ID Source Destination Protocol Service 1 172.16.1.1 172.16.1...
- Question 83: A security analyst is assisting a software engineer with the...
- Question 84: A security analyst is tasked with prioritizing vulnerabiliti...
- Question 85: A vulnerability scan shows several vulnerabilities. At the s...
- Question 86: Following an attack, an analyst needs to provide a summary o...
- Question 87: An organization was compromised, and the usernames and passw...
- Question 88: A security analyst performs various types of vulnerability s...
- Question 89: Which of the following is the best framework for assessing h...
- Question 90: A security analyst found the following vulnerability on the ...
- Question 91: While reviewing the web server logs a security analyst notic...
- Question 92: A security analyst observed the following activity from a pr...
- Question 93: A security team needs to demonstrate how prepared the team i...
- Question 94: A security analyst identified the following suspicious entry...
- Question 95: After completing a review of network activity. the threat hu...
- Question 96: A security analyst needs to provide evidence of regular vuln...
- Question 97: A SIEM alert is triggered based on execution of a suspicious...
- Question 98: While reviewing the web server logs, a security analyst noti...
- Question 99: Which of the following is often used to keep the number of a...
- Question 100: A security analyst is performing an investigation involving ...
- Question 101: A Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) wants to disable...
- Question 102: A SOC team lead occasionally collects some DNS information f...
- Question 103: An incident responder was able to recover a binary file thro...
- Question 104: Which of the following responsibilities does the legal team ...
- Question 105: A systems administrator is reviewing after-hours traffic flo...
- Question 106: A systems administrator is reviewing after-hours traffic flo...
- Question 107: Which of the following best describes the importance of impl...
- Question 108: A company was able to reduce triage time by focusing on hist...
- Question 109: While reviewing web server logs, a security analyst found th...
- Question 110: A recent zero-day vulnerability is being actively exploited,...
- Question 111: A security analyst recently used Arachni to perform a vulner...
- Question 112: The security team at a company, which was a recent target of...
- Question 113: Results of a SOC customer service evaluation indicate high l...
- Question 114: A SOC analyst observes reconnaissance activity from an IP ad...
- Question 115: A security analyst is trying to detect connections to a susp...
- Question 116: Which of following would best mitigate the effects of a new ...
- Question 117: The management team requests monthly KPI reports on the comp...
- Question 118: A SOC analyst determined that a significant number of the re...
- Question 119: The Chief Executive Officer of an organization recently hear...
- Question 120: Which of the following is a reason why proper handling and r...
- Question 121: An analyst is reviewing a vulnerability report and must make...
- Question 122: A cloud team received an alert that unauthorized resources w...
- Question 123: A disgruntled open-source developer has decided to sabotage ...
- Question 124: An organization has tracked several incidents that are liste...
- Question 125: Which of the following best describes the key goal of the co...
- Question 126: A corporation wants to implement an agent-based endpoint sol...
- Question 127: Each time a vulnerability assessment team shares the regular...
- Question 128: A laptop that is company owned and managed is suspected to h...
- Question 129: Which of the following is a circumstance in which a security...
- Question 130: Based on an internal assessment, a vulnerability management ...
- Question 131: Which of the following best describes the process of requiri...
- Question 132: Which of the following is a KPI that is used to monitor or r...
- Question 133: A Chief Information Security Officer has requested a dashboa...
- Question 134: A cybersecurity team has witnessed numerous vulnerability ev...
- Question 135: Which of the following is a nation-state actor least likely ...
- Question 136: A security analyst is writing a shell script to identify IP ...
- Question 137: A high volume of failed RDP authentication attempts was logg...
- Question 138: An organization receives a legal hold request from an attorn...
- Question 139: During a recent site survey. an analyst discovered a rogue w...
- Question 140: A security analyst is reviewing the following alert that was...
- Question 141: A security analyst detects an email server that had been com...
- Question 142: During a security test, a security analyst found a critical ...
- Question 143: A security analyst needs to prioritize vulnerabilities for p...
- Question 144: A new cybersecurity analyst is tasked with creating an execu...
- Question 145: An organization identifies a method to detect unexpected beh...
- Question 146: A security analyst is improving an organization's vulnerabil...
- Question 147: An analyst is reviewing a dashboard from the company's SIEM ...
- Question 148: An older CVE with a vulnerability score of 7.1 was elevated ...
- Question 149: During an incident, an analyst needs to acquire evidence for...
- Question 150: The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) of a large man...
- Question 151: Which of the following attributes is part of the Diamond Mod...
- Question 152: A company brings in a consultant to make improvements to its...
- Question 153: Which of the following should be updated after a lessons-lea...
- Question 154: A regulated organization experienced a security breach that ...
- Question 155: Which of the following is the best action to take after the ...
- Question 156: During the log analysis phase, the following suspicious comm...
- Question 157: An employee is no longer able to log in to an account after ...
- Question 158: Which of the following threat-modeling procedures is in the ...
- Question 159: The SOC received a threat intelligence notification indicati...
- Question 160: An analyst is designing a message system for a bank. The ana...
- Question 161: An organization would like to ensure its cloud infrastructur...
- Question 162: Which of the following tools would work best to prevent the ...
- Question 163: An attacker recently gained unauthorized access to a financi...
- Question 164: A SOC analyst recommends adding a layer of defense for all e...
- Question 165: During an incident involving phishing, a security analyst ne...
- Question 166: Following a recent security incident, the Chief Information ...
- Question 167: Which of the following best explains the importance of utili...
- Question 168: Which of the following best describes the reporting metric t...
- Question 169: Which of the following is a commonly used four-component fra...
- Question 170: After a security assessment was done by a third-party consul...
- Question 171: Which of the following describes the best reason for conduct...
- Question 172: A company recently removed administrator rights from all of ...
- Question 173: An organization is planning to adopt a zero-trust architectu...
- Question 174: A penetration tester submitted data to a form in a web appli...
- Question 175: During an incident, some loCs of possible ransomware contami...

[×]
Download PDF File
Enter your email address to download CuramSoftware.CS0-003.v2025-08-30.q175.pdf

