<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 96/100
SIMULATION
You work as Network Engineer for RADO network Ltd company. You colleague has setup POC simulating customer network to study about the behavior of BGP protocol when routes are exchanged between two different autonomous systems.
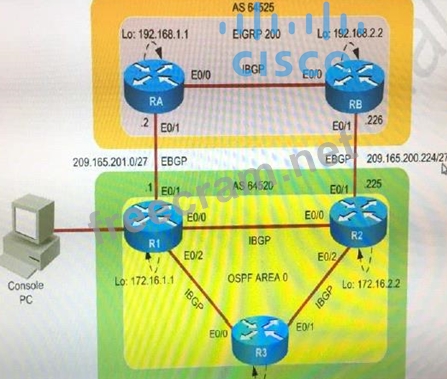
Review the topology. You need to identify and fix IBGP and EBGP issues on R1 router.
Topology Details:
AS64520
* R1, R2 and R3 are three routers on AS 64520 and OSPF is IGP routing protocol configured between them.
* IBGP configured between R1, R2, and R3 routers using peer group.
* Loopback0 address is used for IBGP peering, Loopback0 address configured on R1, R2 and R3 are advertised into BGP domain on AS64525.
AS64525
* RA and RB are two routers on AS64525 and EIGRP is IGP routing protocol configured between them.
* Loopback0 address is used for IBGP peering, Loopback0 address configured on RA and RB advertised into BGP domain on AS64525.
* R1 and RRA from EBGP neighbor relationship using physical interface address.
*R2 and RB from EBGP neighbor relationship using physical interface address.
Simulation requirements:
*Identify and fix EBGP neighbor relationship between R1 and R1 routers.
*Identify and fix IBGP neighbor relationship issue between R1 and R2, R1 and R3.
*You are allowed to remove any misconfiguration or incorrect configuration to only fix the issue and other initial configuration that not impacting the issues should not be changed.
* The Final BGP table, after fixing two issues on R1 router should display as shown below
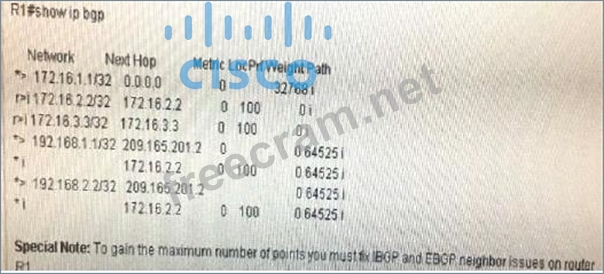
You work as Network Engineer for RADO network Ltd company. You colleague has setup POC simulating customer network to study about the behavior of BGP protocol when routes are exchanged between two different autonomous systems.
Review the topology. You need to identify and fix IBGP and EBGP issues on R1 router.
Topology Details:
AS64520
* R1, R2 and R3 are three routers on AS 64520 and OSPF is IGP routing protocol configured between them.
* IBGP configured between R1, R2, and R3 routers using peer group.
* Loopback0 address is used for IBGP peering, Loopback0 address configured on R1, R2 and R3 are advertised into BGP domain on AS64525.
AS64525
* RA and RB are two routers on AS64525 and EIGRP is IGP routing protocol configured between them.
* Loopback0 address is used for IBGP peering, Loopback0 address configured on RA and RB advertised into BGP domain on AS64525.
* R1 and RRA from EBGP neighbor relationship using physical interface address.
*R2 and RB from EBGP neighbor relationship using physical interface address.
Simulation requirements:
*Identify and fix EBGP neighbor relationship between R1 and R1 routers.
*Identify and fix IBGP neighbor relationship issue between R1 and R2, R1 and R3.
*You are allowed to remove any misconfiguration or incorrect configuration to only fix the issue and other initial configuration that not impacting the issues should not be changed.
* The Final BGP table, after fixing two issues on R1 router should display as shown below




