Valid 200-310 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 200-310 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 200-310 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 200-310 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 200-310 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 200-310 Dumps Premium Version
(392 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 242/351
DRAG DROP
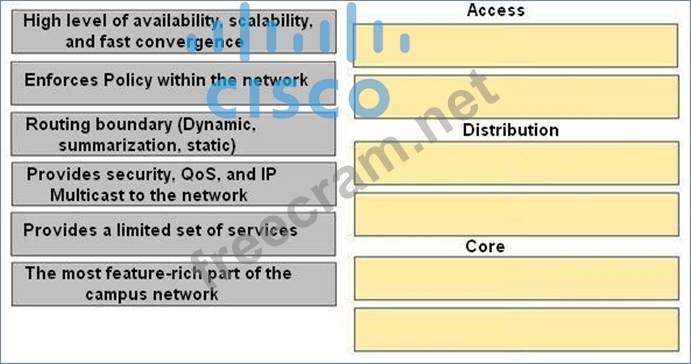
Drag the characteristics of the traditional campus network on the left to the most appropriate hierarchical network layer on the right.
Select and Place:
Drag the characteristics of the traditional campus network on the left to the most appropriate hierarchical network layer on the right.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:
Explanation/Reference:
Explanation:
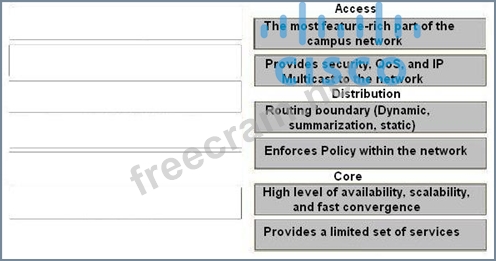
Access
The most feature-rich part of the campus network

Provides security, QoS, and IP Multicast to the network

Distribution
Routing boundary (Dynamic, summarization, static)

Enforces Policy within the network

Core
High level of availability, scalability, and fast convergence

Provides a limited set of services

Large-Building LANs
Large-building LANs are segmented by floors or departments. The building-access component serves one or more departments or floors. The building-distribution component serves one or more building-access components. Campus and building backbone devices connect the data center, building-distribution components, and the enterprise edge-distribution component. The access layer typically uses Layer 2 switches to contain costs, with more expensive Layer 3 switches in the distribution layer to provide policy enforcement. Current best practice is to also deploy multilayer switches in the campus and building backbone.
Cisco Enterprise Architecture Model
Core
Fast transport

High reliability

Redundancy

Fault tolerance

Low latency and good manageability

Avoidance of slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other processes

Limited and consistent diameter

Quality of service (QoS)

Distribution
Policy-based connectivity

Redundancy and load balancing

Aggregation of LAN wiring closets

Aggregation of WAN connections

QoS

Security filtering

Address or area aggregation or summarization

Departmental or workgroup access

Broadcast or multicast domain definition

Routing between virtual LANs (VLAN)

Media translations (for example, between Ethernet and Token Ring)

Redistribution between routing domains (for example, between two different routing protocols)

Demarcation between static and dynamic routing protocols

Access
Layer 2 switching

High availability

Port security

Broadcast suppression

QoS

Rate limiting

Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection

Virtual access control lists (VACL)

Spanning tree

Trust classification

Power over Ethernet (PoE) and auxiliary VLANs for VoIP
Cisco Press CCDA 640-864 Official Certification Guide Fourth Edition, Chapter 3
- Question List (351q)
- Question 1: When designing using the Cisco Enterprise Architecture, in w...
- Question 2: Which three terms describe the primary functions of the dist...
- Question 3: A remote user for a company must periodically connect to the...
- Question 4: Consider the reservation of IP Addressing what mask you will...
- Question 5: An engineer is designing a network that is divided into mult...
- Question 6: When is the Cisco FlexConnect design model recommended?...
- Question 7: Which two routing protocols converge most quickly? (Choose t...
- Question 8: Study the following options carefully. The corporate Interne...
- Question 9: Which IGP provides the fastest convergence by default?...
- Question 10: What DNS entry to use for WLC with firmware version 6.0 or l...
- Question 11: OSPF will be used as the IGP within a campus network. Which ...
- Question 12: Which command is correct for creating a virtual interface on...
- Question 13: What branch design supports 100 to 1000 users and integrates...
- Question 14: Which item is not an SNMP operation?...
- Question 15: Which modules are found in the Enterprise Edge functional ar...
- Question 16: DRAG DROP Drag the WAN characteristics on the left to the br...
- Question 17: Which Cisco device has the sole function at looking at threa...
- Question 18: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. The organization is migratin...
- Question 19: Which consideration is the most important for the network de...
- Question 20: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration can be u...
- Question 21: The network-design process is limited by many external const...
- Question 22: A company would like to distribute a VM hosting cluster betw...
- Question 23: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which IPS location is best f...
- Question 24: What device virtualization technology allows for a single po...
- Question 25: Which two options best describe the top-down design approach...
- Question 26: When designing an EIGRP network, which two things should you...
- Question 27: With respect to IPv6 addressing, from a design perspective, ...
- Question 28: A company is implementing an Identity Management solution wi...
- Question 29: Why would an engineer implement variable-length subnet masks...
- Question 30: What are two advantages of a modular design? (Choose two)...
- Question 31: A network engineer is designing an enterprise managed VPN so...
- Question 32: To provide Layer 2 connectivity between the primary and remo...
- Question 33: Which option can use deep-packet examination to determine th...
- Question 34: Which statement should the designer keep in mind when consid...
- Question 35: A consultant at Company XYZ connects to the Guest wireless n...
- Question 36: Which two options should be used to achieve fast convergence...
- Question 37: When there is a need for immunity to EMI for connecting loca...
- Question 38: Which two considerations are important when designing the co...
- Question 39: The enterprise campus core layer has requirements that are u...
- Question 40: Which of these domain-of-trust security statements is correc...
- Question 41: Which packet-switching topology approach typically requires ...
- Question 42: When designing the infrastructure protection portion for the...
- Question 43: What two components are used when creating an endpoint's mod...
- Question 44: A company requires a managed WAN solution that supports Laye...
- Question 45: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which statement accurately r...
- Question 46: Which two protocols are classful routing protocols? (Choose ...
- Question 47: SNMP is short for Simple Network Management Protocol. Which ...
- Question 48: Which one of these statements is an example of how trust and...
- Question 49: Which WLC interface is dedicated for WLAN client data?...
- Question 50: A network engineer is following the three tiered Network Hie...
- Question 51: An internal network has servers with private IPv4 addresses ...
- Question 52: Data link switching is typically used in which Enterprise Ca...
- Question 53: Which protocol is best when there are circuit connections wi...
- Question 54: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which three modules would ty...
- Question 55: What information should be utilized to identify network appl...
- Question 56: What are the three modes of unicast reverse path forwarding?...
- Question 57: Which two statements about designing the Data Center Access ...
- Question 58: Which option is an example of a fixed two-level hierarchical...
- Question 59: A hierarchical design of the EIGRP domain facilitates which ...
- Question 60: In which phase of the Cisco Design Lifecycle would you ident...
- Question 61: Which three protocols support VLSM? (Choose three.)...
- Question 62: A campus network needs end-to-end QoS tools to manage traffi...
- Question 63: What kind of servers you should place in DMZ?...
- Question 64: Which two design approaches provide management of enterprise...
- Question 65: If a teleworker is required to access the branch office via ...
- Question 66: What two addresses are defined under RFC 1918? (Choose two.)...
- Question 67: Which three of these are components of the North American Nu...
- Question 68: Which two link state routing protocols support IPv6 routing?...
- Question 69: A circuit order has been placed for Gigabit Ethernet and is ...
- Question 70: Which layer in the Cisco Enterprise Architecture model is hi...
- Question 71: Which option is used by OSPF to reduce the flooding domain o...
- Question 72: Which two are characteristics of a Lightweight Access Point?...
- Question 73: Which H.323 protocol monitors calls for factors such as pack...
- Question 74: Which is a factor in enterprise campus design decisions?...
- Question 75: DRAG DROP Drag the description or characteristic on the left...
- Question 76: An engineer has configured a router to send level 7 messages...
- Question 77: A client wants to consolidate applications that are currentl...
- Question 78: Which statement about modular network design in true?...
- Question 79: Which one of these statements describes why, from a design p...
- Question 80: Where do you put DNS and DHCP on Enterprise model? (Choose t...
- Question 81: Which IETF standard technology can be used with data center ...
- Question 82: An engineer wants to ensure that the Spanning Tree topology ...
- Question 83: What part of the network does a top-down network design focu...
- Question 84: Which routing protocol provides the fastest convergence and ...
- Question 85: Which two design decisions can improve network resiliency? (...
- Question 86: An engineer is designing a private WAN infrastructure to sup...
- Question 87: Which three options represents the components of the Telewor...
- Question 88: Which tool captures network traffic, decodes the protocols i...
- Question 89: Which three modular components are part of the Cisco Enterpr...
- Question 90: According to fundamental design principles, which location i...
- Question 91: What tool would you use to decode protocols?...
- Question 92: What submodule is found within the Enterprise Edge module?...
- Question 93: Which H.323 protocol is in charge of call setup and signalin...
- Question 94: Which two solutions are parts of the Cisco Security Manageme...
- Question 95: During the design of a new campus network, the customer requ...
- Question 96: What does FCAPS stand for?
- Question 97: Which option is an advantage of a Layer 3 access model over ...
- Question 98: What are two benefits of the bottom-up design approach? (Cho...
- Question 99: Which format reflects that of the IPv6 global unicast addres...
- Question 100: What are two important aspects to consider when looking at b...
- Question 101: Which statement is true about the Cisco NAC Appliance?...
- Question 102: Which two network services should you host on the DMZ? (Choo...
- Question 103: What are three key areas that need to be considered when des...
- Question 104: What is the key limitation of using Internet circuits as a b...
- Question 105: What two performance considerations must be taken into accou...
- Question 106: Which VPN tunneling technology supports IP multicast?...
- Question 107: What IPv4 addressing technique allows for the division of ad...
- Question 108: Which two techniques can you use to reduce the size of a net...
- Question 109: What type of topology supports WAN redundancy when a balance...
- Question 110: You are designing a network that requires a routing protocol...
- Question 111: Which subnet mask should you use on point-to-point links to ...
- Question 112: What query should you make if you want to find all objects o...
- Question 113: Which address is the broadcast address of subnet 120.20.78.8...
- Question 114: When collecting information about a customer's existing netw...
- Question 115: When selecting which hardware switches to use throughout an ...
- Question 116: Which technology combines two Nexus switches to form a singl...
- Question 117: For the following options, which International Telecommunica...
- Question 118: What is the acronym PDIOO short for?...
- Question 119: A company has dark fiber between headquarters and its data c...
- Question 120: Two companies that want to connect with multiple providers v...
- Question 121: During which phase of the PPDIOO model would you conduct int...
- Question 122: A secure WAN design requires dynamic routing and IP multicas...
- Question 123: Which two processes are included in the Build phase of the C...
- Question 124: The evolution of the Data Center is best represented by the ...
- Question 125: Which STP feature allows an access port to bypass the learni...
- Question 126: Which two major campus design models does the Cisco Unified ...
- Question 127: Which subnet address and mask would you use for all Class D ...
- Question 128: When evaluating network designs, what indicator demonstrates...
- Question 129: Which option is one of the methods that Cisco routers and sw...
- Question 130: What network technology consolidates network and storage tra...
- Question 131: Where in the Cisco Enterprise Architecture model does networ...
- Question 132: Which two Cisco data center devices can participate in Cisco...
- Question 133: One step in characterizing an existing network involves obta...
- Question 134: Which statement describes the recommended deployment of DNS ...
- Question 135: Which three describe challenges that are faced when deployin...
- Question 136: Which item is the fundamental basis of a virtual network?...
- Question 137: What describes the link performance?...
- Question 138: In the enterprise data center, which are the three main comp...
- Question 139: A company wants to use private IP addresses for all its inte...
- Question 140: What does CDP stand for?
- Question 141: DRAG DROP Click and drag the phases of the PPDIOO network li...
- Question 142: Which value must you configure on a Microsoft DHCP server so...
- Question 143: How many switches can be combined into a single network elem...
- Question 144: What design feature should be considered when accessing reso...
- Question 145: Which two of the following are benefits of using a modular a...
- Question 146: A network engineer is following the Cisco enterprise archite...
- Question 147: Which two of these are functions of an access point in a Spl...
- Question 148: What is the best point to deploy the IPS, not to have false ...
- Question 149: Which two methods are used to reduce the mesh links required...
- Question 150: A network engineer must implement a design where LAN clients...
- Question 151: Which protocol is the recommended first-hop redundancy proto...
- Question 152: Which of the following is a component within the Cisco Enter...
- Question 153: Which two benefits are realized by establishing virtualizati...
- Question 154: How does the use of multiple areas in a link state routing p...
- Question 155: What is DHCP?
- Question 156: Which first-hop redundancy protocol dynamically distributes ...
- Question 157: Which technology enables WLCs to peer with each other to ena...
- Question 158: What is a characteristic of campus core designs?...
- Question 159: Which three are associated with the distribution layer withi...
- Question 160: A network engineer is following the Cisco enterprise archite...
- Question 161: As you assign QoS priorities, which Cisco tool can you use t...
- Question 162: A network engineer must connect two sites. Each site has a d...
- Question 163: DRAG DROP The first phase of PPDIOO entails identifying cust...
- Question 164: Which two routing protocols usually converge most quickly? (...
- Question 165: Cisco FabricPath brings the benefits of routing protocols to...
- Question 166: Which two descriptions of Cisco Application Centric Infrastr...
- Question 167: A design engineer must send management information messages ...
- Question 168: Which option is an advanced congestion management mechanism ...
- Question 169: Which one of the following is "synchronous link" design?...
- Question 170: Which voice codec should you use in order to provide toll qu...
- Question 171: What are the three primary functions of the distribution lay...
- Question 172: Which Gigabit Ethernet media type provides the longest reach...
- Question 173: Based on best practices, which QoS profile should be configu...
- Question 174: With deterministic Wireless LAN Controller redundancy design...
- Question 175: Spanning Layer 2 across geographically separate data centers...
- Question 176: What is the reason for switching preferred on shared segment...
- Question 177: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. In this suboptimal design of...
- Question 178: While designing a highly resilient infrastructure, which lay...
- Question 179: ACME Corporation is implementing dynamic routing on the LAN ...
- Question 180: Which type of area should you use in an enterprise OSPF depl...
- Question 181: An engineer receives a resource utilization alert on a route...
- Question 182: For the following protocols, which one maps names to IPv6 ad...
- Question 183: What two factors should be considered when deploying an ente...
- Question 184: Which two of these are the most accurate characteristics of ...
- Question 185: Which type of router connects to two different OSPF areas?...
- Question 186: Which three options are valid Cisco STP tools used to ensure...
- Question 187: An organization needs to implement isolated logical structur...
- Question 188: A network engineer is tasked with summarizing the routes to ...
- Question 189: Which three are considered as technical constraints when ide...
- Question 190: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which three OSPF routers are...
- Question 191: How to reduce the size of a routing table? (Choose two):...
- Question 192: Which virtualization deployment an engineer will execute to ...
- Question 193: Which three series of Cisco wireless controllers support wir...
- Question 194: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which two statements correct...
- Question 195: Which answer is correct about routing metrics?...
- Question 196: What VPN tunneling technology supports multicast?...
- Question 197: Which three technologies are recommended to be used for WAN ...
- Question 198: DRAG DROP Drag the security prevision on the left to the app...
- Question 199: In the traditional hierarchical LAN design, which two statem...
- Question 200: What three customer supported details identifies network req...
- Question 201: Which three statements are true regarding the virtual interf...
- Question 202: When you are designing a large IPv6 multivendor network, whi...
- Question 203: While designing a remote access VPN, a customer has requeste...
- Question 204: What is the maximum number of switches in VSS?...
- Question 205: Which statement correctly describes queuing in environments ...
- Question 206: Under which phase of the Cisco Design Lifecycle would you ev...
- Question 207: A company is using a dynamically routed private line and a s...
- Question 208: Which feature will not transfer packets when there is silenc...
- Question 209: Which two routing protocols operate over NBMA point-to-multi...
- Question 210: A network design engineer is seeking a dynamic routing proto...
- Question 211: At which layer of the network is route summarization recomme...
- Question 212: Which network management protocol allows a network device to...
- Question 213: A network design shows two routers that are directly connect...
- Question 214: When designing a WAN backup for voice and video applications...
- Question 215: When considering the three VoIP design models - single site,...
- Question 216: Which network access control technology is recommended to us...
- Question 217: Which two features are Cisco recommended best practices for ...
- Question 218: What tool would you use to capture, segregate and analyse IP...
- Question 219: Which option best describes the high-level design document?...
- Question 220: Which two enterprise campus layers are combined in a medium-...
- Question 221: What will extend a trust boundary (there is switch interface...
- Question 222: Which three service categories are supported by an ISR? (Cho...
- Question 223: Which two statements best describe an OSPF deployment? (Choo...
- Question 224: Which scenario is the best example of a single-homed connect...
- Question 225: What network virtualization technology can be leveraged with...
- Question 226: Which two considerations are important when designing the ac...
- Question 227: Which layer is in charge of fast transport in the hierarchic...
- Question 228: Which network virtualization technique can you implement wit...
- Question 229: Which is usually used to connect to an upstream ISP?...
- Question 230: Which three are features of LWAPP? (Choose three.)...
- Question 231: Traditionally, the DMZ exists between which two locations? (...
- Question 232: For a VLAN that requires 60 hosts, which subnet is the most ...
- Question 233: A network engineer is using the Cisco enterprise architectur...
- Question 234: Directory services and electronic messaging are performed at...
- Question 235: What should be considered when scaling EIGRP? (Choose three)...
- Question 236: According to Cisco, which four improvements are the main ben...
- Question 237: Which Cisco technology can connect more than two switches so...
- Question 238: Which two statements are true regarding a hierarchical netwo...
- Question 239: In which network location should an external DNS server be p...
- Question 240: An engineer wants to find all of the objects of a certain ty...
- Question 241: Which Cisco technology using Nexus NX-OS infrastructure allo...
- Question 242: DRAG DROP Drag the characteristics of the traditional campus...
- Question 243: DRAG DROP Drag the WAN technology on the left to the most ap...
- Question 244: Which H.323 protocol is responsible for the exchanging of ca...
- Question 245: When designing using the Cisco Enterprise Architecture, in w...
- Question 246: Which model of ISR is utilized for the teleworker design pro...
- Question 247: Which option can hinder efficient IP address allocation?...
- Question 248: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer at a tech...
- Question 249: Which factor would be most influential in choosing multimode...
- Question 250: You are asked to design a new branch office that will need t...
- Question 251: Which statement about VSS is true?...
- Question 252: Which IPv4 addressing technique can be used with proper addr...
- Question 253: A network architect working for a large financial institutio...
- Question 254: DRAG DROP Drag the technology on the left to the type of ent...
- Question 255: What technology can secure data over an insecure medium and ...
- Question 256: Which is the North American RIR for IPv4 addresses?...
- Question 257: Which VPN tunneling technology supports IP multicast?...
- Question 258: What two features are advantages of adding a secondary WAN l...
- Question 259: Which statement is true about using a DNS server to discover...
- Question 260: High availability is a key design consideration in the enter...
- Question 261: In an EAP-enabled WLAN, which component sends the EAP identi...
- Question 262: Which two Cisco products can be used in a data center to sup...
- Question 263: Your supervisor wants you to recommend a management protocol...
- Question 264: A network engineer is designing a solution that will monitor...
- Question 265: Which network virtualization technology involves creating vi...
- Question 266: Which three are security services offered through Cisco Rout...
- Question 267: Which WAN technology is a cost-effective method to deliver 1...
- Question 268: Which option is the greatest concern when a network design r...
- Question 269: Which connection provides cost effective backup connectivity...
- Question 270: You need to connect to a remote branch office via an Interne...
- Question 271: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Based on the following outpu...
- Question 272: Which two devices would you place in your DMZ to ensure ente...
- Question 273: When integrating services with Cisco ACI Service Graphs, whi...
- Question 274: Which feature must be configured on a switch port that conne...
- Question 275: Which network layer is the best fit for security features su...
- Question 276: In which two modes can you deploy Cisco IPS appliances? (Cho...
- Question 277: You are performing an audit of a customer's existing network...
- Question 278: Which of the following is a modular component within the Cis...
- Question 279: What business trend allows employees to use personal devices...
- Question 280: DRAG DROP Match the bandwidth usage optimization technique o...
- Question 281: Which of these is the equation used to derive a 64 Kbps bit ...
- Question 282: While designing the LAN core to distribution infrastructure ...
- Question 283: In a network with Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol...
- Question 284: What is the maximum number of groups that is supported by GL...
- Question 285: WAN backup over the Internet is often used to provide primar...
- Question 286: What does the Cisco SLM define as the component used to spec...
- Question 287: Company ABC has intermittent problems registering remote-sit...
- Question 288: Directory services and electronic messaging are performed at...
- Question 289: Which one of these statements is true concerning the data ce...
- Question 290: How often does a RIPv1 router broadcast its routing table by...
- Question 291: The BodMech online fitness organization specializes in creat...
- Question 292: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Assuming that a network will...
- Question 293: A data center is being deployed, and one design requirement ...
- Question 294: Which two common cable management strategies are used in hig...
- Question 295: Which technology can help prevent attacks from the Internet ...
- Question 296: An enterprise campus module is typically made up of four sub...
- Question 297: When designing for a remote worker, which two are typical re...
- Question 298: What statement about EVN is true?...
- Question 299: Which technology allows multiple instances of a routing tabl...
- Question 300: Refer to the list of requirements. Which IP telephony design...
- Question 301: According to Cisco best practices, which traffic control sho...
- Question 302: Which statement about using STP in a redundant-link scenario...
- Question 303: An engineer is planning branch WAN links to support unified ...
- Question 304: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Where should routes in the r...
- Question 305: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which element or elements of...
- Question 306: Characterizing an existing network requires gathering as muc...
- Question 307: Which layer of the OSI model does Cisco recommend to place t...
- Question 308: DRAG DROP Drag the associated virtualization tool or solutio...
- Question 309: Which three are valid Layer 2 access designs? (Choose three....
- Question 310: What access policies to set up for remote VPN access (Choose...
- Question 311: Which two high-level design components are included in Unifi...
- Question 312: What virtualization technology is used to provide device vir...
- Question 313: What is the most compact representation of the following IPv...
- Question 314: When designing IP addressing schemes, which options are two ...
- Question 315: You have a campus network that consists of only Cisco device...
- Question 316: Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which statement is true conc...
- Question 317: When designing a high availability network, which option can...
- Question 318: Which two wireless attributes should be considered during a ...
- Question 319: When monitoring voice traffic on a converged network, which ...
- Question 320: Which IP telephony component supports VoIP, PoE, and QoS?...
- Question 321: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which next hop will the rout...
- Question 322: Which two options should be considered when designing an OSP...
- Question 323: A remote office has a T1 WAN link to headquarters and a T1 I...
- Question 324: Your supervisor has asked you to deploy a routing protocol w...
- Question 325: Which virtualization solution provides redundancy using a pa...
- Question 326: Which statement about using VSS on a pair of switches is tru...
- Question 327: Which one of the following represent correct IPv6 Global Uni...
- Question 328: DRAG DROP Drag the network characteristic on the left to the...
- Question 329: Which of these statements is true concerning the data center...
- Question 330: To what Layer 2 technology does VRF closely compare?...
- Question 331: When designing changes to an existing network, which two opt...
- Question 332: Which two of these practices are considered to be best pract...
- Question 333: Which statement describes a unique advantage of EIGRP?...
- Question 334: For which type of topology are modern fast-converging routin...
- Question 335: Which three items pertain to EIGRP? (Choose three.)...
- Question 336: Which two design methodology steps relate, at least in part,...
- Question 337: At which layer of the network should you perform traffic fil...
- Question 338: Which three solutions are part of the Borderless Network Ser...
- Question 339: Which three of these are layers in the Cisco SONA Architectu...
- Question 340: In an enterprise Layer 2 switched network, which protocol mu...
- Question 341: Which servers that reside in the data center require direct ...
- Question 342: Which routing protocol classification should you use when fu...
- Question 343: Which is the equation used to derive a 64 Kbps bit rate?...
- Question 344: What three design requirements are key to designing a campus...
- Question 345: Which two statements about the Enterprise Data Center Aggreg...
- Question 346: When designing the threat detection and mitigation portion f...
- Question 347: A network engineer is attempting to separate routing domains...
- Question 348: What type of device can be installed to increase a broadcast...
- Question 349: DRAG DROP Drag the network function on the left to the funct...
- Question 350: Your company's Cisco routers are operating with EIGRP. You n...
- Question 351: From which DNS record can a Cisco wireless AP, running Cisco...


