Valid 200-310 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing 200-310 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest 200-310 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com 200-310 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com 200-310 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access 200-310 Dumps Premium Version
(392 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 116/160
Your company is opening a branch office that will contain 29 host computers. Your company has been allocated the 192.168.10.0/24 address range, and you have been asked to conserve IP address space when creating a subnet for the new branch office.
Which of the following network addresses should you use for the new branch office? (
Which of the following network addresses should you use for the new branch office? (
Correct Answer: D
Explanation/Reference:
Section: Addressing and Routing Protocols in an Existing Network Explanation Explanation:
You should use the 192.168.10.64/27 network address for the new branch office. The /27 notation indicates that 27 bits are used for the network portion of the address and that five bits remain for the host portion of the address, which allows for 32 (25) usable host addresses. Therefore, this address range is large enough to handle the number of hosts on the new branch office subnet. The first address is the network address, the last address is the broadcast address, and the other 30 (25-2) addresses are usable host addresses. Therefore, this address range is large enough to handle a subnet containing 29 host computers.
You should always begin allocating address ranges starting with the largest group of hosts to ensure that the entire group has a large, contiguous address range available. Subnetting a contiguous address range in structured, hierarchical fashion enables routers to maintain smaller routing tables and eases administrative burden when troubleshooting.
You should not use the 192.168.10.0/25 network address for the new branch office. The /25 notation indicates that 25 bits are used for the network portion of the address and that 7 bits remain for the host portion of the address, which allows for 126 (27-2) usable host addresses. Although this address range is large enough to handle the new branch office subnet, it does not conserve IP address space, because a smaller range can successfully be used.
You should not use the 192.168.10.32/26 network address for the new branch office. Although a 26bit mask is large enough for 62 usable host addresses, the 192.168.10.32 address is not a valid network address for a 26-bit mask. The 192.168.10.0/24 address range can be divided into four ranges, each with
64 addresses, by using a 26-bit mask:
192.168.10.0/26
192.168.10.64/26
192.168.10.128/26
192.168.10.192/26
You should not use the 192.168.10.64/26 network address for the new branch office. The /26 notation indicates that 26 bits are used for the network portion of the address and that six bits remain for the host portion of the address, which allows for 62 (26-2) host addresses. Although this address range is large enough to handle the new branch office subnet, it does not conserve IP address space, because a smaller range can successfully be used.
Although it is important to learn the formula for calculating valid host addresses, the following list demonstrates the relationship between common subnet masks and valid host addresses:
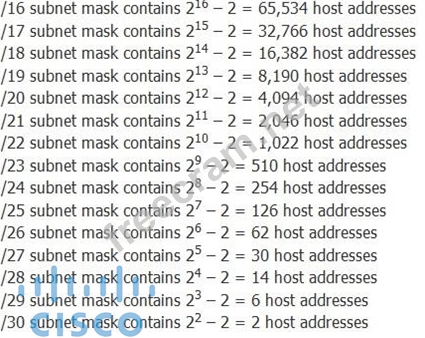
Reference:
CCDA 200-310 Official Cert Guide, Chapter 8, IPv4 Address Subnets, pp. 302-310 CCDA 200-310 Official Cert Guide, Chapter 8, Plan for a Hierarchical IP Address Network, pp. 311-312 Cisco: IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users
Section: Addressing and Routing Protocols in an Existing Network Explanation Explanation:
You should use the 192.168.10.64/27 network address for the new branch office. The /27 notation indicates that 27 bits are used for the network portion of the address and that five bits remain for the host portion of the address, which allows for 32 (25) usable host addresses. Therefore, this address range is large enough to handle the number of hosts on the new branch office subnet. The first address is the network address, the last address is the broadcast address, and the other 30 (25-2) addresses are usable host addresses. Therefore, this address range is large enough to handle a subnet containing 29 host computers.
You should always begin allocating address ranges starting with the largest group of hosts to ensure that the entire group has a large, contiguous address range available. Subnetting a contiguous address range in structured, hierarchical fashion enables routers to maintain smaller routing tables and eases administrative burden when troubleshooting.
You should not use the 192.168.10.0/25 network address for the new branch office. The /25 notation indicates that 25 bits are used for the network portion of the address and that 7 bits remain for the host portion of the address, which allows for 126 (27-2) usable host addresses. Although this address range is large enough to handle the new branch office subnet, it does not conserve IP address space, because a smaller range can successfully be used.
You should not use the 192.168.10.32/26 network address for the new branch office. Although a 26bit mask is large enough for 62 usable host addresses, the 192.168.10.32 address is not a valid network address for a 26-bit mask. The 192.168.10.0/24 address range can be divided into four ranges, each with
64 addresses, by using a 26-bit mask:
192.168.10.0/26
192.168.10.64/26
192.168.10.128/26
192.168.10.192/26
You should not use the 192.168.10.64/26 network address for the new branch office. The /26 notation indicates that 26 bits are used for the network portion of the address and that six bits remain for the host portion of the address, which allows for 62 (26-2) host addresses. Although this address range is large enough to handle the new branch office subnet, it does not conserve IP address space, because a smaller range can successfully be used.
Although it is important to learn the formula for calculating valid host addresses, the following list demonstrates the relationship between common subnet masks and valid host addresses:

Reference:
CCDA 200-310 Official Cert Guide, Chapter 8, IPv4 Address Subnets, pp. 302-310 CCDA 200-310 Official Cert Guide, Chapter 8, Plan for a Hierarchical IP Address Network, pp. 311-312 Cisco: IP Addressing and Subnetting for New Users
- Question List (160q)
- Question 1: Which of the following network issues are not likely to be m...
- Question 2: Which of the following methods is always used by a new LAP t...
- Question 3: RouterA has interfaces connected to the 172.16.0.0/24 throug...
- Question 4: Which of the following statements is true regarding route su...
- Question 5: Which of the following statements regarding VPNs are true? (...
- Question 6: You administer a router that contains five routes to the sam...
- Question 7: Which of the following is a Cisco-proprietary link-bundling ...
- Question 8: Which of the following statements is true regarding physical...
- Question 9: Which of the following WLC interfaces is used for Layer 2 di...
- Question 10: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You administer the network shown...
- Question 11: Which of the following are recommended campus network design...
- Question 12: Which of the following is a type of attack that can be mitig...
- 2 commentQuestion 13: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Which of the following data cent...
- Question 14: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You administer the network shown...
- Question 15: You are routing traffic between company departments that res...
- Question 16: To which of the following high-availability resiliency level...
- Question 17: Which of the following is a hierarchical routing protocol th...
- Question 18: In which of the following situations would static routing be...
- Question 19: You issue the show ip bgp neighbors command on RouterA and r...
- Question 20: Which of the following queuing methods provides bandwidth an...
- Question 21: DRAG DROP Select the attributes from the left, and place the...
- Question 22: In which of the following situations would eBGP be the most ...
- Question 23: Which of the following network issues can most likely be mit...
- Question 24: In a Layer 3 hierarchical design, which enterprise campus mo...
- Question 25: Which of the following does NetFlow use to identify a traffi...
- Question 26: Which of the following is a network architecture principle t...
- Question 27: DRAG DROP Select the subnet masks on the left, and place the...
- Question 28: Which of the following statements are true regarding a Cisco...
- Question 29: Which of the following queuing methods is the most appropria...
- Question 30: Which of the following statements best describes the purpose...
- Question 31: Which of the following statements are true regarding the dis...
- Question 32: DRAG DROP Select the network layers from the left, and drag ...
- Question 33: How many valid host IP addresses are available on a /21 subn...
- Question 34: Which of the following AP modes do not provide client connec...
- Question 35: Which of the following IPv6 address spaces contains an inher...
- Question 36: Which of the following statements is not true?...
- Question 37: Your supervisor wants you to reduce the range of IP addresse...
- Question 38: You are planning a network by using the top-down design meth...
- Question 39: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You administer the network shown...
- Question 40: Which of the following subnet masks contains 4,094 valid hos...
- Question 41: View the Exhibit: (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which of t...
- Question 42: Which of the following are not supported by GET VPN? (Choose...
- Question 43: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Refer to the diagram shown above...
- Question 44: Which of the following IPv6 prefixes is used for multicast a...
- Question 45: At which of the following layers of the OSI model does CDP o...
- Question 46: You are planning a network by using the top-down design meth...
- Question 47: Which of the following is a characteristic of the bottom-up ...
- Question 48: Which of the following statements best describes NetFlow?...
- Question 49: Which of the following statements is true regarding VMs?...
- Question 50: On which of the following layers of the hierarchical network...
- Question 51: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You have been asked to use CDP t...
- Question 52: Which of the following can you use to hide the IP addresses ...
- Question 53: Which of the following address blocks is typically used for ...
- Question 54: Which of the following is the QoS model that is primarily us...
- Question 55: You want to implement a protocol to provide secure communica...
- Question 56: Which of the following is a routing protocol that requires a...
- Question 57: Which of the following features are provided by IPSec? (Choo...
- Question 58: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which of t...
- Question 59: Which of the following protocols can provide Application lay...
- Question 60: When using the bottom-up design approach, which layer of the...
- Question 61: You are installing a 4U device in a data center. Which of th...
- Question 62: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit above. The ...
- Question 63: Which of the following are true of the access layer of a hie...
- Question 64: Which of the following is a leased-line WAN technology that ...
- Question 65: Which of the following statements are true regarding standar...
- Question 66: DRAG DROP Select the protocols and port numbers from the lef...
- Question 67: Which of the following statements is true regarding NetFlow?...
- Question 68: Which of the following statements are correct regarding wire...
- Question 69: Which of the following network virtualization techniques doe...
- Question 70: Which of the following should not be implemented in the core...
- Question 71: Which of the following can you configure on a Cisco switch t...
- Question 72: On a Cisco router, which of the following message types does...
- Question 73: Which of the following is the maximum number of chassis that...
- Question 74: Which of the following is least likely to be a concern when ...
- Question 75: Which of the following network virtualization techniques doe...
- Question 76: Which of the following statements are true regarding the fun...
- Question 77: Which of the following actions are you most likely to perfor...
- Question 78: Which of the following technologies can you use to configure...
- Question 79: Which of the following statements regarding WMM is true?...
- Question 80: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit above. PVST...
- Question 81: What AD is assigned to static routes by default?...
- Question 82: The network you administer contains the following network ad...
- Question 83: You issue the following commands on RouterA: (Exhibit) Route...
- Question 84: DRAG DROP From the left, select the characteristics that app...
- Question 85: In a switched hierarchical design, which enterprise campus m...
- Question 86: Which of the following best describes a DMZ?...
- Question 87: Which of the following is not required of a collapsed core l...
- Question 88: Which of the following are reasons to choose a VPN solution ...
- Question 89: Which of the following branch office WAN connectivity method...
- Question 90: You want to install antivirus software on a host that is con...
- Question 91: Which of the following statements is true regarding Cisco be...
- Question 92: In which of the following locations can you not deploy an IP...
- Question 93: DRAG DROP Select the characteristics from the left, and drag...
- Question 94: Which of the following is a BGP attribute that represents th...
- Question 95: Which of the following best describes PAT?...
- Question 96: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which of t...
- Question 97: Which of the following statements regarding Cisco GET VPN ar...
- Question 98: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit above. The ...
- Question 99: DRAG DROP Select each feature from the left, and drag it to ...
- Question 100: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You administer the network shown...
- Question 101: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You are designing an IP addressi...
- Question 102: Which of the following statements are true when VSS is imple...
- Question 103: DRAG DROP You are adding an additional LAP to your current w...
- Question 104: Which of the following statements are correct regarding netw...
- Question 105: Which of the following is not a reason to choose a VPN solut...
- Question 106: Which of the following are you least likely to implement in ...
- Question 107: Which of the following processes is a component of the Manag...
- Question 108: Which of the following is a circuit-switched WAN technology ...
- Question 109: Which of the following is a hierarchical routing protocol th...
- Question 110: On a Cisco router, which of the following commands relies on...
- Question 111: Which of the following address and subnet mask combinations ...
- Question 112: DRAG DROP You are implementing a new two-office network. The...
- Question 113: DRAG DROP Drag the event action on the left to the IPS mode ...
- Question 114: Which of the following is an advantage of SSL VPNs over IPSe...
- Question 115: Which of the following statements are true about OSPF and EI...
- Question 116: Your company is opening a branch office that will contain 29...
- Question 117: In which of the following ways are Cisco IPS and IDS devices...
- Question 118: In which of the following modules of the Cisco enterprise ar...
- Question 119: In which of the following layer or layers should you impleme...
- Question 120: DRAG DROP Select the processes from the left, and place them...
- Question 121: Which of the following queuing methods provides strict-prior...
- Question 122: Which of the following prefixes will an IPv6enabled computer...
- Question 123: Which of the following are most likely to be provided by a c...
- Question 124: Which of the following network virtualization technologies c...
- Question 125: HostA is a computer on your company's network. RouterA is a ...
- Question 126: On a Cisco PE router, you have implemented a VRF instance wi...
- Question 127: The IP address 169.254.173.233 is an example of which of the...
- Question 128: Which of the following standard or standards natively includ...
- Question 129: Which of the following is not true regarding the MPLS WAN de...
- Question 130: You issue the following commands on RouterA: (Exhibit) Packe...
- Question 131: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You administer the network shown...
- Question 132: Which of the following WMM access categories maps to the WLC...
- Question 133: Which of the following tasks can best be achieved with SNMP?...
- Question 134: Which of the following actions are you most likely to perfor...
- Question 135: DRAG DROP From the left, select the characteristics that app...
- Question 136: Which of the following best describes route summarization?...
- Question 137: Confidentiality, integrity, and authentication are features ...
- Question 138: Which of the following is a network architecture principle t...
- Question 139: Which of the following is used by both NetFlow and NBAR to i...
- Question 140: Which of the following statements is true regarding the Cisc...
- Question 141: Which of the following is an advantage of implementing QoS f...
- Question 142: In which of the following situations would iBGP be the most ...
- Question 143: Which of the following is true of the core layer of a hierar...
- Question 144: Which of the following is a Layer 2 high-availability featur...
- Question 145: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Which of the following terms mos...
- Question 146: You have configured NIC teaming on a Microsoft Windows Serve...
- Question 147: STP is disabled by default in which of the following Layer 2...
- Question 148: What AD is assigned to iBGP routes by default?...
- Question 149: View the Exhibit. (Exhibit) You administer the network shown...
- Question 150: You are designing a routed access layer for a high availabil...
- Question 151: Which of the following VPN tunnels support encapsulation of ...
- Question 152: Which of the following best describes a hypervisor?...
- Question 153: Which of the following is defined in the IEEE 802.3ad standa...
- Question 154: Which of the following are BGP attributes that are used to d...
- Question 155: Which of the following OSPF areas accept all LSAs? (Choose t...
- Question 156: Which of the following are not true of the access layer of a...
- Question 157: You want to implement a WAN link between two sites. Which of...
- Question 158: Which of the following protocols can IPSec use to provide th...
- Question 159: You want to load share traffic from two VLANs across two FHR...
- Question 160: Which of the following features are provided by IPSec? (Choo...


