Valid H12-811_V1.0 Dumps shared by ExamDiscuss.com for Helping Passing H12-811_V1.0 Exam! ExamDiscuss.com now offer the newest H12-811_V1.0 exam dumps, the ExamDiscuss.com H12-811_V1.0 exam questions have been updated and answers have been corrected get the newest ExamDiscuss.com H12-811_V1.0 dumps with Test Engine here:
Access H12-811_V1.0 Dumps Premium Version
(352 Q&As Dumps, 35%OFF Special Discount Code: freecram)
<< Prev Question Next Question >>
Question 56/132
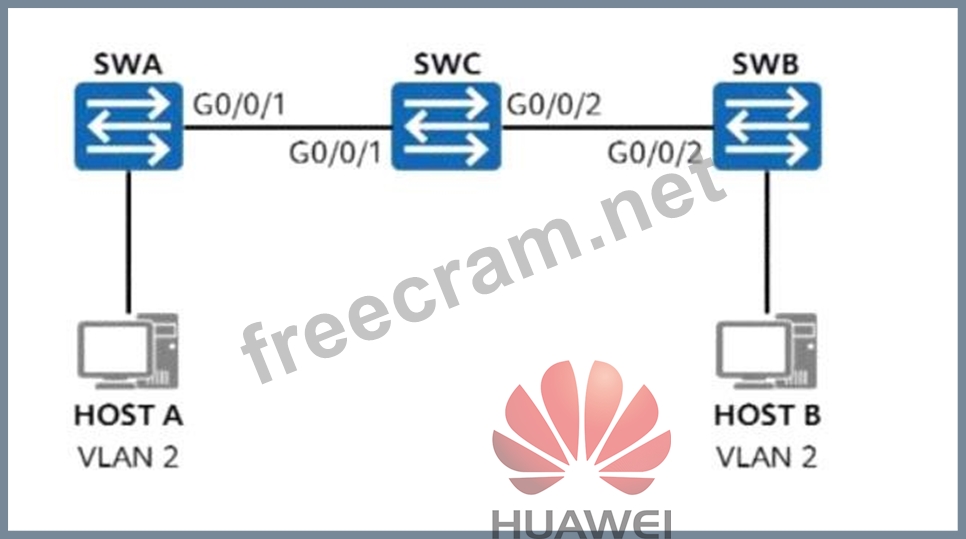
On the network shown in the figure, VLAN 2 is created on SWA and SWB, and interfaces connected to hosts are access ports added to VLAN 2. G0/0/1 on SWA and G0/0/2 on SWB are trunk interfaces allowing all VLANs. What additional configuration is needed on SWC to ensure communication between Host A and Host B?

Correct Answer: C
To ensure communication between Host A and Host B, we need to analyze the network topology, VLAN configuration, and the role of SWC as an intermediate switch. Let's break it down step by step, based on VLAN and trunking principles as outlined in HCIA Datacom documentation:
* Understanding the Current Network Configuration:
* Host A and Host B: Both are connected to SWA and SWB, respectively, via access ports assigned to VLAN 2. Access ports carry untagged traffic for a single VLAN (in this case, VLAN
2), so Host A and Host B are part of VLAN 2.
* SWA and SWB Trunk Interfaces: G0/0/1 on SWA and G0/0/2 on SWB are configured as trunk interfaces allowing all VLANs. Trunk ports carry tagged traffic for multiple VLANs (including VLAN 2 in this case) and are used to interconnect switches, enabling VLAN traffic to pass between them. Since these trunk ports allow all VLANs, VLAN 2 traffic can traverse between SWA and SWB.
* SWC: SWC is the intermediate switch connecting SWA and SWB via its G0/0/1 (connected to SWA's G0/0/1) and G0/0/2 (connected to SWB's G0/0/2). However, the diagram and question do not specify SWC's current VLAN or port configurations. By default, if no VLAN or trunk configuration exists on SWC, VLAN 2 traffic cannot pass through SWC, preventing communication between Host A and Host B.
* Requirements for Communication Between Host A and Host B:
* For Host A and Host B (both in VLAN 2) to communicate across the network, VLAN 2 traffic must be able to traverse SWC. This requires:
* VLAN 2 to be created on SWC so that the switch recognizes and processes traffic for that VLAN.
* The interfaces on SWC (G0/0/1 and G0/0/2) connecting to SWA and SWB must be configured as trunk ports to carry tagged VLAN 2 traffic, matching the trunk configuration on SWA's G0/0/1 and SWB's G0/0/2.
* Trunk ports are necessary because they can carry traffic for multiple VLANs (tagged) and are typically used between switches to maintain VLAN consistency across the network.
* Evaluating Each Option:
* A. Create VLAN 2 on SWC.
* Creating VLAN 2 on SWC is necessary, but it alone is insufficient. Without configuring the ports (G0/0/1 and G0/0/2) as trunk interfaces allowing VLAN 2, the VLAN traffic cannot pass through SWC. This option is incomplete and incorrect.
* B. Configure G0/0/1 on SWC as a trunk interface that allows packets from VLAN 2 to pass through.
* Configuring G0/0/1 as a trunk interface allowing VLAN 2 is part of the solution, but it only addresses the connection to SWA. G0/0/2 (connected to SWB) also needs to be configured as a trunk interface allowing VLAN 2 for bidirectional communication between Host A and Host B. This option is incomplete and incorrect.
* C. Create VLAN 2 on SWC, and configure G0/0/1 and G0/0/2 as trunk interfaces that allow packets from VLAN 2 to pass through.
* This option addresses all requirements:
* Creating VLAN 2 on SWC ensures the switch recognizes VLAN 2 traffic.
* Configuring both G0/0/1 and G0/0/2 as trunk interfaces allowing VLAN 2 ensures that tagged VLAN 2 traffic can pass between SWA and SWB through SWC, enabling communication between Host A and Host B.
* This is the complete and correct solution, aligning with VLAN and trunking principles in HCIA Datacom.
* D. On SWC, configure G0/0/1 as a trunk interface that allows packets from VLAN 2 to pass through, configure G0/0/2 as an access interface, and set the PVID to 2.
* Configuring G0/0/1 as a trunk interface allowing VLAN 2 is correct for the connection to SWA. However, configuring G0/0/2 as an access interface with PVID 2 (Port VLAN ID) is incorrect for this scenario:
* Access ports carry untagged traffic for a single VLAN and are typically used for end devices, not for interconnecting switches. Since SWB's G0/0/2 is a trunk interface allowing all VLANs, G0/0/2 on SWC must also be a trunk interface to match and carry VLAN 2 traffic.
* Using an access port on G0/0/2 would prevent VLAN 2 traffic from passing correctly, as it would expect untagged traffic only for VLAN 2, which conflicts with SWB's trunk configuration.
* This option is incorrect because it mixes access and trunk port types inappropriately for inter-switch links.
* Conclusion:
* To ensure communication between Host A and Host B (both in VLAN 2), SWC must:
* Create VLAN 2.
* Configure G0/0/1 and G0/0/2 as trunk interfaces allowing VLAN 2 traffic.
* Option C fulfills these requirements, making it the correct answer.
References from HCIA Datacom Documents:
* HCIA Datacom V3.0, Chapter 4: VLAN Technologies - Access and Trunk Port Configurations
* HCIA Datacom V3.0, Chapter 4: VLAN Trunking and Inter-VLAN Routing - Configuring Trunk Ports for VLAN Traffic
* Huawei VLAN Configuration Guide (HCIA Datacom Certification Material) - VLAN Creation and Port Link Types
* Understanding the Current Network Configuration:
* Host A and Host B: Both are connected to SWA and SWB, respectively, via access ports assigned to VLAN 2. Access ports carry untagged traffic for a single VLAN (in this case, VLAN
2), so Host A and Host B are part of VLAN 2.
* SWA and SWB Trunk Interfaces: G0/0/1 on SWA and G0/0/2 on SWB are configured as trunk interfaces allowing all VLANs. Trunk ports carry tagged traffic for multiple VLANs (including VLAN 2 in this case) and are used to interconnect switches, enabling VLAN traffic to pass between them. Since these trunk ports allow all VLANs, VLAN 2 traffic can traverse between SWA and SWB.
* SWC: SWC is the intermediate switch connecting SWA and SWB via its G0/0/1 (connected to SWA's G0/0/1) and G0/0/2 (connected to SWB's G0/0/2). However, the diagram and question do not specify SWC's current VLAN or port configurations. By default, if no VLAN or trunk configuration exists on SWC, VLAN 2 traffic cannot pass through SWC, preventing communication between Host A and Host B.
* Requirements for Communication Between Host A and Host B:
* For Host A and Host B (both in VLAN 2) to communicate across the network, VLAN 2 traffic must be able to traverse SWC. This requires:
* VLAN 2 to be created on SWC so that the switch recognizes and processes traffic for that VLAN.
* The interfaces on SWC (G0/0/1 and G0/0/2) connecting to SWA and SWB must be configured as trunk ports to carry tagged VLAN 2 traffic, matching the trunk configuration on SWA's G0/0/1 and SWB's G0/0/2.
* Trunk ports are necessary because they can carry traffic for multiple VLANs (tagged) and are typically used between switches to maintain VLAN consistency across the network.
* Evaluating Each Option:
* A. Create VLAN 2 on SWC.
* Creating VLAN 2 on SWC is necessary, but it alone is insufficient. Without configuring the ports (G0/0/1 and G0/0/2) as trunk interfaces allowing VLAN 2, the VLAN traffic cannot pass through SWC. This option is incomplete and incorrect.
* B. Configure G0/0/1 on SWC as a trunk interface that allows packets from VLAN 2 to pass through.
* Configuring G0/0/1 as a trunk interface allowing VLAN 2 is part of the solution, but it only addresses the connection to SWA. G0/0/2 (connected to SWB) also needs to be configured as a trunk interface allowing VLAN 2 for bidirectional communication between Host A and Host B. This option is incomplete and incorrect.
* C. Create VLAN 2 on SWC, and configure G0/0/1 and G0/0/2 as trunk interfaces that allow packets from VLAN 2 to pass through.
* This option addresses all requirements:
* Creating VLAN 2 on SWC ensures the switch recognizes VLAN 2 traffic.
* Configuring both G0/0/1 and G0/0/2 as trunk interfaces allowing VLAN 2 ensures that tagged VLAN 2 traffic can pass between SWA and SWB through SWC, enabling communication between Host A and Host B.
* This is the complete and correct solution, aligning with VLAN and trunking principles in HCIA Datacom.
* D. On SWC, configure G0/0/1 as a trunk interface that allows packets from VLAN 2 to pass through, configure G0/0/2 as an access interface, and set the PVID to 2.
* Configuring G0/0/1 as a trunk interface allowing VLAN 2 is correct for the connection to SWA. However, configuring G0/0/2 as an access interface with PVID 2 (Port VLAN ID) is incorrect for this scenario:
* Access ports carry untagged traffic for a single VLAN and are typically used for end devices, not for interconnecting switches. Since SWB's G0/0/2 is a trunk interface allowing all VLANs, G0/0/2 on SWC must also be a trunk interface to match and carry VLAN 2 traffic.
* Using an access port on G0/0/2 would prevent VLAN 2 traffic from passing correctly, as it would expect untagged traffic only for VLAN 2, which conflicts with SWB's trunk configuration.
* This option is incorrect because it mixes access and trunk port types inappropriately for inter-switch links.
* Conclusion:
* To ensure communication between Host A and Host B (both in VLAN 2), SWC must:
* Create VLAN 2.
* Configure G0/0/1 and G0/0/2 as trunk interfaces allowing VLAN 2 traffic.
* Option C fulfills these requirements, making it the correct answer.
References from HCIA Datacom Documents:
* HCIA Datacom V3.0, Chapter 4: VLAN Technologies - Access and Trunk Port Configurations
* HCIA Datacom V3.0, Chapter 4: VLAN Trunking and Inter-VLAN Routing - Configuring Trunk Ports for VLAN Traffic
* Huawei VLAN Configuration Guide (HCIA Datacom Certification Material) - VLAN Creation and Port Link Types
- Question List (132q)
- Question 1: VLAN 4095 is reserved for system use and VLAN 1 cannot be de...
- Question 2: Which of the following VRP commands can be used to enter are...
- Question 3: A company applies for a class C IP address for subnetting. I...
- Question 4: Refer to the following VLAN configurations on a Huawei switc...
- Question 5: Which of the following statements about the commands shown i...
- Question 6: Wi-Fi 6 is also known as the IEEE 802.11ax standard....
- Question 7: When a router is powered on, the router reads the configurat...
- Question 8: For an Eth-Trunk in LACP mode, what is the default LACP syst...
- Question 9: If the application-layer protocol is Telnet, what is the val...
- Question 10: Which of the following is not a characteristic of small camp...
- Question 11: Only the WPA2-PSK security policy supports TKIP data encrypt...
- Question 12: To provide the information about the IP addresses that a use...
- Question 13: Which of the following network types are supported by OSPF?...
- Question 14: On the command line interface of Huawei AR routers, the role...
- Question 15: If the network administrator assigns the IPv4 address 192.16...
- Question 16: Which of the following port states is not included in Rapid ...
- Question 17: Which of the following network parameters can be allocated u...
- Question 18: Which of the following statements is true about link aggrega...
- Question 19: Which of the following commands sets the data forwarding mod...
- Question 20: UDP does not guarantee data transmission reliability and doe...
- Question 21: (Which of the following is a dynamic IGP routing protocol?)...
- Question 22: Which of the following is NOT an open API of Huawei controll...
- Question 23: By referring to the network structure and OSPF areas shown i...
- Question 24: If the packet matches the deny rule in an ACL, the packet is...
- Question 25: Which of the following MAC addresses cannot be used as the M...
- Question 26: Which of the following protocols can be used to prevent Laye...
- Question 27: The TCP protocol uses the three-way handshake mechanism to e...
- Question 28: With what kind of routers does a DRother router exchange lin...
- Question 29: When the ACL in the following figure is configured on a Teln...
- Question 30: The following figure shows the configuration of a sub-interf...
- Question 31: If the value of the "Type/Length" field of an Ethernet data ...
- Question 32: Which of the following fields are contained in an ARP packet...
- Question 33: Which of the following is not a common network layer in a mi...
- Question 34: On an STP-enabled switch, a port in the forwarding state can...
- Question 35: You can run the user-interface maximum-vty command to config...
- Question 36: Which of the following configurations can prevent Host A and...
- Question 37: Which of the following methods can be used to add APs on an ...
- Question 38: Which of the following statements about static routes on Hua...
- Question 39: When the "delete vrpcfg.zip" command is run on the Huawei VR...
- Question 40: (Which of the following methods can be used to assign servic...
- Question 41: On the VRP CLI, files cannot be permanently deleted using th...
- Question 42: The rules in an ACL may overlap. If packets match the rules ...
- Question 43: Which of the following statements about the routing table sh...
- Question 44: Which of the following statements about switches is false?...
- Question 45: What are the advantages of OSPF?...
- Question 46: Which of the following sources of routes can be obtained by ...
- Question 47: After a switch restarts, static MAC address entries saved on...
- Question 48: For STP, the default root path cost of the root bridge is 0....
- Question 49: The priority of static routes cannot be manually specified....
- Question 50: (The administrator performs the configuration shown in the f...
- Question 51: Refer to the graphic: 00e0-fc99-9999 is a specific host MAC ...
- Question 52: Which of the following descriptions regarding the TTL field ...
- Question 53: Which of the following is not a type of OSPF LSA?...
- Question 54: What is the total length of the port ID in STP?...
- Question 55: Refer to the display startup command output shown in the fig...
- Question 56: On the network shown in the figure, VLAN 2 is created on SWA...
- Question 57: What is the length range of an Ethernet_II frame that contai...
- Question 58: Refer to the captured three packets shown in the figure. Whi...
- Question 59: Which SNMP version focuses on two main aspects, namely secur...
- Question 60: On the VRP, when the mkdir test command is run, the system c...
- Question 61: As shown in the figure, RTA uses NAT and has an address pool...
- Question 62: Which of the following statements are true about transport-l...
- Question 63: A Layer 2 ACL can match information such as the source MAC a...
- Question 64: Which of the following parameters is not contained in STP co...
- Question 65: (Each network device running SNMP runs an agent process loca...
- Question 66: It is advised to assign static IP addresses to servers durin...
- Question 67: Refer to the following configuration of an interface on a sw...
- Question 68: (By default, in the SNMP protocol, which port number is used...
- Question 69: In RSTP, an edge port becomes a common STP port after receiv...
- Question 70: During STP calculation, the port cost is associated with the...
- Question 71: Which of the following statements about hybrid interfaces is...
- Question 72: In STP, the bridge ID on the switching network is as follows...
- Question 73: Fit APs can provide wireless services independently of an AC...
- Question 74: A router in the backbone area has complete LSDBs of routers ...
- Question 75: (Which of the following routing protocols are dynamic routin...
- Question 76: When an AP and an AC are located on different Layer 3 networ...
- Question 77: Which is a valid EUI-64 address?...
- Question 78: On the network shown in the figure, router A adopts link agg...
- Question 79: After the administrator performs the configuration shown in ...
- Question 80: Which of the following operations are mandatory to restore t...
- Question 81: The network administrator has decided to configure link aggr...
- Question 82: Assuming that OSPF has been enabled on all routers in the fo...
- Question 83: As shown in the figure, all switches run STP. Assume that th...
- Question 84: (ICMP packets do not contain port numbers. Therefore, NAPT c...
- Question 85: What is the protocol number of OSPF at the network layer?...
- Question 86: On Huawei AR G3 Series routers, which authentication modes d...
- Question 87: (An administrator cannot log in to a Huawei router through T...
- Question 88: While inspecting packets in the network, a network administr...
- Question 89: What is the default lease time of the IP address allocated b...
- Question 90: In STP, which of the following items may affect the selectio...
- Question 91: < Huawei > system-view [Huawei]command-privilege level...
- Question 92: Which of the following parameters is used to elect the root ...
- Question 93: The following configuration commands implement route backup ...
- Question 94: How many bytes are there in a basic IPv6 header?...
- Question 95: Which of the following advantages is/are provided by inter-V...
- Question 96: A trunk interface allows frames from multiple VLANs includin...
- Question 97: When a switch receives a unicast data frame, if the destinat...
- Question 98: Which of the following parts compose SNMP?...
- Question 99: As shown in the figure, the configuration of Router A is as ...
- Question 100: Which of the following is a valid default route configuratio...
- Question 101: According to OSI reference model, which layer is responsible...
- Question 102: RADIUS is a common protocol for implementing AAA....
- Question 103: An administrator wishes to configure a floating static route...
- Question 104: Refer to the network diagram. (Exhibit) Which of the followi...
- Question 105: When a host uses the IP address 192.168.1.2 to access the In...
- Question 106: Network devices running SNMP can proactively report traps to...
- Question 107: The load balancing modes at both ends of an Eth-Trunk can be...
- Question 108: Which of the following is a link-state routing protocol?...
- Question 109: Which of the following ACLs can match the transport layer po...
- Question 110: Which of the following parameters is used to elect the root ...
- Question 111: (Which of the following descriptions regarding the STP forwa...
- Question 112: On the network shown in the figure, Host A and Host B cannot...
- Question 113: Only one SSID can be bound to each radio of an AP....
- Question 114: (An Eth-Trunk interface can be used only as a Layer 2 interf...
- Question 115: (You can run the "pwd" and "dir" commands on the Versatile R...
- Question 116: The following figure shows the display interface Eth-Trunk 1...
- Question 117: Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT) allows multiple ...
- Question 118: Which of the following packets are exchanged between STAs an...
- Question 119: Which of the following OSPF packets can be sent to request t...
- Question 120: How many VLANs are created when using the following commands...
- Question 121: According to the VTY user interface configuration shown in t...
- Question 122: In RSTP, a backup port can replace a faulty root port....
- Question 123: The network administrator performs the configuration shown i...
- Question 124: The data link layer uses PPP encapsulation. The IP addresses...
- Question 125: Which of the following is the default port number of the Tel...
- Question 126: Which of the following traffic can be filtered by an advance...
- Question 127: VLANs can be assigned based on service types during campus n...
- Question 128: Trunk interfaces can send both tagged and untagged frames....
- Question 129: The tree topology is a hierarchical star topology, facilitat...
- Question 130: Loops may cause broadcast storms on a Layer 2 network....
- Question 131: A switch receives a unicast data frame with a VLAN tag but c...
- Question 132: In the case of Huawei routers, what is the "-i" parameter in...


